Vietnam War
Template:TOC-right The Vietnam War was a mid-20th century struggle between the Communist Party of Vietnam and South Vietnam, the United States, and, depending on when the war is thought to have begun, France. It is correct to say that there were varying levels of warfare, or covert preparations, between 1945 and 1975. These do break into at least two hot wars, one against the French colonial administration, and one primarily between the Communist north and non-Communist south. The United States and other countries, especially in the latter war, were involved, sometimes intensely.
This is not to suggest that 1945-1975 was the only conflict seen in the region. A Japanese invasion in 1941 triggered U.S. export embargoes to Japan, which affected the Japanese decision to attack Western countries in December 1941; see Vietnam, war, and the United States . Vietnamese nationalism goes back through the first French presence, but there was opposition to Chinese influence dating back to the Two Trung Sisters in the first century A.D.
In English-speaking circles, it is said to have begun in 1954 or 1959 and ended in 1975.[1] Nevertheless, the following article follows a common usage by historians, to cover a two-part conflict that began in 1945 and ended in 1975.
From the perspective of some Vietnamese, the war was the military effort of the Communist Party of Vietnam under Ho Chi Minh to defeat France (1946-54), and the same party, now in control of North Vietnam, to overthrow the government of South Vietnam (1958-75) and take control of the whole country, in the face of military intervention by the United States (1964-72). Others discuss the Viet Minh resistance, in the colonial period, to the French and Japanese, and the successful Communist-backed overthrow of the post-partition southern government, as separate wars. Unfortunately for naming convenience, there is a gap between the end of French rule and the start of partition in 1954, and the Northern decision to commit to controlling the South in 1959.
Without trying to name the wars, the key timeline events in modern history are:
- 1941: Japanese invasion of French Indochina
- 1945: End of World War II and return of Indochina to French authority
- 1954: End of French control and beginning of partition under the Geneva agreement; CIA covert operation started
- 1955: First overt U.S. advisors sent to the South
- 1959: North Vietnamese decision, in May 1959 to create the 559th (honoring the date) Transportation Group and begin infiltration of the South
- 1964: Gulf of Tonkin incident and start of U.S. combat involvement; U.S. advisors and support, as well as covert operations, had been in place for several years
- 1972: Withdrawal of last U.S. combat forces as a result of negotiation
- 1975: Overthrow of the Southern government by regular Northern troops, followed by reunification under a Communist government.
Summary
In terms of terminology, over 90% of civilian and military writers and analysts use "Vietnam War" but some use "First Indochina War" (for 1946-54, when the French played a major role) and "Second Indochina War" (for 1954-75, when the U.S. played a major role). [2]
In terms of scholarly articles in refereed journals, 94% of article titles and abstracts in one database search used "Vietnam War" while only 6% used "Indochina War." Such searches admittedly do not establish whether historians are using "Vietnam War" to name a conflict that began in 1945, however.
The first stage, 1946-1954, or First Indochina War involved driving out the French colonial power. During that period, the Communist-dominated military wing of the anticolonialist force was called the Viet Minh, which had earlier fought the Japanese who had invaded in 1941. The U.S. became deeply involved from 1950, and soon was paying for 90% of the French effort.
1955 marked the first year in which the U.S. sent overt military advisers to train the Army of the Republic of Vietnam (ARVN) in 1955; a Central Intelligence Agency mission, including paramilitary specialists, began in 1954. The first U.S. military advisor accompanying combat troops, as well as combat fighting began in Laos, covertly in 1959 and more overtly in 1961; the first American soldier was killed in 1962. When President John F. Kennedy first increased the commitment to Southeast Asia, he expected the area of conflict in Laos, not Vietnam.
War between North and South
War between North and South began in the late 1950s when the Communists used supporters in the South, officially called the National Front for the Liberation of South Vietnam or "National Liberation Front" (NLF)[3] (the term "Viet Cong" was widely used but considered derogatory by the NLF) to destabilize and overthrow the government. The key date was May 1959, when the orders for creating the Ho Chi Minh trail were issued.
For a time, the NLF did have noncommunist leadership, primarily as figureheads. The term VC, however, most precisely referred to the military wing of the NLF, a common practice in insurgencies, as with, the somewhat oversimplified example of Sinn Fein and the Irish Republican Army The military of the North was officially the People's Army of Viet Nam (PAVN, also called the North Vietnamese Army (NVA)
In South Vietnam, there was a gradual evolution from early military advice, beginning in 1955, trying to build the ARVN into a conventional military , rather like that of South Korea, and then various kinds of counterinsurgency advice and assistance.
In Vietnam proper, American advisors began accompanying ARVN troops into battle in 1962-1963, most visibly at the Battle of Ap Bac in January 1963. U.S. began to bring in combat troops with a limited mission of protecting advisors. While there had been covert operations against North Vietnam well before, the first overt attack by U.S. air came in August 1964, in response to the Gulf of Tonkin incident. By 1965, U.S. combat aircraft were in the RVN, with battalion-strength units providing ground security. Larger units began operations in mid-1965.
The U.S. moved from financial aid and advice (before 1964), to large scale military involvement, beginning 1965, to save the government in the South in order to maintain the credibility of its Cold War policy of containment. At first, American involvement was through the embassy staff, but military involvement grew. First, a Military Assistance & Advisory Group was formed, one for Indochina and then one for Vietnam. When U.S. combat and combat support troops became directly involved, the Military Assistance Command, Vietnam, was created as a major command, a "sub-unified command" of the United States Pacific Command. There continued to be diplomatic, foreign aid (U.S. Agency for International Development), and Central Intelligence Agency linkages; coordinating the many U.S. and other country agencies became immensely complex.
The U.S. sent in over 500,000 troops (about a fifth in combat roles, the rest in support roles), in addition to many others at airbases in Thailand and elsewhere. Over 2.5 million Americans rotated through Vietnam, usually on a strict 365-day policy.
As the U.S. involvement increased, so did the effect of the war on U.S. domestic politics, as well as on both U.S. and Vietnamese relationships with the allies of both. Public antiwar opinion, some in the form of public protest, escalated in the U.S. and worldwide, reaching a climax in 1968.Vietnam-related conflict had a direct relationship to Lyndon Baines Johnson not seeking re-election, and for the 1968 Presidential victory of Republican Richard Nixon over Democrat Hubert Humphrey, Johnson's Vice President. In 1969, Nixon began to "Vietnamize" the war by turning the fighting over to the South Vietnamese military, and systematically withdrew American forces.
South Vietnam suffered at least 110,000 soldiers killed in action, plus at least 400,000 civilians. Estimates of total casualties, 1960-75, vary widely. Of the Americans, 31,000 died in combat (not counting accidents), of whom 66% were from the Army, 26% Marines, 4% Navy, and 4% Air Force. 4400 soldiers from South Korea were killed, along with 423 from Australia, 351 from Thailand, and 83 from New Zealand. Estimates of the deaths of Communist soldiers have run from 670,000 to 1.1 million.[4]
After the defeat of the South in 1975 a million Vietnam refugees fled to the U.S. The war spilled over into Laos and Cambodia, which came under Communist control in 1975. Otherwise, the long-feared "domino effect" whereby other countries in the region would turn Communist, did not happen.
Origins
To appreciate the complexity it is necessary to start with French colonialism in the 19th century, or, quite possibly, to go to Vietnamese drives for independence in the 1st century, with the Trung Sisters' revolt against the Chinese; the citation here mentions the 1968th anniversary of their actions.[5]
French Indochina Background
In the late 19th century the French expanded their global empire to southeast Asia, by acquiring control of Vietnam, and the neighboring countries of Cambodia and Laos. The Chinese war lords who had been in charge were expelled, replaced by a French governor supported by rotating units of the French army and several thousand French civil servants. Few Frenchmen permanently settled in Indochina. Below the top layer of imperial control, the civil service comprised French-speaking Catholic Vietnamese; a nominal "Emperor" resided in Hue. Paris had hoped to make a profit from its empire, but instead the expenses of building roads, railroads, ports, utilities, schools and other infrastructure, not to mention the military and civil service salaries, far outpaced the modest profits from rice and rubber exports. Little industry developed and 80% of the population lived in villages of about 2000 population; they depended on rice growing. Most were nominally Buddhist; about 10% were Catholic. Minorities included the Chinese merchants who controlled most of the commerce, and Montagnard tribesmen in the thinly populated Central Highlands. Vietnam was a relatively peaceful colony; sporadic independence movements were quickly suppressed by the efficient French secret police.
Ho Chi Minh (1890–1969) and fellow students founded the Vietnamese Communist Party party in Paris in 1929, but it was of marginal importance until World War II.[6] In 1940 and 1941 the Vichy regime yielded control of Vietnam to the Japanese, and Ho returned to lead an underground independence movement (which received a little assistance from the O.S.S., the predecessor of the Central Intelligence Agency CIA).[7]
President Franklin D. Roosevelt (in office 1933-45) detested French colonialism, but Harry S. Truman (in office 1945-53) was more interested in helping restore French prestige in Europe, so he helped them to return in 1946. An Office of Strategic Services (OSS was the predecessor to CIA) observed the situation from Kunming, China, starting in 1942, and then in French Indochina, including direct discussions with Ho Chi Minh.[7]
In contrast with other Asian colonies like India, Burma, the Philippines and Korea, Vietnam was not given its independence after the war. As in Indonesia (the Dutch East Indies), an indigenous rebellion demanded independence. While the Netherlands was too weak to resist the Indonesians, the French were strong enough to just barely hold on. As a result Ho and his Viet Minh[8] launched a guerrilla campaign, using Communist China as a sanctuary when French pursuit became hot.
When the Korean War erupted in 1950, and NSC-68 redefined American objectives, Washington saw Vietnam as another target of Communist expansion, and began to fund about three-fourths of the French military efforts. However, the goals of Washington and Paris were incompatible. Washington wanted a democratic Vietnam independent of both France and Communism, while Paris was more interested in restoring its old empire than in fighting Communism. In 1950 the U.S. officially recognized the theoretical independence of the "State of Vietnam," even though Paris kept control of its foreign and military policy.
Dien Bien Phu
To cut Viet Minh supply lines from China, the French built a fort at remote Dien Bien Phu. In 1954, 12,000 defenders were surrounded and battered by General Vo Nguyen Giap (1911- ), who were surprised by the enemy's artillery, supplied by China but carried by human porters over seemingly impassible terrain. [9] Paris begged Washington for air strikes. The US Navy wanted to send its aircraft carriers into action but the US Army demurred, arguing it would be "a dangerous strategic diversion of limited U.S. military capabilities... [to] a non-decisive theatre." For the Army, containment meant holding back the Russian divisions in central Europe, not chasing guerrillas in Asian jungles. President Dwight D. Eisenhower (in office 1953-61), the man who led the war against Germany in 1944-45 and who commanded NATO in 1950, agreed with the Army. With the Korean stalemate resolved only a few months earlier, he rejected recommendations to intervene and refused to fight another land war in Asia.
Dien Bien Phu surrendered, the French government collapsed, and a Socialist government with Communist support came to power in Paris, pledged to get out of Vietnam in 30 days.
Geneva accords
At the 1954 Geneva Conference, the French signed agreements with the Viet Minh that amounted to a surrender; the French did not consult the government in Saigon. Vietnam was split into the Democratic Republic of Vietnam (DRV) (Communist North Vietnam}, and the Republic of Vietnam (RVN) (South Vietnam, supported by the United States). The split was a result of a Geneva conference, which also created an International Control Commission (ICC). The ICC, composed of Canada, India and Poland, provided some communications between the sides, but had little effect.
Because of American pressure, however, Paris did not give Ho Chi Minh all he demanded (he demanded all of Vietnam). A permanent cease fire was promised, and the country was split along the 17th parallel, with the north turned over to Ho's Democratic Republic of Vietnam (DRV). The French promised to leave the southern half, which for the time being would continue as the independent State of Vietnam with the Emperor as head of state and a Catholic anti-communist as premier. The Geneva Accords called for "free general elections by secret ballot" in 1956 to unify the country.
Washington and Saigon both rejected the Geneva Accords: they were both determined to build an independent, anti-Communist South Vietnam, but, in the militant anticommunism of the time, a democratic Vietnam was not a priority.
A Central Intelligence Agency team, the "Saigon Military Mission", that came to Saigon in 1954, just before partition had attempted to set up intelligence and covert action networks in the North. had been covert political operations and preparation for guerilla warfare in the North prior to partition in 1954.
The Diem Regime, 1954-63
In July 1954 Ngo Dinh Diem became premier in Saigon. Diem and his powerful brothers were nationalists who were both anti-French, of an authoritarian Mandarin/Confucianist ethos and anticommunist. As leaders of the Catholic minority, they won considerable sympathy and support in the Catholic anticommunist circles in the US, notably from Francis Cardinal Spellman of New York and the Kennedy family. As soon as the Communists came to power in the North, some 800,000 refugees (mostly Catholic) fled to South Vietnam. They provided most of the leadership and support for its government (GVN) and its army (ARVN), in part because the Diem government discriminated against mainstream Buddhists and various Vietnamese sects, such as the Cao Dai and Hoa Hao. American financial aid and military advisors replaced the French, and SVN under Diem took its place among the world's newly independent nations.
The United States rejected the Geneva Accords as a violation of the principle of containment. The Eisenhower Administration, eager to formalize the containment system by treaty, in 1954 set up the Southeast Asia Treaty Organization (SEATO). The US promised to aid SEATO signatories that were attacked by a Communist power. The French, still committed to the Geneva Accords, vetoed membership for the RVN. To get around this French veto, Washington had inserted in the Treaty a vague protocol that seemed to give Saigon some sort of guarantee, even though it was not allowed to sign the Treaty or become part of SEATO.
Furthermore, Eisenhower decided not to sign a mutual defense treaty with the RVN in order to avoid over-commitment. Instead the US relied on the SEATO Treaty, which was ratified by the Senate with little discussion of Vietnam. By default it became the chief legal base for US involvement in Vietnam, until the subsequent Congressional resolution granted to Lyndon Johnson in response to the claim that the North Vietnamese had attacked U.S. Navy vessels in the Gulf of Tonkin incident.
In 1960, Eisenhower had 900 American advisors in SVN to bring its army up to what were perceived as basic standards, against the sort of conventional invasion launched by North Korea in 1950. That same year Hanoi's ruling Politburo established the NLF as its political arm in the South, and the Viet Cong as the military arm.
The rank and file were southerners, the leadership was northern, but it is incorrect to say that the NLF was solely led by northerners. North Vietnamese certainly dominated it, but they were politically astute enough to have visible southern opponents of the RVN, who were not Communist-identified. Like many insurgencies, the NLF acted as a shadow government in contested areas, both providing services, but also demanding taxes and draftees.
The NLF kept a low profile in the cities, in part because its intelligence services had deply penetrated the GVN; the leadership of the Johnson Administration was baffled why it did so well in the country side. Defense Secretary Robert S. McNamara (in office 1961-68) told President John F. Kennedy (in office 1961-63) in 1961 it was "absurd to think that a nation of 20 million people can be subverted by 15-20 thousand active guerrillas if the government and the people of that country do not wish to be subverted."[10] McNamara, a manufacturing executive and expert in statistical management, had no background in guerilla warfare or other than Western culture, and rejected advice from area specialists and military officers. He preferred to consult with his personal team, often called the "Whiz Kids"; his key foreign policy advisor was a law professor, John McNaughton, while economist Alain Enthoven was perhaps his closest colleague.
Neither side holding power was interested in democratic reform. The Communists would never permit free campaigning against Communism. The southern leader, Ngo Dinh Diem (1901-63) refused to hold free and honest elections in the Republic of Vietnam, reserving power for a largely Catholic minority.
Weaknesses of South Vietnam
While Diem himself was an ascetic that probably did not personally profit, members of his family, and numerous southern officials, were motivated by opportunities for corruption rather than government by the consent of the governed. Diem demonstrated no real understanding of democracy, and kept power with the Catholic minority. Increasingly bitter interactions with a Buddhist opposition led to a crisis in 1963, with iconic images of monks burning themselves alive in protest. Eventually, Diem was overthrown by a military coup, but, while there was a parliament, general democratic governement never emerged.
Just as Diem's government (GVN) was factionalized and inefficient, its army, the ARVN, suffered inefficiencies due to patronage, favoritism, and corruption.[11] Commands and promotions went to political insiders, regardless of their skills and experience. Food, uniforms, munitions and information were sold for cash. Intrigue was the game, and the generals usually spent most of their time on politics rather than command. Few senior officers had any real military training. Draftees did not want to fight any more than their officers did. Although hardware was abundant and of good quality, training was mediocre, food and pay were unattractive, and morale was poor. Desertion rates were high (home was nearby).
Diem (and his successors) were primarily interested in using the ARVN as a device to secure power, rather than as a tool to unify the nation and defeat its enemies. Despite American efforts from 1960 through 1972, the situation never decisively improved. Saigon would ultimately lose the war because its large and very well equipped army lacked motivation to support a government.
Viet Cong guerrillas and regular North Vietnam Army
The North had clearly defined political objectives, and a grand strategy, involving military, diplomatic, covert action and psychological operations to achieve those objectives. Whether or not one agreed with those objectives, there was a clear relationship between long-term goals and short-term actions. Its military first focused on guerilla and raid warfare in the south, simultaneously improving the air defensives of the north.
Eventually, following the Maoist doctrine of protracted war, the final "Phase III" offensive was by conventional forces, the sort that the U.S. had tried to build a defense against when the threat was from guerrillas. T-54 tanks that broke down the gates of the Presidential Palace in Saigon were not driven by ragged guerrillas.
In the Viet Cong, and in the North Vietnam regular army (PAVN), every unit down to the company level had a cadre of political officers who monitored ideological correctness on a daily basis. The Viet Cong had many unwilling draftees of its own; tens of thousands deserted to the government, which promised them protection. The Viet Cong executed deserters if it could, and threatened their families, all the while closely monitoring the ranks for any sign of defeatism or deviation from the party line.[12]
In December 1963, a decisive meeting of the Communist Party (VWF) Central Committee in Hanoi set basic policy. Le Duan (1907-86) was in full control. Overruling Giap (who wanted to build up the regular army), and Ho (who, like the Soviets, did not want to antagonize the U.S.), Le Duan and the new leadership decided that the government of South Vietnam was on the verge of collapse. They escalated NLF attacks, but did not send regular troops.
At this time, the Soviet Union and China were bitterly contesting control of the Communist movement worldwide. Hanoi's decision marked a decisive break with the Soviets, who had recommended that instead of overthrowing the South and risking a major war with the U.S., it was better to concentrate on rapid development of the poverty-striken economy of North Vietnam.[13]
From 1959 to the end of 1963, more than 40,000 PAVN troops, primarily soldiers born in South Vietnam who had gone north, were sent back to South Vietnam. Included were 2,000 senior and midlevel officers (field grade and above) and technical personnel. As of 1963, they constituted, half the full-time soldiers and 80% of the officers and technical cadres in command and leadership organizations of the Communist army in South Vietnam. Those that had gone north often still had family and village ties. Unwilling villagers, however, were impressed into the Communist forces.
To provide logistic support from 1961 through 1963, 559th Transportation Group (the Ho Chi Minh Trail command] transported to the South 165,600 weapons of all types, including artillery, mortars, and anti-aircraft machine guns. In addition in 1962-63, 759th Sea Infiltration Group, using transport vessels camouflaged as fishing junks, delivered 25 shiploads totaling 1,430 tons of weapons and ammunition to covert docks and landing sites in the Mekong Delta and in the coastal provinces east of Saigon.
American perspective
The Vietnam War had a major effect on U.S. politics and public opinion. The U.S. strategy, over time, changed. From 1964 to 1972 debate raged between "doves" (who wanted the US to cut its losses and get out) and "hawks" (who wanted to win, for some definition of "win"). From 1945 to 1964, people with expertise in the area, but with no special ornithological definition, argued about the proper role of the United States in the region. Speaking of wars in general,
Nothing is more divisive for a government than having to make peace at the price of major concessions. The proces of ending a war almost inevitably invokes an intense internal struggle if it means abandoning an ally or giving up popularly accepted objectives...the power structure of a government is not made of one piece — even in dictatorships. Political factions contend for influence, government agencies and military service maintain their own separate loyalties and pursue partisan objectives, and popular support keeps shifting. — Fred Charles Iklé, [14] pp. 59-60
It was the position of the Johnson Administration that the entire opposition was organized and directed by Hanoi, a position consistent with the strict Communist vs. anti-Communist view of the fifties. This view, at times, may have interfered with pressuring for reforms in the South Vietnamese government, such as removing inefficient officers with good political connections, and reducing corruption.
With the Gulf of Tonkin resolution as authority, the U.S. sent more and more combat units into South Vietnam, also bringing in allied nations. In some cases, such as with the excellent South Korean troops, the U.S. paid their expenses.
The Administration also was of the position that any Communist government was unacceptable, and was dismissive of any neutralist roles. Other than a general fear of Communist expansion, no U.S. administration clearly articulated a direct threat to the U.S. that justified large-scale U.S. land involvement in Asia. For some policymakers, the general threat was sufficient reason. For others, as seen in the McNaughton memo, it was more that the U.S. had no clean way to reduce its involvement without harming its "role as a guarantor".Perhaps the most telling document of the lack of strategic vision of McNamara and his staff was a 1965 memorandum from McNaughton, attempting to define goals. McNaughton defined the U.S. aims as:
- "70%--To avoid a humiliating US defeat (to our reputation as a guarantor).
- 20%--To keep SVN (and then adjacent) territory from Chinese hands.
- 10%--To permit the people of SVN to enjoy a better, freer way of life. Also-To emerge from crisis without unacceptable taint from methods used. Not--To "help a friend," although it would be hard to stay if asked out." [15]
Note that generic anticommunism was not an objective, and the welfare of South Vietnam was low on the list. McNaughton's emphasis on Chinese domination ignored a history of Vietnamese enmity to the Chinese, going back to the revolt of the Two Trung Sisters in the first century A.D. North Vietnam was Stalinist, not Maoist, and far more a Soviet than Chinese client.
The Johnson Administration always insisted that aggression was organized and directed by Hanoi; it rejected arguments by opponents of intervention in Vietnam that Hanoi was innocent, or intermediate positions that there were southern dissidents used by the North. U.S. opposition had no single cause, but one theme was that it was extremely unwise to become involved in a land war in Asia, with no critical U.S. interests at stake. Others, perhaps more naive, saw it as purely a civil war.
There was never a unified command in South Vietnam, as there was in South Korea, for complex reasons. Since there was no multinational mandate, such as the UN issued for the Korean War, there was sensitivity about the U.S. creating the perception of being a colonial power making the RVN a "puppet", which was already a Communist propaganda theme. Had this issue not existed, there were concerns about Communist intelligence agents in the Southern government.
Weak Diem regime
Even if the Communist military threat could be countered by U.S. action, there remained an enormous problem with the Diem regime itself-- militarily ineffective and politically unpopular. It tried to suppress the non-Communist opposition by large-scale arrests. Its downfall came when it bungled the demands of organized Buddhist monks for a larger voice in political affairs. The multiple interest groups and centers of power in the nation had become alienated from Diem, and gave him no support as he raided the pagodas and arrested demonstrators. Furthermore, he increasingly rejected American demands for political and economic reforms. Washington sadly concluded that Diem had outlived his usefulness, so it stood silent during a military coup on November 1, 1963, that assassinated Diem and installed the first of a long series of unstable governments.[16]
Kennedy himself was assassinated three weeks later, and Lyndon Johnson took charge. Diem's death led to chaos; the strategic hamlet program collapsed, and the Viet Cong recouped their losses and pressed forward across the countryside. ARVN battalions one after another crumbled under intense local attacks. The CIA gave GVN only an "even chance" of surviving.[17]
Fear of China, 1960-1964
Rusk worried that a Communist victory in Vietnam would cause neighboring countries to fall like dominoes to pro-Chinese Communists. The threat was greatest in Indonesia, an island nation with a large population, significant oil wealth, and an active Communist movement. Rusk was concerned about what was called the "falling domino" effect; he thought the fall of neighboring states would be rapid, but others looked for great damage in slow motion, as in a a 1964 CIA estimate:
We do not believe that the loss of South Vietnam and Laos would be followed by the rapid, successive communization of other states of Southeast Asia. Instead of a shock wave passing from one to the next, there would be a simultaneous, direct effect on all Far Eastern countries. With the possible exception of Cambodia, it is likely that no nation of the area would quickly succumb to communism as a result of the fall of Laos and South Vietnam. Further, a spread of communism in the area would not be inexorable, and any spread that would happen would take time — time in which the situation might change in any of a number of ways unfavorable to the Communist cause....The loss of South Vietnam and Laos to the Communists would be profoundly damaging to the US position in the Far East, most especially because the US has committed itself persistently, emphatically, and publicly to preventing Communist takeover of the two countries.[18]
In 1965, however, the anti-communist army seized power and totally destroyed the Communist movement in Indonesia with wholesale arrests and executions. This was a surprise to the U.S., which was giving covert aid to some anti-communist factions, but the Army action followed Communist killing of several generals.
Escalation by Viet Cong
In the early 1960s the Viet Cong escalated its attacks; the Diem regime lost ground every month. In 1961 the Viet Cong had 25,000 regular soldiers and 17,000 underground operatives. The NLF controlled villages containing about a fifth of the rural population of ten million (six million people lived in SVN's cities and towns, where the NLF remained weak.) American observers reported that the Saigon regime lacked legitimacy in the villages. The GVN never generated spontaneous support or a sense of patriotism because it was too much like the French system: too autocratic, too urban, Catholic, aloof, corrupt, arrogant, inefficient, self-indulgent and predatory. The challenge was not to restore legitimacy but get it in the first place.
In January 1963, an apparently overwhelming ARVN force, with armored vehicles, artillery and air support, and U.S. advisors including John Paul Vann went confidently against an inferior force at the Battle of Ap Bac, and were routed. [19]. This has been considered the triggered for an increasingly skeptical, although small, American press corps in Vietnam.
By October, 1963, Kennedy had sent 16,000 advisors who were working feverishly to shape up the ARVN; 100 had already been killed. The U.S. Air Force began training pilots; the Army sent in helicopter transports. The choppers terrorized the Viet Cong, until they figured out how to ambush them when they landed. After 9,000 combat sorties, 21 airplanes and 13 helicopters had been shot down. Viet Cong influence had been pushed back, but the NLF still controlled a tenth of the rural villages.
NLF as shadow government
By contrast, peasants at first found the NLF appeared to be honest, caring and basically like themselves. It had considerable support--it especially appealed to idealistic youth, and in any case was always feared by the villagers who knew the assassination squads would eliminate any dissent. From 1957 through 1972, the Viet Cong Security Service carried out 37,000 assassinations of government officials, religious and civic leaders, teachers, informers, landowners, and moneylenders.
The role of landowners was critical to the dissatisfaction of villagers with the government. Absentee landlords formed a significant part of Diem's power base, in a quasi-feudal system that contained resentments the NLF could exploit. Much of Vietnamese rural culture was tied to the ancestral lands where they were located, yet the villagers did not own their fields and homes.[20] Gibson quotes a landlord interviewed by Samson:
In the past, the relationship between the landlord and his tenants was paternalistic. The landlord considered the tenant as an inferior member of his extended family. When the tenant's father dieed, it was the duty of the landlord to give money to the tenant for the funeral; if his wife was pregnamt, the landlord gave mone for the birth; if he was in financial ruin, the landlord gave assistance; therefore, the tenant had to behave as an inferior member of the extended family. The landlord enjoyed great prestige vis-a-vis the tenant. [21]
During this period of paternalism, the landlord also received 40 to 60 percent of the tenants' crops as rent. When the Viet Minh fought the French, they also fought an economic war, and drove large landowners into the cities, or variously lowered or ended rent payments. According to Gibson, when Diem's ARVN forces established security, they put landlords back in control, often demanding back rent. [22]
Separarately from the land reform and economic issues, the Government of Vietnam were unable to provide security for the villages. The Diem government response was to create defensible "strategic hamlets" and forcibly move the villagers to them. The strategic hamlet might have government-appointed or military leaders; the villagers' locally chosen leadership was destroyed. The tombs of ancestors was abandoned, in a culture where it was proper to show ancestral respect.
Changes in U.S. commitment following Johnson's election
Equally important to Johnson than what happened in Asia was what was happening at home, especially in the minds of the voters.[23] To Johnson, Vietnam was a "political war" only in the sense of U.S. domestic politics, not a political settlement for the Vietnamese.
Johnson's plan to settle war
Johnson believed that all disputes arose out of mutual misunderstandings, and could be resolved through negotiation. His strategy was to offer Hanoi billions of dollars in foreign aid if they would play along, or else bomb them into negotiations, from which a permanent peace would result that allowed South Vietnam to continue as an independent nation.
Johnson did not reject the possibility that the Communists could become part of some sort of coalition government. He apparently was unaware that Vietnamese history was against him, as when the VNQDD was purged from the "broad front" Viet Minh by the Communists.
The military, which saw its mission in terms of winning wars, not facilitators for negotiations, never agreed with Johnson, or, perhaps more to the point, with McNamara. In the 1950s, when Chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff Arthur Radford recommended major U.S. intervention at Dien Bien Phu, possibly including nuclear weapons, Eisenhower was quite confident in refusing Radford. The other members of the JCS had not supported Radford.
By the time Johnson took office, there was already a significant U.S. involvement in Vietnam, although large-scale combat forces had not been committed. McNamara, who had been appointed by Kennedy, continued to push an economic and signaling grand strategy to Johnson. Johnson and McNamara, although it would be hard to find two men of more different personality, formed a quick bond. McNamara appeared more impressed by economics and Schelling's compellance theory [24] than by Johnson's liberalism or Senate-style deal-making, but they agreed in broad policy.
Ironically, after Johnson said he would not run for re-election in 1968, Creighton Abrams, who took over MACV from William Westmoreland, was far more oriented toward a holistic approach to nation building than Westmoreland's attritional strategy.
Johnson, committed to containment, refused to withdraw, but also refused to take decisive action. Since South Vietnamese were unable to defeat the threat with American advice and supply; Johnson made the fateful decision to supplement them US combat troops. He planned to first rescue GVN (Government of South Vietnam) from imminent collapse by guerrilla attacks, then negotiate a settlement with Hanoi that would allow it to survive. He vetoed two other options: US command and control of the ARVN (unwise because GVN would never learn to defend itself) and invasion of North Vietnam to strike the threat at its source.
In mid-1964, LBJ assembled a new team:
- Maxwell Taylor, from Chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff to Ambassador to the Republic of Vietnam, continuing the Kennedy policy that the Chief of Mission had authority over all U.S. organizations in a country
- Harold Johnson to Chief of Staff of the Army
- General Earle Wheeler (1908-75) replaced Taylor at Chairman of the JCS; his mission was to keep the senior commanders loyal to the White House.[25]
- General William Westmoreland (1914-2005) became head of Military Assistance Command, Vietnam (MACV), with authority over US Army and Marine ground operations, and some naval and tactical air operations.
- Admiral Ulysses S. Grant Sharp (1906-2001) at Pearl Harbor, became head of all US forces in the Pacific. He had charge of the naval blockade that kept Hanoi from running supplies by sea, and most importantly, of strategic bombing operations over North Vietnam (which were launched from Sharp's four aircraft carriers or from Air Force B-52 bases in Thailand and Guam).
Nominally Westmoreland reported to Taylor for policy guidance and Sharp for theater-level military command; in practice he dealt directly with McNamara or LBJ. Westmoreland could always be counted upon for a public statement exuding optimism; he reassured LBJ that the war would be won in time for the 1968 elections. The intricate division of responsibility was set up so that there would be no powerful theater commander like MacArthur; it also guaranteed a steady flow of disputes that could only be resolved by McNamara or the president. The military thus never had control of the war it was called upon to fight, or of the tactics to use.
Gulf of Tonkin incident: 1964
In early August 1964 Johnson seized on an ambiguous incident in which North Vietnamese PT boats reportedly fired on a US destroyer; this became known as the Gulf of Tonkin incident. The public message was that the destroyer was on general patrol.
Less well known, however, were that simultaneous covert attacks on the North Vietnamese coast, coordinated by MACV-SOG operating under Operations Plan (OPPLAN) 34A, and the North Vietnamese were on high alert. The destroyer was actually collecting signals intelligence under a program called the DESOTO patrol,[26] and tecently declassified National Security Agency signals intelligence reports indicate that the U.S. commanders knew that the North Vietnamese were uncertain if the destroyers were part of the same attacks as 34A. There has never been clear-cut sonar or SIGINT information that the North Vietnamese initiated an attack on the destroyer patrol, although one of the destroyers may have fired warning shots.
Although there was no immediate and continuing threat to U.S. forces, Johnson ordered retaliatory airstrikes on the North. His television address to the U.S. public, explaining he had ordered it under his authority as commander-in-chief, was delivered while the strikes were still inbound and the North Vietnamese air defenses not yet alerted. According to McMaster, Johnson insisted on an early announcement so that he would be sure to make the late evening news, as well as the deadline for morning newspapers. [23]
He pressed for the "Gulf of Tonkin Resolution" through Congress, saying it would deter Hanoi. The Resolution was itself vague, endorsing the Commander-in-Chief's right to "take all necessary measures to repel any armed attack...and to prevent further aggression." Not only did the Resolution give Johnson a boost during his heated 1964 reelection campaign, it also provided just enough legality for him to avoid going back to Congress; see War Powers Resolution and the Total Force concept developed by Creighton Abrams (the last commander of U.S. combat forces) as future checkpoints on Presidential adventurism. The role of the President and Congress in initiating combat, however, remains intensely controversial. See Vietnam, war, and the United States.
At the time of the Gulf of Tonkin incident, North Vietnamese air defense was fairly unsophisticated, but steadily improved. As opposed to the North Koreans in the Korean War, they established an integrated air defense system (IADS), and seemed more intent on training their own people rather than rely on Russian, Chinese or Korean pilots. In many cases, they got quite good performance out of obsolescent weapons, such as the MiG-17 fighter, of which they had more than the first-line MiG-21.
Escalation 1965
The NLF was on the verge of announcing a provisional government in the northernmost six provinces; three elite regiments from the North Vietnamese Main Force moved into South Vietnam. Hanoi thought it could win quickly. It was a tragic miscalculation that would bring endless misery to the Vietnamese.
While there was not a
After his reelection, Johnson sent in the first American combat troops in March, 1965, to protect the air bases.
Rejecting the Air Force's strategy of strategic bombing against 94 critical targets[27] in the North, Johnson and McNamara instead launched an alternative air power strategy called "Rolling Thunder." It entailed retaliatory bombing anytime Communists struck at American forces, together with a gradual buildup of 22 bombing attacks against small military targets in the North, in complete opposition to the JCS recommendations that if there were to be air strikes
To reverse the downhill slide in the villages, Westmoreland called for 24 more maneuver battalions (of approximately 800-1000 men each) added to the 20 he had, plus more artillery, aviation (helicopters), and support units; McNamara rounded the total to 175,000 troops, with 27 more maneuver battalions to come in 1966. Westmoreland's "ultimate aim" was:
"To pacify the Republic of [South] Vietnam by destroying the VC—his forces, organization, terrorists, agents, and propagandists—while at the same time reestablishing the government apparatus, strengthening GVN military forces, rebuilding the administrative machinery, and re-instituting the services of the Government. During this process security must be provided to all of the people on a progressive basis."[28]
Westmoreland complained that, "we are not engaging the VC with sufficient frequency or effectiveness to win the war in Vietnam." He said that American troops had shown themselves to be superb soldiers, adept at carrying out attacks against base areas and mounting sustained operations in populated areas. Yet, the operational initiative— decisions to engage and disengage—continued to be with the enemy.
Simple search and destroy approach that consisted of attacking and blocking forces would not work in Vietnam's jungles because the VC demonstrated the ability to "slip out from between the hammer and the anvil." Thus, the Americans needed to cover all likely escape routes. Westmoreland rejected the Marine Corps alternative program of building up a close rapport with the peasant and defending their villages.
By the end of 1965 there were 184,000 Americans inside Vietnam, plus 22,400 Allies (from Korea, Australia and New Zealand). Having quietly become so deeply involved, meant the US could no longer easily back out; the war had become a quagmire. On the other hand it had to be kept low key lest it interfere with Johnson's domestic goals, and the geostrategic goals became increasingly vague.
Rolling Thunder: The Failure of Strategic Bombing
Johnson did not see the North Vietnamese as having a significant degree of independence, although, with Sino-Soviet tensions, the Administration was not always clear as to who did direct them. In spite of two millenia of Sino-Vietnamese conflict, there seemed a special fear of Chinese control, although the more significant weaponry came from the Soviets, and the North Vietnamese leadership was more Stalinist than Maoist. He defined Vietnam as a proxy for containing worldwide Communist action, and generally ignored both the nationalist sentiments in both Vietnams, and the problems of popular support for the Southern government. This is not to say that the North was not a police state, but it had both exerted more efficient control than had the South, and also could portray the U.S. as a common "enemy of the people".
Johnson and McNamara adopted a three-tier strategy to save SVN.
- Protect US bases and repel enemy ground attacks with U.S. ground troops
- Attack the Ho Chi Minh Trail in Laos.
- Initiate Operation ROLLING THUNDER bombing over North Vietnam.
The air campaign had a triple purpose:
- boost Saigon's morale
- weaken Hanoi's war-making capabilities
- force the North to the bargaining table.
To the civilian decisionmakers of the Johnson Administration, who prepared detailed bombing plans at Tuesday luncheons from which anyone with military bombing experience was excluded, bombing seemed a cheap solution: the Air Force and Navy had plenty of air power to spare, and the raids would cause few American casualties. The extremely detailed bombing orders, down to the number and type of bombs and the direction of approach, rarely considered how to attack targets while minimizing the effectiveness of enemy air defense.
The targets were primarily transportation lines, bridges, railway yards, storage dumps, and oil tanks; civilian areas were to be avoided. In line with a "signaling" model proposed by Harvard economist Thomas Schelling, LBJ refused to allow the most valuable installations, those around Hanoi and Haiphong, to be attacked. The idea was that damage future was more harrowing than damage present. In practice, the slow escalation gave Hanoi time to camouflage and decentralize its installations, and thus minimize the damage.The raids were closely controlled by the White House, which saw them as "signals" in a negotiating process with Hanoi. There is no indication, however, that Hanoi even perceived that signals were sent.
Raids were calibrated so that each month they became more punitive, at least in the American value system. This theory, centered in the Office of the Secretary of Defense, was that sooner or later Hanoi's pain threshold would be crossed and they would agree to negotiate a plan that would allow SVN to survive.
A classic error, which generations of professional intelligence analysts have been taught to avoid, is mirror-imaging. The Johnson Administration treated the North Vietnamese as mirror images of themselves, rather than people with a radically different mindset.
Historians (on all sides) are unanimous that Rolling Thunder was a total failure.[29] North Vietnam was a very poor agricultural country with few likely targets in the first place. Unlike Germany and Japan in World War Two, it did not manufacture its own munitions, but imported them from China and Russia. LBJ vetoed plans to mine Haiphong harbor and cut the railroad lines at the Chinese border. Johnson, who had been a member of the Senate Armed Services Committee in 1950, vividly remembered the Chinese intervention in Korea that year, and refused to permit any military action that might somehow trigger another intervention. In striking contrast to the attacks on Berlin, Tokyo and a hundred other World War Two targets, the vast majority of bombs landed on empty jungle.
Air war in the south
Vietnamese jungle caused much military difficulty. In the 1964 election, Barry Goldwater never recovered from speculation about possibility of using low-yield nuclear weapons to defoliate infiltration routes in Vietnam, he never actually advocated the use of nuclear weapons against the North Vietnamese. Nevertheless, the Democrats easily painted Goldwater as a warmonger who would drop atomic bombs on Hanoi.[30]
Under Operation RANCH HAND, the U.S. military sprayed large areas with a defoliant called Agent Orange. While Agent Orange itself was considered nontoxic to humans, and was primarily composed of conventional herbicides 2,4-D and 2,4,5-T, many batches had an exceptionally toxic byproduct of the manufacturing process, which caused caused significant contamination, and long-term health consequences, including defects, on both Vietnamese and Americans. This was also used by Canadian Forces in Canada, who documented the later-understood health effects. [31]
It cost the US a billion dollars a year to destroy $100 million in PAVN supplies--but Washington had the tens of billions and Hanoi did not have the tens of millions. It did have friends, however, and Moscow and Peking doubled their shipments of munitions. Moscow sent in sophisticated air defense systems; 922 planes went down. Rolling Thunder dropped 640,000 tons of bombs, but pilots protested angrily that political restrictions radically reduced their effectiveness. As one Navy flier growled in his diary:
We fly a limited aircraft, drop limited ordnance, on rare targets in a severely limited amount of time. Worst of all we do this in a limited and highly unpopular war....What I've got is personal pride pushing against a tangled web of frustration.[32]
Rolling Thunder did reduce the southward flow of arms somewhat, and definitely forced Hanoi to divert more and more of its resources to logistics, air defense and rebuilding. More than half of the North's electric power, oil storage, bridges and railroad yards had to be rebuilt. Supplies were hidden in small caches or buried underground, which further attenuated Hanoi's logistics capability. The suffering of its people held a lower priority for the Politburo than its quest for victory, and its actions were consistent with its goals, especially considered in Mao's concept of protracted war.
McNamara and other civilians, who had placed blind trust in the invincibility of air power, developed a growing sense of frustration and defeatism. McNamara himself concluded the bombing was a failure, and that therefore the whole war was doomed.
After Nixon replaced Johnson, the new national security team reviewed the situation. Henry Kissinger asked the Rand Corporation to provide a list of policy options, prepared by Daniel Ellsberg. On receiving the report, Kissinger and Schelling asked Ellsberg about the apparent absence of a victory option; Ellsberg said "I don't believe there is a win option in Vietnam." While Ellsberg eventually did send a withdrawal option, Kissinger would not circulate something that could be perceived as defeat. [33].
Westmoreland's Attrition Strategy
Despite some shortages, the US Army had never been in nearly as good shape at the start of a war. At peak Westmoreland had 100 infantry battalions, the main maneuver and fighting unit of the war. Routinely it received 500 hours a month of helicopter support from corps' command. Above the battalion were brigades and divisions; in this war they handled paperwork, letting the battalions do the fighting. Overall, 20% of the soldiers were in "teeth" (combat) roles; the rest were "tail," assigned to advisory missions, logistics, maintenance, construction, medicine and administration.
Westmoreland's first challenge was figuring out a strategy to defeat the Viet Cong.
- Phase I: stabilize the situation (by the end of 1965)
- Phase II: (scheduled for 1966-67) would push the enemy back in key areas
- Phase III: total victory (1968).
Marine plan
The Marines, with responsibility for "I Corps," the northern third of the country, had a plan for Phase I. It reflected their historic experience in pacification programs in Haiti and Nicaragua early in the century. [34]
Noting that 80% of the population lived in 10% of the land, they proposed to separate the Viet Cong from the populace. It was a major challenge, since the NLF controlled the great majority of villages in I Corps. Working outward from Da Nang and two other enclaves, 25,000 Marines of the III Marine Amphibious Force[35] systematically eliminated Viet Cong soldiers and guerrilla forces, and sought to weed out NLF cadres from the villages.
The main device was the Combined Action Platoon, with a 15-man rifle squad and 34 local militia. Rather than having separate "advisory" units, the bulk of the CAP members served alongside the local militia, building personal relationships. It would "capture and hold" hamlets and villages. The Marines put heavy stress on honesty in local government, land reform (giving more to the peasants) and MEDCAP patrols that offered immediate medical assistance to villagers. In some respects, the CAP volunteers had assignments similar to the much more highly trained United States Army Special Forces, but they would make use of whatever skills they had. One young Marine, for example, was a graduate of a high school in an agricultural area in the U.S., came from a family hog farm that went back several generations, and won competitions for teenagers who raised prized hogs. While he was no military expert, he was recognized as helping enormously with the critical pork production in villages.
Marines in CAP had the highest proportion of volunteering for successive Vietnam tours of any branch of the Marine Corps. Many villages considered the CAP personnel part of their extended family. Westmoreland distrusted the Marine village-oriented policy as too defensive for Phase II--only offense can win a war, he insisted. The official slogan about "winning hearts and minds" gave way to the Army's "Get the people by the balls, and their hearts and minds will follow." Ambassador Taylor welcomed the Marine strategy as the best solution for a basically political problem; it would also minimize American casualties.[36]
While the Army and Marines had their approaches to the village, yet another came from a joint project of the CIA and United States Army Special Forces. The CIDG (Civilian Irregular Defense Groups) program was created for the Montagnard peoples in the sparsely populated mountanous areas of the Central Highlands. The Montagnards disliked all Vietnamese, and had supported first the French, then the Americans. About 45,000 were enrolled in militias whose main role was defending their villages from the Communists. In 1970 the CIDG became part of the ARVN Rangers.[37] Indeed, the tensions were high between the Army (which was in charge) and the Marines.
By mid-January 1968, III MAF was the size of a U.S. corps or field army, consisting of what amounted to two Army divisions, two reinforced Marine Divisions, a Marine aircraft wing, and supporting forces, numbering well over 100,000. GEN Westmoreland believed that Marine [[LTG[[ Robert E. Cushman, Jr., who had relieved General Walt, was "unduly complacent."{{citation
| title = A Soldier Reports | first = Will Westmoreland worried about what he perceived as the Marine command's ``lack of followup in supervision, its employment of helicopters, and its generalship. [38]Westmoreland sent his deputy Creighton Abrams to take command of I Corps, and gave his Air Force commander control of Marine aviation. The Marines protested vehemently but were rebuffed by the Joint Chiefs of Staff.[39]
Westmoreland vs. Taylor
Taylor's strategy was to use superior American mobility and firepower to locate, attack and destroy the Viet Cong main forces. Once they were destroyed, he reasoned, the villages would be easy to pacify. Westmoreland proposed instead a "search and destroy" strategy that would win the war by attrition. The idea was to track down and fight the larger Viet Cong units, hoping to grind them down faster than they could be replaced. The measure of success in a war of attrition was not battles won or territory held or villages pacified, it was the body count of dead enemy soldiers. The body counts often were demanded by the chain of command, under pressure from Washington, even though the numbers were guesses and had little to do with realistic battle damage assessment. A number of field commanders and CIA analysts found that a much better predictor was the number of weapons recovered from a battlefield.
Westmoreland promised his three phase strategy could get the job done--whereas the defensive enclaves would prolong the conflict indefinitely into the future. Johnson could not wait forever, so he bought Westmoreland's plan and removed Taylor.
While there have been exceptions, especially in recent wars, Marines and Army troops do not always mix well, as they have some very different doctrinal assumptions. Army troops have much heavier artillery, and will wait for it to suppress the enemy before attacking on the ground, while Marines rely both on fast movement, and their own air support substituting for heavy artillery (i.e.,Marine Air-Ground Task Forces, which put land and air elements under a common commander). In 1968, Westmoreland sent his deputy Creighton Abrams to take command of I Corps, and gave his Air Force commander control of Marine aviation. The Marines protested vehemently but were rebuffed by the Joint Chiefs of Staff.
General Vo Nguyen Giap, head of the PAVN since 1946, reinforced the forces in the South, to counter the U.S. reinforcement. While Giap was not a devotee of Mao's concepts of government, he did agree with Mao's concept of protracted war, as well as the Marxist theory that the enemy would eventually defeat himself. His goal was to outlast the enemy.
The enemy will pass slowly from the offensive to the defensive. The blitzkrieg will transform itself into a war of long duration. Thus, the enemy will be caught in a dilemma: he has to drag out the war in order to win it and does not possess, on the other hand, the psychological and political means to fight a long drawn-out war[40]
The flow rose from 3,000 a month in 1965 to 8,000 a month throughout 1966 and 1967, and then 10,000 in 1968. By November 1965 the enemy had 110 battalions in the field, with 64,000 combat troops, 17,000 in combat support, and 54,000 part- time militia.
First Airmobile Battles: Ia Drang and Bong Son
- See also: Battle of the Ia Drang
- See also: Battle of Bong Son
At Ia Drang (river Drang) in late 1965 the first major confrontation shaped up between Giap and Westmoreland. Giap wanted to continue his successful guerrilla war, but was overruled by the Politburo; they demanded victory in a hurry. The new plan was for Giap to use three regiments, but with a new controlling divisional headquarters, across the neck of SVN, cutting the country in two. The division threatened the Plei Me special forces camp with one regiment, but put a second regiment across the road over which South Vietnamese forces, without helicopters, would have to drive to Plei Me from the larger base in Pleiku. Intelligence identified the presence, but at first not the position, of a third regiment, which could attack Pleiku if the reserve based there went to the assistance of Plei Me.
The South Vietnamese recognized they were stretched too thin, and asked for U.S. help. The U.S. Field Force (corps equivalent) commander for the area, MG Stanley Larsen, told GEN Westmoreland that he thought the 1st Cavalry Division (Airmobile) was ready, and got permission for it to use its mobility to bypass the road ambushes. Since the PAVN along the road had planned to ambush trucks, there was not an issue of not being able to find the relieving troops. While the heliborne U.S. troopers could be heard miles away, their actual attack zones could not be determined until they swooped to a landing.
It should be noted that the PAVN's practice of listening for helicopters was realized by Harold Moore, promoted to brigade command after leading a battalion in the Ia Drang. In the larger Battle of Bong Son approximately a month later, Moore used obvious helicopters to cause the PAVN to retreat onto very reasonable paths to break away from the Americans -- but different Americans had silently set ambushes, earlier, across those escape routes.
Giap's troops infiltrated the area of operations, carrying their supplies, hiding from reconnaissance during the day. They contested the helicopter landing zones, but never tried to hold ground; pitched battles were avoided, unless they could not break contact. If there was no exit, they did try to kill as many Americans as possible, with seemingly little concern about their own losses.
The PAVN preferred hit-and-run ambushes, or what they called "catch and grab." When their retreat was blocked, their next tactic was called "hugging the belt" [41] the Americans would not dare calling in artillery and gunships because of the risk of friendly fire casualties. The surprise attack would give a short window of opportunity before superior American mobility could be brought to bear.
Giap was surprised that the U.S. and RVN knew the positions of two of his three regiments, and had an approximate location for the third. PAVN launched a series of violent attacks against the Americans, who clustered around their landing zones. Only four choppers were shot down. Heavy doses of tactical air power, including area, then radar-controlled saturation bombing from B-52s, overwhelmed the PAVN. The invasion was stopped; the survivors fled back into their Cambodian sanctuaries. Giap excused his failure by saying he only wanted to discover the American's tactics; he convinced the Politburo that it was necessary to return to low-level guerrilla tactics because he could not beat the Americans in battle. The 101st Airborne Division converted to an airmobile formation, but the true airmobile structure was not used by other units. Nevertheless, helicopter augmentation became far more common.
Westmoreland selects new tactics
The tide had turned, and Westmoreland called for more troops and helicopters to enlarge the search and destroy operation across the country. McNamara and LBJ agreed, doubling the number of infantry maneuver battalions from 35 in October 1965 (22 Army, 13 Marines) to 70 a year later (50 and 20). The number of artillery battalions also doubled to 79. By the end of 1966 the US Army had 244,000 personnel in Vietnam, the Marines 69,000, Air Force 57,000 and Navy 25,000, a total of 395,000. They faced 100,000 enemy riflemen in 152 combat battalions and two hundred separate companies. The doubling of combat forces, Washington realized, would entail a doubling of US losses from 400 deaths a month to 800.
Most of the fighting in Vietnam was done by companies that deliberately went in harms way for a couple days at a time-- into the jungles of the Central Highlands, or the rice paddies of the heavily populated lowlands. As Marine Lt. Philip Caputo observed, "There was no pattern to these patrols and operations. Without a front, flanks or rear, we fought a formless war against a formless enemy who evaporated like the morning jungle mists, only to materialize in some unexpected place."[42]
Number and causes of casualties
Of two million small unit operations, 99% never encountered the enemy. What are now called improvised explosive devices, "booby traps" at the time, and land mines together caused a third of American deaths. The war was fought out in the other one percent, and most of the time combat was initiated by "Charlie" (the Viet Cong). The "hot landing zone" (enemy attacking choppers as they landed) accounted for 13% of the fights. American platoons on patrol were hit by ambush in 23% of the engagements, and their camps were hit by rocket or grenade attacks in 30%. In 27% of the battles the Americans took the initiative, including 9% ambushes, 5% planned attacks on known positions, and 13% attacks on unsuspected enemy positions. In 7% of the engagements both sides were surprised as they stumbled upon each other in the jungle.
By the end of the war, 30,600 soldiers and 12,900 Marines had been killed in combat, together with 1,400 sailors and Navy pilots, and 1,000 Air Force fliers. As is classic guerilla doctrine, when units with heavier power arrived, the weaker force dispersed. By American standards, they could not win, they could scarcely replace their losses, yet they kept trudging down the Ho Chi Minh Trail day after day. Given the current government of Vietnam, the American standards were incorrect.
Communist concept of attrition and American understanding of it
The enemy, however, was willing to accept those casualties. [43] McNamara was insistent that the enemy would comply with his concepts of cost-effectiveness, of which Ho and Giap were unaware. They were, however, quite familiar with attritional strategies.[44] While they were not politically Maoist, they were also well versed in Mao's concepts of protracted war (see insurgency).[45]
Ground war 1966-68
- See also: Vietnam War Ground Technology
With more aggressive pursuit, including airmobile operations, Westmoreland's tactics worked in terms of defeating the threat of larger enemy units (i.e., battalion or larger) to South Vietnam. With the US increasing the pace of search and destroy (and the ARVN avoiding combat), the NLF was systematically pushed back. "Search and Destroy" gave way after 1968 to "clear and hold", when Creighton Abrams replaced Westmoreland.
The Viet Cong was forced to disperse into smaller and smaller units, and so too did the US forces, until they were running platoon and even squad operations that blanketed far more of the countryside, chasing the fragmented enemy back into remote, uninhabited areas or out of the South altogether. Not only low-level NLF sympathizers but even Viet Cong officers and NLF political cadres started to surrender, accepting the resettlement terms offered by the GVN. At the end of 1964, the Pentagon estimated that only 42% of the South Vietnamese people lived in cities or villages that were securely under GVN control. (20% were in villages controlled by the NLF, and 37% were in contested zones.) At the end of 1967, 67% of the population was "secure," and only a few remote villages with less than 2% of the population were still ruled by the NLF.
Hanoi seemed to believe that the rugged Central Highlands region (South Vietnamese Military Region II, also known as RVN II Corps), which contained a third of the area but only 7% of SVN's people, would make a good base for guerrilla warfare. United States Army Special Forces ("Green Berets") armed and led the Montagnard tribesmen against the Communists.
In 1967, the Saigon political scene stabilized, as the Buddhist and student protesters ran out of steam and General Nguyen Van Thieu (1923-2001), a competent, fiercely anti-Communist Catholic, became president (in office 1967-75). The NLF failed to disrupt the national legislative election of 1966, or the presidential elections of 1967, which consolidated Thieu-ARVN control over GVN. Thieu failed to eliminate the systematic politicization, corruption, time-serving and favoritism in the ARVN.
Pacification/Revolutionary Development
Westmoreland was principally interested only in overt military operations, while Abrams looked at a broader picture. MACV advisors did work closely with 900,000 local GVN officials in a well-organized pacification program called CORDS (Civil Operations and Revolutionary Development.) It stressed technical aid, local self government, and land distribution to peasant farmers. A majority of tenant farmers received title to their own land in one of the most successful transfer projects in any nation. On the other hand, hundreds of thousands of peasants entered squalid refugee camps when CORDS moved them out of villages that could not be protected.[46] In the Phoenix Program (part of CORDS with a strong CIA component) GVN police identified and arrested (and sometimes killed) the NLF secret police agents engaged in assassination.
Psychological tension and breakdown of discipline
The more the American soldiers worked in the hamlets, the more they came to despise the corruption, inefficiency and even cowardice of GVN and ARVN. The basic problem was that despite the decline of the NLF, the GVN still failed to pick up popular support. Most peasants, refugees and city people remained alienated and skeptical. The superior motivation of the enemy troubled the Americans (especially in contrast with South Koreans, who fought fiercely for their independence.) "Why can't our Vietnamese do as well as Ho's?" Soldiers resented the peasants (ridiculing them as "gooks") who seemed sullen, unappreciative, unpatriotic and untrustworthy. The Viet Cong resorted more and more to booby-traps that (during the whole war) killed about 4,000 Americans and injured perhaps 30,000 (and killed or injured many thousands of peasants.)
It became more and more likely that after an ambush or boobytrap angry GIs would take out their frustrations against the nearest Vietnamese they perceived as potential enemies. MACV did not appreciate the danger that atrocities might be committed by Americans. In March 1968, just after the Tet offensive, one Army company massacred several hundred women and children at the hamlet of My Lai. High ranking American officers wre not charged, but the company captain was tried and acquitted. Platoon commander Lt. William Calley was sentenced to life imprisonment by a 1971 court martial. His sentence was reduced and he was released in 1975. The case became a focus of national guilt and self-doubt, with antiwar leaders alleging there were many atrocities that had been successfully covered up.[47]
Other factors contributed to reduced U.S. discipline and efficiency. Recreational drugs were readily available; this may not have been critical in rear areas, but a combat patrol cannot afford any reduction of its situational awareness. General social changes, including racial tension, also challenged authority. The practice of "fragging" involved U.S. soldiers killing their own leaders with a fragmentation grenade or other weapon. Fragging sometimes was a response to a crackdown on rebellion, but, in some cases, it was a way to remove a thoroughly incompetent leader that could get his men killed.
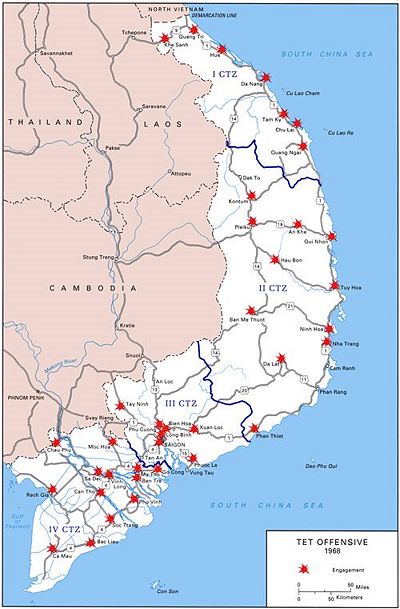
Tet Offensive, 1968
The climactic moment of the war came in February 1968 during the truce usually observed during the "Tet" holiday season. Hanoi used its NLF and Viet Cong forces to destroy the government of South Vietnam an incite a popular uprising. It was decisively defeated by U.S. standards, as it had been apparently defeated again and again.[43] However, the Tet Offensive had a devastating impact on Johnson's political position in the U.S., and in that sense was a strategic victory for the Communists.[48]
The "tail" of the PAVN had grown as its teeth receded, for the bombing had made resupply extraordinarily difficult. The solution was the "Tet offensive," an all-out effort, aimed especially at a new target, the GVN bureaus and ARVN complexes in the cities. The Politburo theorized that the GVN was a hollow shell held together only by American firepower. They truly believed the proletariat would, given the opportunity, fight Marxist class warfare and throw off their exploiters. Yhe very legitimacy of their enterprise hinged on the premise that the people of South Vietnam hated their government and really wanted Communist control.
As a diversion, PAVN sent a corps-strength unit to start the Battle of Khe Sanh, at what had been an isolated U.S. Marine location. Johnson personally took control of the defense. When the media back home warned darkly of another disaster like Dien Bien Phu, LBJ made his generals swear they would never surrender Khe Sanh. They committed 5% of their ground strength to the outpost (about 6,000 men) and held another 15-20% in reserve just in case. The enemy was blasted with 22,000 airstrikes and massive artillery bombardments. When the siege was lifted, the Marines had lost 205 killed, the PAVN probably 10,000.[49]
Hoping that Khe Sanh had tied down Westmoreland, the PAVN and Viet Cong struck on January 31, throwing 100,000 regular and militia troops against 36 of 44 provincial capitals and 5 of 6 major cities. They avoided American strongholds and targeted GVN government offices and ARVN installations, other than "media opportunities" such as attempting to a fight, by a small but determined squad, of the U.S. Embassy.
The harshest fighting came in the old imperial capital of Hue. The city fell to the PAVN, which immediately set out to identify and execute thousands of government supporters among the civilian population. The allies fought back with all the firepower at their command. House to house fighting recaptured Hue on February 24. In Hue, Five thousand enemy bodies were recovered, with 216 U.S. dead, and 384 ARVN fatalities. A number of civilians had been executed while the PAVN held the city.
Nationwide, the enemy lost tens of thousands killed, and many more who were wounded or totally demoralized. US lost 1,100 dead, ARVN 2,300. The people of South Vietnam did not rise up. However, the pacification program temporarily collapsed in half the country, and a half million more people became refugees. Despite the enormous damage done to the GVN at all levels, the NLF was in even worse shape, and it never recovered.
ABout 40,000 Communist soldiers in the South--probably about half--were killed in 1968; many others deserted to the GVN. By sending its main force into the cities during Tet, the NLF left a vacuum in the countryside that GVN and US pacification agents could fill.
By the end of 1968 the Saigon had pulled itself together and restored GVN authority in every province. By 1969 Saigon forces were able to sustain the pressure on the NLF and Viet Cong and dramatically expand their control over both population and territory.[50] Indeed, for the first time GVN found itself in control of more than 90% of the population. The Tet objectives were beyond our strength, concluded General Tran Van Tra, the commander of Vietcong forces in the South:
We suffered large sacrifices and losses with regard to manpower and materiel, especially cadres at the various echelons, which clearly weakened us. Afterwards, we were not only unable to retain the gains we had made but had to overcome a myriad of difficulties in 1969 and 1970.[51] [52]
Nixon and Vietnamization
The "falling domino" threat was greatest in Laos, where a low-intensity civil war gave the Communist Pathet Lao control of much of that remote land. Hanoi made systematic use of Laotian and Cambodian jungle trails as supply routes to the Viet Cong--the "Ho Chi Minh Trail." Cambodia's leader Prince Norodom Sihanouk repeatedly denied the existence of the Ho Chi Minh Trail, and denounced pursuit of Viet Cong across his border. In fact, the Viet Cong and the North Vietnamese created an elaborate infrastructure in his supposedly neutral country.
1968: Vietnamization
Worldwide opposition to the war built up inexorably after 1968. The media emphasized the lack of progress; hawks were frustrated by Nixon's abandonment of victory as a goal. Democrats who kept their peace while Johnson, a fellow Democrat, was in the White House now tried to weaken a Republican president. Nixon and his chief adviser Henry Kissinger were basically "realists" in world affairs, interested in the broader constellation of forces, and the biggest powers. H Melvin Laird, Nixon's Secretary of Defense, was a career politician keenly aware that Americans had soured on the war. His solution was to make troop withdrawal announcements a measure of the administration's progress. Laird worried that further involvement would postpone modernization of the military and hasten the deterioration of morale. Nixon's challenge was to maintain the national honor, keep SVN alive, and withdraw American troops. His plan to end the war was to make it irrelevant by moving the basic American strategy from containment to detente.
Instead of perpetual cold war, Nixon and Kissinger believed the time had come to narrow foreign policy to a realistic and limited view of the nation's own interests. It was necessary to maintain a strategic nuclear deterrent, and, since Western Europe was considered critical to U.S. interests, NATO would continue as a safeguard against Warsaw Pact attack. However, the US would seek detente, even friendship, with both the Soviet Union and China, would try to stop the arms race, and would tell countries threatened by subversion to defend themselves. Nixon rejected "a purely military victory on the battlefield," and also an immediate pullout that would cost the nation its honor. Like Johnson he rejected the "rollback" strategy favored by most hawks (and favored by his most important GOP rival, California governor Ronald Reagan).
1969-1971, Attacks on sanctuaries in Cambodia
In 1969, Nixon ordered B-52 strikes against PAVN supply routes in Cambodia. The orders for U.S. bombing of Cambodia were classified, and thus kept from the U.S. media and Congress. In a given strike, each B-52 normally dropped 42,000 pounds of bombs, and the strike consistedflying in groups of 3 or 6. Surviving personnel in the target area were apt to know they had been bombed, and, since the U.S. had the only aircraft capable of that volume, would know the U.S. had done it.
The "secrecy" may have been meant to be face-saving for Sihanouk, but there is substantial reason to believe that the secrecy, in U.S. military channels, was to keep knowledge of the bombing from the U.S. Congress and public. Actually, a reasonable case could be made that the bombing fell under the "hot pursuit" doctrine of international law, where if a neutral (Sihanouk) could not stop one country from attacking another from the neutral sanctuary, the attacked country(ies) had every right to counterattack.
When he ordered a joint US-Vietnamese ground invasion of Cambodia in 1970, many of these events first became known in the U.S., and there were intense protests, including deaths in a confrontation between rock-throwing protesters and poorly-trained National Guardsmen at Kent State University.
Nixon's larger strategy was to convince Moscow and Bejing they could curry American favor by reducing or ending their military support of Hanoi. He assumed that would drastically reduce Hanoi's threat. Second, "Vietnamization" would replace attrition. Let the Vietnamese fight and die for their own freedom. Vietnamization meant heavily arming the ARVN and turning all military operations over to it; all American troops would go home. By giving SVN with the capability of holding its own, Nixon believed, America could depart with honor. To the amazement of the world Nixon's plan seemed to work. The "era of confrontation" had passed, he announced, replaced by an "era of negotiation."
The Vietnamization policy achieved limited rollback of Communist gains inside South Vietnam only, and was primarily aimed at providing the arms, training and funding for the South to fight and win its own war, if it had the courage and commitment to do so. By 1971 the Communists lost control of most, but not all, of the areas they had controlled in the South in 1967. The Communists still controlled many remote jungle and mountain districts, especially areas that protected the Ho Chi Minh Trail. Saigon's effort to strike against one of these strongholds, Operation Lam Son 719, was a humiliating failure in 1971. The SVN forces, with some U.S. air support, were unable to defeat PAVN regulars.
The two dissenters to Nixon's plan were Saigon and Hanoi. President Thieu was, reasonably, concerned his fragile nation would not survive American withdrawal. Hanoi intended to conquer the South, with or without its Soviet and Chinese allies. It did start negotiations believing the sooner the Americans left the better.
With the Viet Cong forces depleted, Hanoi sent in its own PAVN troops, and had to supply them over the Ho Chi Minh Trail despite systematic bombing raids by the B-52s. American pressure forced Hanoi to reduce its level of activity in the South. In 1970 there were only 2 battles of any size. Nixon started withdrawing American troops in 1969, and by 1970 the remaining soldiers did very little fighting. In 1970 Cambodia erupted into a battle ground, with the Communists making a direct bid to seize that nation. Nixon in April 1970 authorized a large scale (but temporary) US-ARVN incursion into Cambodia to directly hit the PAVN headquarters and supply dumps. The forewarned PAVN had evacuated most of their soldiers, but they lost a third of its arms stockpile, as well as a critical supply line from the Cambodian port of Sihanoukville. The incursion prevented the takeover by Pol Pot and his "Khymer Rouge" (Cambodian Communists). Pot broke with his original North Vietnamese sponsors, and aligned with China.
The incursion into Cambodia in 1970 made the southern parts of SVN somewhat safer, but antiwar groups felt it proved Nixon's Vietnamization policy was all a deceit. At Kent State University a confrontation with the National Guard left seven protesters dead, and touched off a firestorm that shut down numerous academic institutions. Nixon ignored the protests and continued to Vietnamize the war. In 1971 all remaining American combat ground troops left, though air attacks continued.
1971-72, buildups and back-and-forth combat
During the quiet year 1971, Hanoi was building up forces for conventional invasion, while Nixon sent massive quantities of hardware to the ARVN, and gave Thieu a personal pledge to send air power if Hanoi invaded. The NLF and Viet Cong had largely disappeared. They controlled a few remote villages, and contested a few more, but the Pentagon estimated that 93% of the South's population now lived under secure GVN control. The year 1971 was quiet, with no large campaigns, apart for the ARVN defeat in Laos, Operation Lam Son 719.
In March, 1972 Hanoi invaded at three points from north and west with 120,000 PAVN regulars spearheaded by tanks. This was conventional warfare, reminiscent of North Korea's invasion in 1950. They expected the peasants to rise up and overthrow the government; they did not. They expected the South's army to collapse; instead the ARVN fought very well indeed. Saigon had started to exert itself; new draft laws produced over one million well-armed regular soldiers, and another four million in part-time, lightly armed self-defense militia.
Nixon ordered Operation LINEBACKER I, with 42,000 bombing sorties over North Vietnam. Hanoi was evacuated. Nixon also ordered the mining of North Vietnam's harbors, a stroke LBJ had always vetoed for fear of Soviet or Chinese involvement, But thanks to detente the Societs and Chinese held quiet. The ARVN, its morale stiffened by massive tactical air support from the US, held the line. As in Tet, the peasants refused to rise up against the GVN. "By God, the South Vietnamese can hack it!" exclaimed a pleasantly surprised General Abrams.
Since the PAVN's conventional forces required continuous resupply, the air campaign broke the momentum of the invasion and the PAVN forces retreated north. However they did did retain control of a slice of territory south of the DMZ. There the NLF, renamed the "Provisional Revolutionary Government of South Vietnam" (PRG) was established; it welcomed diplomats from the Communist world, including Fidel Castro, and served as one of the launch points of the 1975 invasion.[53][54] [55]
1972, South loses initiative
After the failed Easter Offensive the Thieu government made a fatal strategic mistake. Overconfident of its military prowess, it adopted a policy of static defense that made its units vulnerable; worse, it failed to use the breathing space to correct its faulty command structure. The departure of American forces and American money lowered morale in both military and civilian South Vietnam. Desertions rose as military performance indicators sank, and no longer was the US looking over the shoulder demanding improvement. Politics, not military need, still ruled the South Vietnamese Army.
On other side, the PAVN had been badly mauled--the difference was that it knew it and it was determined to rebuild. Discarding guerrilla tactics, Giap three years to rebuild his forces into a strong conventional army. Without constant American bombing it was possible to solve the logistics problem by modernizing the Ho Chi Minh trail with 12,000 more miles or raods. Brazenly, he even constructed a pipeline along the Trail to bring in gasoline for the next invasion.[56]
Major 1972 airstrikes to force negotiations
Late in 1972 election peace negotiations bogged down; Thieu demanded concrete evidence of Nixon's promises to Saignon. Nixon thereupon unleashed the full fury of air power to force Hanoi to come to terms. Operation Operation LINEBACKER II, in 12 days smashed many targets in North Vietnam cities that had always been sacrosanct. 59 key targets were attacked, often using new weapons. In particular, precision guided munitions destroyed bridges previously resistant to attack. US policy was to try to avoid residential areas; the Politburo had already evacuated civilians not engaged in essential war work.
The Soviets had sold Hanoi 1,200 S-75 Dvina/NATO: SA-2 GUIDELINE surface-to-air missiles (SAM) that proved effective against the B-52s for the first three days. In a remarkable display of flexibility, the Air Force changed its bomber tactics overnight--and Hanoi ran out of SAMs. An American negotiator in Paris observed that, "Prior to LINEBACKER II, the North Vietnamese were intransigent... After LINEBACKER II, they were shaken, demoralized, and anxious to talk about anything." Beijing and Moscow advised Hanoi to agree to the peace accords;they did so on January, 23, 1973.
The Air Force interpreted the quick settlement as proof that unrestricted bombing of the sort they had wanted to do for eight years had finally broken Hanoi's will to fight; other analysts said Hanoi had not changed at all.[57][58][59]
Peace accords and invasion, 1973-75
Peace accords were finally signed on 27 January 1973, in Paris. There would be an immediate in-place permanent cease-fire. The U.S. agreed to withdraw all its troops in 60 days (but could continue to send military supplies); North Vietnam was allowed to keep its 200,000 troops in the South but was not allowed to send new ones. Prisoners were exchanged. South Vietnam and the PRG was to start negotiations on free elections. Although a low-intensity war continued, the world rejoiced. In February 591 surviving POWs (mostly pilots) came home to a joyous welcome.
For many years there were dark rumors and suspicions that some American POWs were left behind. Nixon accepted Hanoi's assurances there were no more POWs; no missing POW has ever been located or identified by name.
All American military now departed Vietnam, including advisors to ARVN. The war seemed to be over--with vague guarantees by Hanoi not to attack the South, and Nixon's personal assurance that if peace held the US would eventually give Hanoi billions of dollars for rebuilding. Hanoi kept large forces in the unpopulated SVN's Central Highlands. The NLF and Viet Cong were ciphers by this time, and nearly all the population in the South was under GVN control. With Nixon wounded by Watergate, Congress forbad American military activity anywhere in Indochina.
After Nixon resigned in 1974, the US was legally unable and psychologically unwilling to fight in Indochina. The 1973 Peace Agreement, instead of ending a war made continuation inevitable, for it allowed North Vietnam to keep troops in the South. The North, badly damaged by the bombings of 1972, recovered quickly and remained committed to the destruction of its rival. The main reason for the fall of South Vietnam in 1973 was the continued failure of the Saigon government to run an effective administration. Its weaknesses were compounded by exaggerated confidence that the U.S. would return if and when needed.[60]Although it had plenty of weapons available--its 2100 modern aircraft comprised the fourth largest air force in the world--the ARVN had never mastered high tech and lost confidence in its capabilities when US advisers departed. Saigon felt betrayed.
Invasion and the fall of the south, 1975
After probing action showed surprising weakness in ARVN forces, Hanoi decided to make a major attack they expected would succeed in a year or so. It took four weeks. Starting in March, 1975, Hanoi sent 18 divisions, with 300,000 of its 700,000, soldiers to invade the South again, in conventional fashion with marching armies spearheaded by 600 Russian-built tanks and 400 pieces of artillery. Instead of crawling along jungle trails they used 12,000 miles of roads they had built (and even a pipeline) since the truce. The U.S had provided South Vietnam with $4.9 billion in military supplies since the truce, giving it a powerful army and the world's fourth strongest air force.
The air force, however, performed poorly, and often abandoned its bases. For the time, the PAVN had competent mobile anti-aircraft artillery. [61][62]
The ARVN, with 1.1 million soldiers, still had a 2-1 advantage in combat soldiers and 3-1 in artillery, but it misused its resources badly. The South's doctrine was called "light at the top, heavy at the bottom", meaning that it would resist lightly in the northern party of the country (I Corps), but stiffen resistance as the North extended. That was an attritional strategy, and the DRV had not broken under the much heavier attrition imposed by U.S. troops.
Some ARVN units fought well; most collapsed under the 16-division onslaught. The North Vietnamese regular army, the PAVN, began a full-scale offensive by seizing Phuoc Long Province in January, 1975. In March, 1975, they continued their offensive campaigns by conducting diversionary attacks in the north threatening Pleiku and then attacking the lightly defended South Vietnamese rear area.
The PAVN captured the Central Highlands and moved to the sea to divide the South Vietnamese Army (ARVN). The PAVN blocked the South Vietnamese attempt to retreat from the Central Highlands and destroyed the ARVN II corps. Of the 314 M-41 and M-48 ARVN tanks assigned to the Highlands, only three made it through to the coast.[63]
ARVN resistance was sometimes heroic, but it kept losing battles and territories. In three weeks lost half its main force units, and more than half its aircraft. Hundreds of thousands of refugees clogged the roads making retreat nearly impossible. Many ARVN units disintegrated as soldiers deserted to care for their families.
President Thieu released written assurances dated April 1973 from President Nixon that the U.S. would "react vigorously" if North Vietnam violated the truce agreement. But Nixon had resigned in August 1974 and his personal assurances were meaningless; After Nixon made the promises, Congress had prohibited the use of American forces in any combat role in Laos, Cambodia, and Vietnam without prior congressional approval. This was well known to the Saigon government. [64] President Gerald R. Ford tried to get new money for the South, but refused to consider any military action whatever.
About 140,000 refugees managed to flee the country, chiefly by boat. The PAVN then concentrated its combat power to attack the six ARVN divisions isolated in the north. After destroying these divisions, the PAVN launched its "Ho Chi Minh Campaign" that with little fighting seized Saigon on April 30, ending the war.[65]
No American military units had been involved until the final days, when Operation FREQUENT WIND was launched to evacuate Americans and 5600 senior Vietnamese government and military officials, and employees of the U.S. Vietnam was unified under Communist rule, as nearly a million refugees escaped by boat. Saigon was renamed Ho Chi Minh City. The new rulers sent thousands of political opponents to detention camps,.
Regional effects after 1975
After Congress cut off aid to Cambodia, the Khymer Rouge came to power in 1975. What followed was one of the most horrific massacres of the century, as Pol Pot systematically executed hundreds of thousands of Cambodians, including anyone with a trace of western contacts. The two Communist neighbors went to war in 1978-79, when Vietnam invaded and conquered Cambodia and forced the Khymer Rouge back into the jungles.
Aftermath and memory
Casualties
International effects
Cambodia and Laos
Vietnam and China
War in film and literature
References
- ↑ For example, the Encyclopedia Britannica puts the starting year at 1954 or 1955, while Encarta puts it at 1959. Many historians date it earlier, to include what some call the "First Indochina War," but this usage is not widely known or followed by the general public.
- ↑ William J. Duiker, Vietnam: Nation in Revolution, (1983) uses First and Second, pp. 43, 53; also William S. Turley, The Second Indochina War: A Short Political and Military History, 1954-1975 (1986).
- ↑ Pike, Douglas (1966), Viet Cong, MIT
- ↑ Spencer C. Tucker, "Casualties," in Tucker, ed. Encyclopedia of the Vietnam War (2001) p. 64 online
- ↑ "Ha Noi celebrates Trung sisters 1,968th anniversary", Viet Nam News, 14 March 2008
- ↑ By the 1960s, Ho was primarily a symbol rather than an active leader. William J. Duiker, Ho Chi Minh: A Life (2000)
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 Patti, Archimedes L. A (1980). Why Viet Nam?: Prelude to America's Albatross. University of California Press.
- ↑ Originally a Communist-led anti-Japanese insurgency, such as the Hukbalahap in the Phillipines. Unfortunately, Vietnam had no Ramon Magsaysay to form a unity government
- ↑ Cecil B. Currey, Victory at Any Cost: The Genius of Viet Nam's Gen. Vo Nguyen Giap (2005)
- ↑ Rusk/McNamara memorandum.Nov. 11, 1961, online at Pentagon Papers
- ↑ Robert K. Brigham, ARVN: Life And Death in the South Vietnamese Army (2006)
- ↑ Pike, PAVN (1986)
- ↑ Although still nominal president, Ho Chi Minh was a powerless figurehead. William J. Duiker, Ho Chi Minh: A Life (2001), pp 534-37 online; Ilya Gaiduk, Confronting Vietnam: Soviet Policy toward the Indochina Conflict, 1954-1963 (2003) online pp 203-4
- ↑ Iklé, Fred Charles (1991), Every War Must End, revised edition, Columbia University Press
- ↑ McNaughton, John T. (10 March 1965), Paper Prepared by the Assistant Secretary of Defense for International Security Affairs (McNaughton): Action for South Vietnam, vol. Foreign Relations of the United States, "McNaughton Paper 1965 - FRUS 193"
- ↑ Washington did not approve or order the coup, but it did not try to stop it.
- ↑ Quoted in Pentagon Papers v. 3 ch. 1
- ↑ Sherman Kent for the Board of National Estimates, Memo 6-9-64 (for the Director of Central Intelligence): Would the Loss of South Vietnam and Laos precipitate a "Domino Effect"
- ↑ Sheehan, Neil (1989), A Bright and Shining Lie, Vintage
- ↑ Gibbs, James William (1986), The Perfect War: Technolwar in Vietnam, Atlantic Monthly Presspp. 70-71
- ↑ Samson, Robert L. (1970), The Economics of Insurgency in the Mekong Delta of Vietnam, MIT Press p. 29
- ↑ Gibson, pp. 71-72
- ↑ 23.0 23.1 McMaster, H.R. (1997), Dereliction of Duty : Johnson, McNamara, the Joint Chiefs of Staff, and the Lies That Led to Vietnam, HarperCollins, ISBN 0060187956
- ↑ Carlson, Justin, "The Failure of Coercive Diplomacy: Strategy Assessment for the 21st Century", Hemispheres: Tufts Journal of International Affairs
- ↑ Charles F. Brower, "Strategic Reassessment in Vietnam: the Westmoreland "Alternate Strategy" of 1967-1968." Naval War College Review 1991 44(2): 20-51. Issn: 0028-1484
- ↑ National Security Agency (11/30/2005 and 05/30/2006). Gulf of Tonkin. declassified materials, 2005 and 2006. Retrieved on 2007-10-02.
- ↑ The document listing these targets, 7 Sep 1964 JCS Talking Paper for CJCS, "Next Courses of Action for RVN" [ indeed starts with 1 and ends with 94, but it only contains 93 distinct targets
- ↑ John M. Carland, "Winning the Vietnam War: Westmoreland's Approach in Two Documents." Journal of Military History" 2004 68(2): 553-574. Issn: 0899-3718 in Project Muse, with full text of "DIRECTIVE NUMBER 525-4 (MACJ3) 17 September 1965: TACTICS AND TECHNIQUES FOR EMPLOYMENT OF US FORCES IN THE REPUBLIC OF VIETNAM."
- ↑ Col. Dennis Drew, Rolling Thunder 1965: Anatomy of a Failure (1986); Merle L., Pribbenow, II, "Rolling Thunder and Linebacker Campaigns: the North Vietnamese View." Journal of American-East Asian Relations 2001 10(3-4): 197-210. Issn: 1058-3947
- ↑ The History Channel (September 22, 1964), Goldwater attacks Johnson's Vietnam policy
- ↑ Defence Canada, The Use of Herbicides at CFB Gagetown from 1952 to Present Day
- ↑ Quoted in Clodfelter, p. 134
- ↑ Gibson, p. 170
- ↑ United States Marine Corps, Small Wars Manual (Reprint of 1940 Edition)
- ↑ The normal Marine term is "Marine Expeditionary Force", but "Expeditionary" had unfortunate colonialist connotations in Vietnam. Current USMC terminology is MEF.
- ↑ David M. Berman, "Civic Action," in Spencer Tucker, ed. Encyclopedia of the Vietnam War p. 73-74
- ↑ Tucker, ed., Encyclopedia of the Vietnam War (2000) pp 74-75, 276-77
- ↑ Shulimson, Jack, The Marine War: III MAF in Vietnam, 1965-1971, U.S. Marine Corps Historical Center
- ↑ William C. Westmoreland, A Soldier Reports (1976), pp 164-66. Marine General Victor Krulak devotes ch 13 of his memoirs, First to Fight: An Inside View of the U.S. Marine Corps (1984) to the dispute. First to Fight pp 195-204 online; see also Douglas Kinnard, The War Managers American Generals Reflect on Vietnam (1991) discusses the tension on p 60-1, online
- ↑ Fall, Bernard (1961), Street Without Joy, Stackpole
- ↑ Moore, Harold & Joseph Galloway (1992), We were soldiers once, and young: Ia Drang--The Battle That Changed The War In Vietnam, Random House
- ↑ Philip Caputo 88
- ↑ 43.0 43.1 Adams, Sam (1994), War of Numbers: An Intelligence Memoir, Steerforth Press
- ↑ Vo Nguyen Giap (2001), People's War People's Army: The Viet Cong Insurrection Manual for Underdeveloped Countries, University Press of the Pacific
- ↑ Mao Tse-tung (1967), On Protracted War, Foreign Languages Press
- ↑ Thomas W. Scoville, Reorganizing for pacification support (1982) online edition
- ↑ Michal R. Belknap, The Vietnam War on Trial: The My Lai Massacre and the Court-Martial of Lieutenant Calley (2002). excerpt and text search; "Famous American Trials: The My Lai Courts-Martial 1970" online
- ↑ Don Oberdorfer, Tet!: The Turning Point in the Vietnam War (2001) excerpt and text search; James H. Willbanks, The Tet Offensive: A Concise History (2006) excerpt and text search
- ↑ John Prados and Ray W. Stubbe, Valley of Decision: The Siege of Khe Sanh (2004)
- ↑ Elliott, The Vietnamese War: (2002) p. 1128
- ↑ Quoted in Robert D. Schulzinger, Time for War: The United States and Vietnam, 1941-1975 (1997) p. 261 online
- ↑ Tran Van Tra, Vietnam: History of the Bulwark B2 Theatre, Vol. 5: Concluding the 30-Years War (1982), pp. 35-36.
- ↑ Lewis Sorley, "Courage and Blood: South Vietnam's Repulse of the 1972 Easter Invasion," Parameters, Summer 1999, pp. 38-56;
- ↑ Dale Andradé, Trial by Fire: The 1972 Easter Offensive, America's Last Vietnam Battle (1995) 600pp.
- ↑ For firsthand accounts by a ARVN general see Lam Quang Thi, The Twenty-Five Year Century: A South Vietnamese General Remembers the Indochina War to the Fall of Saigon (2002), online edition.
- ↑ Bruce Palmer, 25 Year War 122; Clodfelter 173; Davidson ch 24 and p. 738-59.
- ↑ Karl J. Eschmann, Linebacker: The Untold Story of the Air Raids over North Vietnam (1989)
- ↑ Henry Kissinger, White House Years 1:1454
- ↑ Clodfelter, Limits of Air Power" ch 6
- ↑ William P. Bundy, A Tangled Web: Making of Foreign Policy in the Nixon Presidency (1998) pp 497-500
- ↑ Ray L. Bowers, "Air Power in Southeast Asia" in Alfred F. Hurley and Ehrhart, eds. Air Power & Warfare: The Proceedings of the 8th Military History Symposium: United States Air Force Academy: 18-20 October 1978 (1978) pp 309-29 esp p. 323-4 full text online
- ↑ Momyer, William W. (1985), The Vietnamese Air Force, 1951 - 1975: An Analysis of Its Role in Combat
- ↑ William J. Duiker, The Communist Road to Power, (2nd ed. 1996) 335, 338-42
- ↑ "Seeking the Last Exit from Viet Nam", Time Magazine, April 21, 1975
- ↑ Duiker, The Communist Road to Power, 341-49; David Butler, Fall of Saigon, (1986); Military History Institute of Vietnam, Victory in Vietnam: The Official History of the People's Army of Vietnam, 1954-1975 (2002), Hanoi's official historyexcerpt and text search