Rhombus: Difference between revisions
imported>Peter Schmitt m (rhom) |
imported>Peter Schmitt m (→Properties: remove spurious </ref>) |
||
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
As with all quadrilaterals, the sum of the interior angles of a rhombus is 360 degrees; as with a parallelogram, it can be shown that the angles of opposite pairs of vertices are equal. | As with all quadrilaterals, the sum of the interior angles of a rhombus is 360 degrees; as with a parallelogram, it can be shown that the angles of opposite pairs of vertices are equal. | ||
The perimeter of a rhombus is equal to 4 times the length of one side. The area of a square is equal to the length of the side multiplied by itself, multiplied by the [[sine]] of the angle between the sides.<ref>Since the sum of the four angles is 360 degrees, and pairs of angles are equal, the sum of the angles of two adjacent vertices is 180 degrees. Since sin(180-x)=sin(x), the formula produces the same result no matter which vertex angle is chosen. | The perimeter of a rhombus is equal to 4 times the length of one side. The area of a square is equal to the length of the side multiplied by itself, multiplied by the [[sine]] of the angle between the sides.<ref>Since the sum of the four angles is 360 degrees, and pairs of angles are equal, the sum of the angles of two adjacent vertices is 180 degrees. Since sin(180-x)=sin(x), the formula produces the same result no matter which vertex angle is chosen. | ||
Any rhombus can [[tile (mathematics)|tile]] a plane with no voids. | Any rhombus can [[tile (mathematics)|tile]] a plane with no voids. | ||
Revision as of 15:25, 19 November 2009
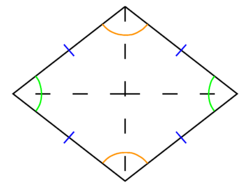
A rhombus or rhomb is a polygon of four sides of equal length. The angles of each pair of opposite vertices are equal. A rhombus is a special case of a parallelogram where all four sides are of equal length. A square is a special case of rhombus, where all four vertex angles are equal.
Properties
As with all quadrilaterals, the sum of the interior angles of a rhombus is 360 degrees; as with a parallelogram, it can be shown that the angles of opposite pairs of vertices are equal.
The perimeter of a rhombus is equal to 4 times the length of one side. The area of a square is equal to the length of the side multiplied by itself, multiplied by the sine of the angle between the sides.<ref>Since the sum of the four angles is 360 degrees, and pairs of angles are equal, the sum of the angles of two adjacent vertices is 180 degrees. Since sin(180-x)=sin(x), the formula produces the same result no matter which vertex angle is chosen.
Any rhombus can tile a plane with no voids.