Norway: Difference between revisions
imported>Kjetil Ree m (→History) |
John Leach (talk | contribs) m (Text replacement - "Ireland" to "Ireland") |
||
| (40 intermediate revisions by 7 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
'''Norway''' ( | {{subpages}} | ||
[[Image:Flag of Norway.svg|160px|right]] | |||
'''Norway''' ([[Nynorsk]] [[Norwegian]]: ''Noreg''; [[Bokmål]] [[Norwegian]]: ''Norge'') or officially the ''Kingdom of Norway'' (Nynorsk: ''Kongeriket Noreg''; Bokmål: ''Kongeriket Norge'') is a country in Northern Europe. Norway has a population of 4,681,100 (2007 estimate)<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.ssb.no/english/subjects/02/befolkning_en/ |title=Focus on Population |publisher= Statistics Norway|accessdate=2007-05-24 }}</ref> and an area of 385,155 km² (148,746 mi²). The capital is [[Oslo]]. | |||
==Geography== | ==Geography== | ||
[[Image:Geirangerfjord from Flydalsjuvet.jpg|thumb|240px|{{#ifexist:Template:Geirangerfjord from Flydalsjuvet.jpg/credit| | |||
Norway occupies the western | {{Geirangerfjord from Flydalsjuvet.jpg/credit}}<br/>|}}The Geirangerfjord in western Norway. Norway is famous for its [[fjord]]s.]] | ||
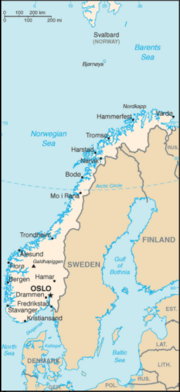
Norway occupies the western part of the [[Scandinavia]]n peninsula, bordering [[Sweden]] to the east, and [[Finland]] and [[Russia]] to the northeast. Norway has a land border of 2,542 km (1,580 miles). | |||
Norway has a continental coastline of 25,148 km (15,626 miles). It borders the [[North Sea]] and the [[Norwegian Sea]] in the west, the [[Skagerrak]] in the south and the [[Barents Sea]] in the north. Norway's long coastline is famous for its [[fjord]]s. | Norway has a continental coastline of 25,148 km (15,626 miles). It borders the [[North Sea]] and the [[Norwegian Sea]] in the west, the [[Skagerrak]] in the south and the [[Barents Sea]] in the north. Norway's long coastline is famous for its [[fjord]]s. | ||
| Line 10: | Line 13: | ||
==History== | ==History== | ||
[[Image:Norway map.png|180px|right]] | |||
Norway consisted of [[petty kingdom]]s until it was united in 872, when [[Harald Fairhair]] was victorious at the [[Battle of Hafrsfjord]] and became the first king of Norway. | Norway consisted of [[petty kingdom]]s until it was united in 872, when [[Harald Fairhair]] was victorious at the [[Battle of Hafrsfjord]] and became the first king of Norway. | ||
During the Norse era, | During the Norse era, Norwegian explorers discovered and colonized [[Iceland]] and [[Greenland]], and even reached [[Newfoundland]] in present-day [[Canada]]. Norse settlers established colonies in parts of Ireland and [[Britain]], and the infamous [[Viking]]s were a constant menace to [[Western Europe]]. The Norsemen were engaged in trade with distant places such as the [[Middle East]]. | ||
[[Christianity]] came to Norway in the late 900s. After [[Saint Olaf]]s victory in the [[Battle of Stiklestad]] in 1030 Norway was mostly Christianized, even though paganism still existed in remote areas for some time. | [[Christianity]] came to Norway in the late 900s. After [[Saint Olaf]]s victory in the [[Battle of Stiklestad]] in 1030 Norway was mostly Christianized, even though paganism still existed in remote areas for some time. | ||
The [[Black Plague]] came to Norway in 1349, and hit Norway hard. From [[Bergen]] it spread | The [[Black Plague]] came to Norway in 1349, and hit Norway hard. From [[Bergen]] it spread rapidly to other parts of Norway, and decimated the population. The mortality is estimated to be 40-50%.<ref>Oeding P. ''[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/query.fcgi?cmd=Retrieve&db=PubMed&list_uids=2197762&dopt=Abstract The black death in Norway]''. Tidsskrift for Den norske lægeforening. 1990</ref> The high death toll left Norway vulnerable to foreign influence, and Norway joined the [[Kalmar Union]] in 1523. Norway remained in a union with [[Denmark]] until 1814. | ||
Protestantism was introduced in Denmark-Norway in 1537, and the king took control over church property and affairs. King [[Christian III of Denmark and Norway]] declared [[Lutheranism]] as the official religion of the realm, and after [[Absolute monarchy|absolutism]] was introduced in the 17th century, all clerics were appointed by the King. Evangelical-Lutheran protestantism is still the official religion of Norway, with the King as the head of the official [[Church of Norway]].<ref name="embassy">The Norwegian Embassy in the UK. ''[http://www.norway.org.uk/facts/religion/general/gereral.htm Religion in Norway]''. Retrieved 2007-05-24</ref><ref name="church">The Church of Norway (2007-04-30). ''[http://www.kirken.no/english/news.cfm?artid=134384 The current state–church-process in Norway]''. Retrieved 2007-05-24</ref> | Protestantism was introduced in Denmark-Norway in 1537, and the king took control over church property and affairs. King [[Christian III of Denmark and Norway]] declared [[Lutheranism]] as the official religion of the realm, and after [[Absolute monarchy|absolutism]] was introduced in the 17th century, all clerics were appointed by the King. Evangelical-Lutheran protestantism is still the official religion of Norway, with the King as the head of the official [[Church of Norway]].<ref name="embassy">The Norwegian Embassy in the UK. ''[http://www.norway.org.uk/facts/religion/general/gereral.htm Religion in Norway]''. Retrieved 2007-05-24</ref><ref name="church">The Church of Norway (2007-04-30). ''[http://www.kirken.no/english/news.cfm?artid=134384 The current state–church-process in Norway]''. Retrieved 2007-05-24</ref> | ||
Denmark-Norway sided with [[Napoleon]] during the [[Napoleonic Wars]], and Norway was ceded to [[Sweden]]. Norway did not accept this, and declared independence and adopted a constitution in 1814. However, after a short war, Norway was forced into a [[personal union]] with Sweden. | Denmark-Norway sided with [[Napoleon]] during the [[Napoleonic Wars]], and Norway was ceded to the king of [[Sweden]]. Norway did not accept this, and declared independence and adopted a constitution in 1814. However, after a short war, Norway was forced into a [[personal union]] with Sweden. | ||
Norway became independent in 1905, when the union with Sweden was dissolved peacefully. A Danish prince was chosen as King of Norway, and became [[Haakon VII of Norway]]. | Norway became independent in 1905, when the union with Sweden was dissolved peacefully. A Danish prince was chosen as King of Norway, and became [[Haakon VII of Norway]]. | ||
During [[World War | During [[World War II]], Germany invaded Norway on April 9, 1940. The southern parts of Norway quickly fell to the invading forces, but the war saw some allied success in the northern theater. The Norwegian forces surrendered on June 10, after [[France|French]] and [[United Kingdom|British]] forces had to withdraw to fight in the campaign on continental Europe. The German occupation lasted until May 1945, with the support of a puppet government led by [[Vidkun Quisling]]. | ||
Norway joined [[NATO]] in 1949. Norway has had referendums for joining the [[European Union]] twice (1972 and 1994), both times with a narrow victory for the opposers. Norway is a member of the [[European Free Trade Association]], and is thus associated with the EU through the [[European Economic Area]] and other treaties. | Norway joined [[NATO]] in 1949. Norway has had referendums for joining the [[European Union]] twice (1972 and 1994), both times with a narrow victory for the opposers. Norway is a member of the [[European Free Trade Association]], and is thus associated with the EU through the [[European Economic Area]] and other treaties. | ||
| Line 31: | Line 34: | ||
==Politics== | ==Politics== | ||
Norway is a [[parliamentarism|parliamentary]] [[monarchy]]. | Norway is a [[parliamentarism|parliamentary]] [[monarchy]]. King Harald V, born 21 February 1937, succeeded his father as king of Norway on 17 January 1991. | ||
The legislative branch consists of the parliament, [[Stortinget]] (approximate translation: “The Great Assembly”). The parliament | The legislative branch consists of the parliament, [[Stortinget]] (approximate translation: “The Great Assembly”). The parliament cannot be dissolved, and the representatives are elected by popular vote for a four-year term. | ||
The executive is nominally | The executive is nominally led by the King, but his powers are mainly symbolic. The parliamentary system ensures that the government needs the confidence of the Storting, and the King will usually ask the leader of the largest party or block to form the government. | ||
The judicial branch is | The judicial branch is led by the Supreme Court (“Høyesterett”). The first level is the city court or county court (“Byretten” and “Herredsretten”), and the mid level (court of appeal) is called “Lagmansretten.” | ||
==Administrative divisions== | ==Administrative divisions== | ||
| Line 44: | Line 47: | ||
===Counties=== | ===Counties=== | ||
{| | |||
| | |||
*[[Akershus]] | *[[Akershus]] | ||
*[[Aust-Agder]] | *[[Aust-Agder]] | ||
| Line 49: | Line 55: | ||
*[[Finnmark]] | *[[Finnmark]] | ||
*[[Hedmark]] | *[[Hedmark]] | ||
| | |||
*[[Hordaland]] | *[[Hordaland]] | ||
*[[Møre og Romsdal]] | *[[Møre og Romsdal]] | ||
| Line 54: | Line 61: | ||
*[[Nord-Trøndelag]] | *[[Nord-Trøndelag]] | ||
*[[Oppland]] | *[[Oppland]] | ||
| | |||
*[[Oslo]] | *[[Oslo]] | ||
*[[Østfold]] | *[[Østfold]] | ||
| Line 59: | Line 67: | ||
*[[Sogn og Fjordane]] | *[[Sogn og Fjordane]] | ||
*[[Sør-Trøndelag]] | *[[Sør-Trøndelag]] | ||
| | |||
*[[Telemark]] | *[[Telemark]] | ||
*[[Troms]] | *[[Troms]] | ||
*[[Vest-Agder]] | *[[Vest-Agder]] | ||
*[[Vestfold]] | *[[Vestfold]] | ||
|} | |||
==Demographics== | ==Demographics== | ||
| Line 72: | Line 82: | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
Latest revision as of 08:53, 2 March 2024
Norway (Nynorsk Norwegian: Noreg; Bokmål Norwegian: Norge) or officially the Kingdom of Norway (Nynorsk: Kongeriket Noreg; Bokmål: Kongeriket Norge) is a country in Northern Europe. Norway has a population of 4,681,100 (2007 estimate)[1] and an area of 385,155 km² (148,746 mi²). The capital is Oslo.
Geography
Norway occupies the western part of the Scandinavian peninsula, bordering Sweden to the east, and Finland and Russia to the northeast. Norway has a land border of 2,542 km (1,580 miles).
Norway has a continental coastline of 25,148 km (15,626 miles). It borders the North Sea and the Norwegian Sea in the west, the Skagerrak in the south and the Barents Sea in the north. Norway's long coastline is famous for its fjords.
The landscape of Norway is dominated by mountains, and much of the country is barren (32% of continental Norway is above the tree line). However, Norway's valleys are relatively fertile.
History
Norway consisted of petty kingdoms until it was united in 872, when Harald Fairhair was victorious at the Battle of Hafrsfjord and became the first king of Norway.
During the Norse era, Norwegian explorers discovered and colonized Iceland and Greenland, and even reached Newfoundland in present-day Canada. Norse settlers established colonies in parts of Ireland and Britain, and the infamous Vikings were a constant menace to Western Europe. The Norsemen were engaged in trade with distant places such as the Middle East.
Christianity came to Norway in the late 900s. After Saint Olafs victory in the Battle of Stiklestad in 1030 Norway was mostly Christianized, even though paganism still existed in remote areas for some time.
The Black Plague came to Norway in 1349, and hit Norway hard. From Bergen it spread rapidly to other parts of Norway, and decimated the population. The mortality is estimated to be 40-50%.[2] The high death toll left Norway vulnerable to foreign influence, and Norway joined the Kalmar Union in 1523. Norway remained in a union with Denmark until 1814.
Protestantism was introduced in Denmark-Norway in 1537, and the king took control over church property and affairs. King Christian III of Denmark and Norway declared Lutheranism as the official religion of the realm, and after absolutism was introduced in the 17th century, all clerics were appointed by the King. Evangelical-Lutheran protestantism is still the official religion of Norway, with the King as the head of the official Church of Norway.[3][4]
Denmark-Norway sided with Napoleon during the Napoleonic Wars, and Norway was ceded to the king of Sweden. Norway did not accept this, and declared independence and adopted a constitution in 1814. However, after a short war, Norway was forced into a personal union with Sweden.
Norway became independent in 1905, when the union with Sweden was dissolved peacefully. A Danish prince was chosen as King of Norway, and became Haakon VII of Norway.
During World War II, Germany invaded Norway on April 9, 1940. The southern parts of Norway quickly fell to the invading forces, but the war saw some allied success in the northern theater. The Norwegian forces surrendered on June 10, after French and British forces had to withdraw to fight in the campaign on continental Europe. The German occupation lasted until May 1945, with the support of a puppet government led by Vidkun Quisling.
Norway joined NATO in 1949. Norway has had referendums for joining the European Union twice (1972 and 1994), both times with a narrow victory for the opposers. Norway is a member of the European Free Trade Association, and is thus associated with the EU through the European Economic Area and other treaties.
Politics
Norway is a parliamentary monarchy. King Harald V, born 21 February 1937, succeeded his father as king of Norway on 17 January 1991.
The legislative branch consists of the parliament, Stortinget (approximate translation: “The Great Assembly”). The parliament cannot be dissolved, and the representatives are elected by popular vote for a four-year term.
The executive is nominally led by the King, but his powers are mainly symbolic. The parliamentary system ensures that the government needs the confidence of the Storting, and the King will usually ask the leader of the largest party or block to form the government.
The judicial branch is led by the Supreme Court (“Høyesterett”). The first level is the city court or county court (“Byretten” and “Herredsretten”), and the mid level (court of appeal) is called “Lagmansretten.”
Administrative divisions
Norway is divided into 19 counties (“fylker”), and 431 municipalities (“kommuner”). The capital, Oslo, is both a county and a municipality (the same applied the second largest city, Bergen, until 1972).
Counties
Demographics
Languages
Religion
References
- ↑ Focus on Population. Statistics Norway. Retrieved on 2007-05-24.
- ↑ Oeding P. The black death in Norway. Tidsskrift for Den norske lægeforening. 1990
- ↑ The Norwegian Embassy in the UK. Religion in Norway. Retrieved 2007-05-24
- ↑ The Church of Norway (2007-04-30). The current state–church-process in Norway. Retrieved 2007-05-24