Missouri River: Difference between revisions
Pat Palmer (talk | contribs) mNo edit summary |
Pat Palmer (talk | contribs) m (Text replacement - "United States" to "United States") |
||
| (10 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{subpages}} | {{subpages}} | ||
{{Image|Missouri River basin map.png|right|350px|The Missouri River system lies inland in the middle of the United States of America and forms the northeast state line for the state of [[Missouri]].}} | {{dambigbox|Missouri River|Missouri}} | ||
The '''Missouri River''' | {{Image|Missouri River basin map.png|right|350px|The Missouri River system lies inland in the middle of the United States of America and forms the northeast state line for the state of [[Missouri (U.S. state)|Missouri]].}} | ||
The '''Missouri River''' and the [[Mississippi River]] are the two longest [[river]]s in the [[United States of America|United States]] and are of comparable length.<ref name="RiversWorld" /> The Missouri River runs 2300+ miles through the north central [[United States of America|U.S.]], beginning in [[Montana (U.S. state)|Montana]], draining through semi-arid parts of ten U.S. states and two Canadian provinces, until it joins the [[Mississippi River]] in its middle north of [[St. Louis, Missouri]]. Although considered a tributary of the Mississippi, the Missouri River carries a comparable volume of water. When combined with the lower Mississippi River, it forms the world's fourth longest river system.<ref name="RiversWorld" /> | |||
The river was one of the main routes for the westward expansion of the United States during the | == A path for westward expansion by European settlers == | ||
The combined Missouri-Mississippi river was one of the main routes for the westward expansion of the United States during the nineteenth century. The growth of the fur trade in the early nineteenth century laid much of the groundwork, as trappers explored the region and blazed trails. European pioneers headed west ''en masse'' beginning in the 1830s, many traveling by steamboats that entered service on the Missouri River. Conflict between settlers and Native Americans in the Missouri River watershed led to some of the most longstanding and violent wars between European settlers and Native American groups. | |||
During the | == Dams and their environmental impact == | ||
During the twentieth century, the river basin was developed extensively for irrigation, flood control, and to generate [[hydroelectric power]]. Fifteen dams now obstruct the river, with hundreds more on tributaries. Meanders were cut off and the river "channelized" (re-routed to make it straighter and deeper) to improve navigation, reducing its length by almost {{convert|200|mi|km}}.<ref name=Dams /> Although the lower Missouri River valley is now a populous and highly productive agricultural and industrial region, heavy development has taken its toll on wildlife and fish populations as well as water quality. | |||
== Provenance == | == Provenance == | ||
| Line 15: | Line 18: | ||
<ref name="RiversWorld"> | <ref name="RiversWorld"> | ||
{{cite web |author=Howard Perlman, USGS |url=https://water.usgs.gov/edu/riversofworld.html |title=Lengths of major rivers |series=USGS Water-Science School |website=Ga.water.usgs.gov |date=October 31, 2012 |access-date=November 21, 2012 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140309100631/http://water.usgs.gov/edu/riversofworld.html |archive-date=March 9, 2014 |url-status=dead }} | {{cite web |author=Howard Perlman, USGS |url=https://water.usgs.gov/edu/riversofworld.html |title=Lengths of major rivers |series=USGS Water-Science School |website=Ga.water.usgs.gov |date=October 31, 2012 |access-date=November 21, 2012 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140309100631/http://water.usgs.gov/edu/riversofworld.html |archive-date=March 9, 2014 |url-status=dead }} | ||
</ref> | |||
<ref name=Dams> | |||
See the [[Wikipedia:Missouri_River#Dam-building_era|Dam-building era]] section of Wikipedia's article on the Missouri River for details on its many dams and their history. | |||
</ref> | </ref> | ||
</references> | </references> | ||
Latest revision as of 08:44, 24 September 2023
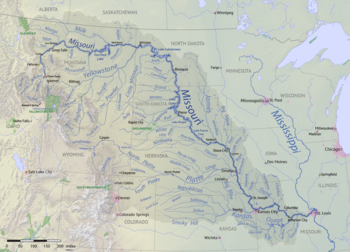
The Missouri River and the Mississippi River are the two longest rivers in the United States and are of comparable length.[1] The Missouri River runs 2300+ miles through the north central U.S., beginning in Montana, draining through semi-arid parts of ten U.S. states and two Canadian provinces, until it joins the Mississippi River in its middle north of St. Louis, Missouri. Although considered a tributary of the Mississippi, the Missouri River carries a comparable volume of water. When combined with the lower Mississippi River, it forms the world's fourth longest river system.[1]
A path for westward expansion by European settlers
The combined Missouri-Mississippi river was one of the main routes for the westward expansion of the United States during the nineteenth century. The growth of the fur trade in the early nineteenth century laid much of the groundwork, as trappers explored the region and blazed trails. European pioneers headed west en masse beginning in the 1830s, many traveling by steamboats that entered service on the Missouri River. Conflict between settlers and Native Americans in the Missouri River watershed led to some of the most longstanding and violent wars between European settlers and Native American groups.
Dams and their environmental impact
During the twentieth century, the river basin was developed extensively for irrigation, flood control, and to generate hydroelectric power. Fifteen dams now obstruct the river, with hundreds more on tributaries. Meanders were cut off and the river "channelized" (re-routed to make it straighter and deeper) to improve navigation, reducing its length by almost 200 mi (321.87 km).[2] Although the lower Missouri River valley is now a populous and highly productive agricultural and industrial region, heavy development has taken its toll on wildlife and fish populations as well as water quality.
Provenance
- Some content on this page may previously have appeared on Wikipedia.
Notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Howard Perlman, USGS (October 31, 2012). Lengths of major rivers.
- ↑ See the Dam-building era section of Wikipedia's article on the Missouri River for details on its many dams and their history.