Canine distemper virus: Difference between revisions
imported>Carolina Mendiguren No edit summary |
imported>Carolina Mendiguren |
||
| Line 30: | Line 30: | ||
<ref>[http://www.merckvetmanual.com/mvm/index.jsp?cfile=htm/bc/56700.htm&hide=1]</ref>. | <ref>[http://www.merckvetmanual.com/mvm/index.jsp?cfile=htm/bc/56700.htm&hide=1]</ref>. | ||
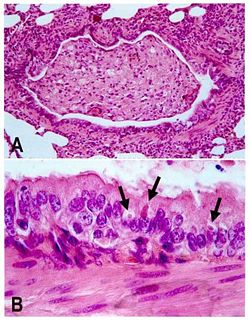
[[Image:466px-Canine_distemper_pathology. | [[Image:466px-Canine_distemper_pathology.jpg|right|250px|Lung lesions in an African wild dog with canine distemper. ]] | ||
==Genome== | ==Genome== | ||
Revision as of 22:37, 13 May 2009
For the course duration, the article is closed to outside editing. Of course you can always leave comments on the discussion page. The anticipated date of course completion is May 21, 2009. One month after that date at the latest, this notice shall be removed. Besides, many other Citizendium articles welcome your collaboration! |
| Canine distemper | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Scientific classification | ||||||||
| ||||||||
| Binomial name | ||||||||
| Canine distemper |
Description and significance
Canine distemper is a virus of the Paramyxoviridae family of the Mononegavirales order in the genus Morbillivirus; it is closely related to the measles virus. It is known to affect animals in the families Ailuridae, Canidae, Hyaenidae, Mephitidae, Mustelidae, Pinnipedia, Procyonidae. While there is a vaccination that can prevent distemper, the highly contagious viral disease is currently untreatable and often lethal in animals have been affected by it.
History
The first case of canine distemper was discovered in 1905 by Henri Carré, a French veterinarian. It was originally believed to be related to the plague and Typhus and was also believed to result from several species of bacteria. A vaccine was developed in 1950 that prevents the disease from affecting a treated animal, yet distemper is still prevalent since the vaccine is not accessible to all animals that are susceptible to the virus. The virus was once believed to be a cause of multiple sclerosis in humans; however, further research has invalidated this theory and Canine distemper virus has no known negative effects on humans. The domestic dog has primarily been responsible for the spread of canine distemper to wildlife, which poses a major ecological threat to several of the disposed species. The virus was a factor in the near-extinction of the black-footed ferret and may have caused the extinction of the Tasmanian tiger. The lion population in Serengeti, Tanzania experienced a 20% decline due to the disease in 1991. The virus has mutated to form “Phocine distemper virus”, which affects seals.
Cell Structure and Transmission
Canine distemper virus is a negative-sense, single-stranded RNA virus that is 150–250 nm in length and the shape ranges from spherical to pleomorphic. It is enveloped in a protein coat which is encased in a fatty envelope. This fatty envelope is easily disrupted, therefore making it difficult for the virus to survive at room temperature for more than a few hours. Cold and moist conditions increase survival, and it can last for several weeks at near freezing temperatures if kept away from light. The enveloping also causes the virus to be easily inactivated by most disinfectants. For infection to occur, an intact fatty envelope is required. Therefore the virus is relatively unstable outside of the host, and virus transmission entails direct contact between animals or contact with infected body secretions that have been exposed to the environment for a short period of time. [1].
Pathology
Transmission of is mainly achieved through direct contact with an infected animals' bodily fluids, making the virus highly communicable and extremely contagious. Canine distemper virus spreads primarily through aerosol droplet secretions from infected animals, which enters through the respiratory system. Viral shedding occurs approximately 7 days after infection. A viremia causes the spread of the virus in the animal and the infection of all lymphatic tissues, after which the virus spreads to the respiratory system, the GI, the urogenital epithelium the central nervous system and the optic nerves, which all become infected and where the virus begins to rapidly reproduce. The intensity of viremia and spread of the virus to other tissues is determined by the level of humoral immunity in the host animal during this period. Once infection occurs throughout the tissues of the body, disease follows. The symptoms of the secondary disease phase include pustular dermatitis and hyperkeratosis of the nose and foot pads and the most life-threatening stage of infection is coupled by neurological disorders, including encephalitis associated with myoclonus, seizures, tremors, imbalance, ataxia, and limb weakness. Encephalomyelitis may occur during this time, decreasing the host’s chances of survival. [2].
Genome
The genome of Morbilliviruses is composed of a single non-segmented strand of negative-sense RNA which is 15-19 kilobases long and contains 6-10 genes. The genes are separated by repeated sequences, a polyadenylation (termination) signal at the end of the gene, the intergenic sequence GAA, which is followed by a translation start signal at the beginning of the next gene. Extracistronic regions contain a 3’ leader sequence that is 50 nucleotides long, which functions as a transcriptional promoter and a 5’ trailer sequence that is 50-161 nucleotides long. The intergenomic areas between each gene are three nucleotides long. The 5' terminal of the negative-sense strand does not include a cap or a covalently attached terminal protein. Each gene includes transcription start and stop signals that are transcribed. Gene sequence within the genome is conserved due to transcriptional polarity, where greater amounts of genes towards the 3’ end of the genome are transcribed compared to those closer to the 5’ end, which helps regulate transcription. [3]
Replication
All replication takes place within the cytoplasm of the host. The virus attaches itself to specific receptors on the surface of the host’s cell membrane and it enters the host cells by fusing its viral envelope to the host’s plasma membrane. The environment must have a neutral pH in order for this to occur. The genome is then transcribed from the 3' end. The negative-sense RNA is transcribed into singular mRNAs and also a positive-sense RNA template, which is then used to create negative-sense RNAs. Short, conserved transcription initiation and termination signals neighboring each transcriptional element help to guide transcription. The 5' ends of mRNAs are capped while the 3' ends of mRNAs have a poly A tract, which is produced by the constant repetition of the termination site. Infected cells create a great excess of nucleocapsids and these in turn form cytoplasmic inclusion bodies and also often forms syncytia. During translation, the viral genome is replicated in the cytoplasm, and the parental genome is not used as a template. Replication is free of the host cell’s nuclear functions. Assembly then occurs independently and the virus capsid matures naturally by budding through the membrane of the host cell; the host’s membrane, in turn, forms the budding virus’ membranes. [4]
Current Research
References
McCarthy, A., Shaw, M., Goodman, S. “Pathogen evolution and disease emergence in carnivores”. Proceedings Biological Sciences December, 2007 Vol. 274, No. 1629 p 3165-74.
Gassen, U., Collins, F., Duprex, P., Rima, B.”Establishment of a Rescue System for Canine Distemper Virus”. Journal of Virology, November, 2000, p. 10737-10744, Vol. 74, No. 22
Bjørnstad, O., Pomeroy, L., Holme. E. “The Evolutionary and Epidemiological Dynamics of the Paramyxoviridae”. Journal of Molecular Evolution. February, 2008.. p.98-106 Vol. 66, No. 2
http://www.merckvetmanual.com/mvm/index.jsp?cfile=htm/bc/56700.htm&hide=1
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Canine_distemper#cite_ref-Jones1997_8-5
http://www.microbiologybytes.com/virology/Paramyxoviruses.html
http://www.caninedistemper.info/canine-distemper-cause.php