Battle of Leyte Gulf: Difference between revisions
imported>Howard C. Berkowitz |
imported>Howard C. Berkowitz (Continuing combat during land operations) |
||
| Line 221: | Line 221: | ||
Halsey, who believed the Japanese carriers were the principal Third Fleet objective, brought them under attack on October 25 and 26. | Halsey, who believed the Japanese carriers were the principal Third Fleet objective, brought them under attack on October 25 and 26. | ||
==Continuing naval combat== | |||
After the major naval battles discussed here, Japan still tried to get reinforcements to their troops, in what were called TA operations by escorted naval transports. Admiral Okochi commanded after Admiral Mizawa became too ill to do so.<ref>{{citation | |||
| title=The TA Operations to Leyte, Part I | |||
| url =http://www.combinedfleet.com/taops1.htm | |||
| author = Allyn D. Nevitt | |||
| publisher = CombinedFleet.com}}</ref> | |||
They also tried stop U.S. convoys supporting land warfare, principally using kamikazes. | |||
==Outcome== | ==Outcome== | ||
After the [[Battle of Pearl Harbor]] and certainly by 1944, it was obvious that aircraft and the [[aircraft carrier]] had replaced the [[battleship]] as the decisive factor in major naval combat. At the [[Battle of the Philippine Sea]], fought before Leyte Gulf, Japanese naval aviation was essentially destroyed—aircraft carriers without | After the [[Battle of Pearl Harbor]] and certainly by 1944, it was obvious that aircraft and the [[aircraft carrier]] had replaced the [[battleship]] as the decisive factor in major naval combat. At the [[Battle of the Philippine Sea]], fought before Leyte Gulf, Japanese naval aviation was essentially destroyed—aircraft carriers without pilots are useless. | ||
Leyte Gulf, however, effectively destroyed the Imperial Japanese Navy as a surface force. Of the 282 warships engaged (216 American, 2 Australian, and 64 Japanese), the Japanese lost 4 carriers, 3 battleships, 10 cruisers, and 11 destroyers. American losses totaled one light carrier, two escort carriers, and three destroyers. | Leyte Gulf, however, effectively destroyed the Imperial Japanese Navy as a surface force. Of the 282 warships engaged (216 American, 2 Australian, and 64 Japanese), the Japanese lost 4 carriers, 3 battleships, 10 cruisers, and 11 destroyers. American losses totaled one light carrier, two escort carriers, and three destroyers. | ||
Revision as of 17:02, 18 June 2010
The Battle of Leyte Gulf (October 23-26, 1944) was the largest naval battle in world history and the last major sea battle of World War Two. It was fought in the seas around and to the east of the Philippine Islands between the Japanese Imperial Navy and Allied naval forces. The battle occurred in reaction to and defense of the Allied invasion of Leyte.
American situation
U.S. Pacific strategy derived from Joint Chiefs of Staff decisions at the Cairo Conference (1943), to obtain "bases from which the unconditional surrender of Japan can be forced."[1] There was, however, little clarity and much argument among the JCS and the two theater commanders, Douglas MacArthur for the Southwest Pacific Area and Chester Nimitz for the [Central] Pacific and Pacific Ocean Areas. JCS guidance to Nimitz and MacArthur, dated 12 March 1944, reflected what was to become an obsolete concept: "The JCS has decided that the most feasible approach to Formosa, Luzon and China is by way of the Marianas, Luzon and China."
Events were to make Formosa, Luzon and China infeasible as the final bases for attacks on the Japanese home islands. In May 1944, the Japanese Army, moved into Eastern China. After this, the JCS suggested considering bypassing all the intermediate bases and directly attacking Kyushu, the target, much later, of Operation OLYMPIC.[2] This suggestion outraged MacArthur, but it reflected the desire of Army Chief of Staff George C. Marshall not to embark on unnecessary land campaigns; MacArthur was told that that personal and political considerations should not override the goal of defeating Japan.Marshall had also been an advocate of a very early cross-Channel invasion in the European theater.[3]
Since leaving the Phillipines in 1942, "The Philippine Islands constituted the main objective of General MacArthur's planning from the time of his departure from Corregidor in March 1942 until his dramatic return to Leyte two and one half years later". [4]MacArthur and his staff responded, on 15 June 1944, with the Reno V plan, which called for an October invasion of Mindanao to cover a November invasion of Leyte, and further movements on a line Luzon-Bicol Peninsula-Mindonoro-Lingayen Gulf-Manila. Admiral King, and even MacArthur's air commander, General Kinney, criticized it.
Eventually, President Franklin D. Roosevelt intervened to break the deadlock between King and Nimitz versus MacArthur. Roosevelt traveled to Honolulu, accompanied by his chief of staff, Admiral Leahy, and met with MaCarthur in July. [5]
Concept of operations
MacArthur had a deep emotional bond to the Phillipines, and both believed the honor of the United States required their liberation and that such an approach was strategically sound. He saw Leyte as the base from which the rest of the Phillipines could be taken. [6] Third and Fifth Fleet staff agreed on three naval objectives in support of land operations:[7]
- Air strikes on Okinawa, Formosa, and Northern Leyte on 10-13 October, by Third Fleet and long-range land-based aircraft
- Attacks on Bicol Peninsula, Leyte, Cebu and Negros, and direct supports of the actual landings, 16-20 October; this was the Seventh Fleet role
- "Strategic support" from 21 October onwards. This was the principal Third Fleet role, and an ambiguous one
Preparatory steps
MacArthur chose to occupy Morotai Island, off Halmahera, as an intermediate base, in September. This island, arguably either part of the Phillipines or New Guinea, is 350 miles from Mindoro.
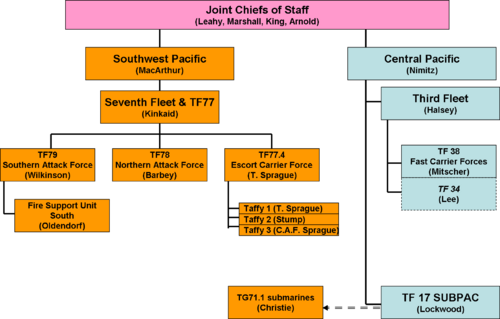
Command structure
United States Third Fleet under Admiral William Halsey reported to Admiral Chester Nimitz, and had the roles of defeating the major Japanese fleet and taking the islands of the Central Pacific. To increase the tempo of operations, the same ships were Third Fleet when under Halsey and his staff, and Fifth Fleet when under Admiral Raymond Spruance. Spruance and Halsey, without friction, alternated in planning and executing operations.
The Joint Chiefs in Washington had never been able to agree on a single commander for the Pacific. Nevertheless, the Third and Seventh Fleets were standing organizations that had reasonable internal communications.
Seventh Fleet mission
Under MacArthur, the Seventh Fleet, commanded by Vice Admiral Thomas Kinkaid (commander, Allied Naval Forces, Southwest Pacific Area) had the mission of landing and supporting the landing force. [8] Although code names were less frequently used to describe Pacific operations, the Seventh Fleet plan was designated Operation MUSKETEER/Operation KING V. Kinkaid's flagship was the amphibious command ship USS Wasatch (AGC-9), where he was accompanied by the Commander of the Sixth United States Army, Lieutenant General Walter Krueger. Kinkaid's deputy, VADM Thomas Wilkinson, was on the secondary flagship, command ship USS Olympus (AGC-8), which also commanded the Southern Attack Force. MacArthur's seagoing headquarters was on the cruiser USS Nashville.
Northern Attack Force, under RADM Daniel Barbey aboard USS Blue Ridge (AGC-2), was to land the X Army Corps under MG F.C. Sibert.
Southern Attack Force carried XXIV Army Corps under MG J.R. Hodge. Transport task groups carried divisions. Fire Support Unit South was made up of old battleships and other heavy gunships under RADM Jesse Oldendorf, and TG 77.4, the Escort Carrier Group, was under RADM Thomas Sprague.
Third Fleet mission
There was much more ambiguity in the mission of Vice Admiral William Halsey's Third Fleet. Nimitz directed him to "cover and support" SWPA forces "in order to assist in the seizure of all objectives in the Central Phillipines", and to "destroy enemy naval and air forces in or threatening the Phillippines area." This was consistent with orders given to Spruance's Fifth Fleet in the Marianas operation.
An additional paragraph"In case opportunity for destruction of major portion of the enemy fleet is offered or can be created, such destruction becomes the primary task". Friedman refers to Potter's biography of Nimitz, observing that the paragraph was not numbered as were the others, and not in the writing style of Nimitz or of Chief of Naval Operations Ernest King.[9] Nevertheless, in September, Halsey had written to Nimitz,
I intend, if possible, to deny the enemy a chance to outrange me in an air duel and also do deny him an opportunity to deploy an air shuttle[10] against me.
Inasmuch as the destruction of the enemy fleet is the principal task, every weapon must be brought into play and the general coordination of these weapons should be in the hands of the tactical commander responsible for the outcome of the battle [emphasis added]]...My goal is the same as yours — to completely annihilate the Jap fleet if the opportunity offers.[11]
Referring to the underlined section, it is unclear who Nimitz would consider the tactical commander, and whether there was an overall tactical commander for the entire Leyte campaign. Twelve days before the landings, Nimits wrote to Halsey,
You are always free to make local decisions in connection with the handling of forces under your command. Often it will be necessary for you to take action not previously contemplated which may develop quickly and may not yet be available to me. My only requirement in such cases is that I be informed as fully and as early as the situation permits.[12]
Halsey, more aggressive than his friend Spruance, interpreted that in his own operation order: "If opportunity exists or can be created to destroy major portion of the enemy fleet, this becomes primary task.[13] This is the classic Mahanian goal, shared by Halsey's opponents, especially VADM Takeo Kurita. Halsey's decisions remain active arguments among naval historians, although more tend to believe he lost sight of the most important mission.[14]
Confusion about Third Fleet organization, however, was not restricted to Halsey's command. VADM Willis Lee held the dual roles of Commander, Battleships, Pacific Fleet, and head of a Third Fleet organization called Task Force 34. During the Battle of Leyte Gulf, TF 34 was never organized as a single surface battle force, although Lee exerted coordination over the heavy gunfire ships distributed to the carrier task groups. Both Nimitz and Kinkaid, however, were uncertain if TF 34 was operating as a single unit, generally assuming that it was, and called for Lee's assistance during the Action off Samar.[15] Lee might have formed TF 34 as Battle Line had Halsey engaged Ozawa's force with a surface gunfire action, but, as a result of the problems in San Bernadino Strait, Halsey called off that action.
Confusion between Halsey and Kinkaid, including Halsey's priority of attacking the Japanese carrier force, led to San Bernadino Strait not being covered and the Action off Samar decided by the desperate fighting of light vessels of the Seventh Fleet. See the Action off Samar for details of communications and miscommunications.
Japanese situation
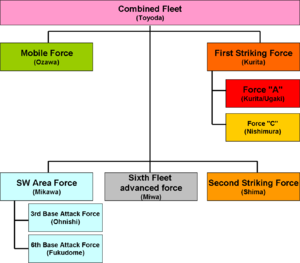
As with the U.S. forces, the only common command was at the national capital. Admiral Soemu Toyoda directed a number of units, which had extremely poor coordination — even rivalry — with one another.
The U.S., however, did not understand either the actual Japanese organization, or that the Mobile Force's role was that of a sacrificial decoy.
Concept of operations
At first, the Japanese concept of Operation SHO-GO sought the Mahanian "decisive battle" of major fleet units. A series of SHO-GO operational plans were developed by Imperial General Headquarters (IGHQ) and Combined Fleet, with contingencies for the invasion coming at Luzon, or the central or southern Phillipines. IGHQ developed policy and Combined Fleet issued the operational orders. [16]
Circumstances affected the specific operational intent. Rear Admiral Toshitane Takata, who had been a senior staff officer of a fleet, Combined Fleet, and the General Staff, felt that it was a reasonably good plan, but broke down especially after U.S. airstrikes on in the Phillipines in September, and later on Formosa, cost the Japanese too many land-based aircraft. He also said there was no intention to combine Kurita's and Ozawa's forces, based in the Inland Sea and Lingga. "There was such a desire but it was impossible to do that because of shortage of fuel and personnel...
Command structure
The U.S. had a poor understanding of the Japanese command structure, sometimes looking for complex strategic reasons when the positioning of a unit was simply due to fuel supply. MacArthur's Air Evaluation Board after the war, "Enemy intentions rather than capabilities were prominent [in U.S. planning]]." [17]
Mobile Fleet
The carrier-centric Mobile Fleet, under Vice Admiral Jizaburo Ozawa, had stayed in the Inland Sea of Japan, training new air groups. Due to its proximity to Combined Fleet, and the high regard in which Ozawa was held, even by his American interrogators after the war, he was an important adviser to Toyoda.
Still, Ozawa had limited authority and information. When asked if he knew who commanded the U.S. forces, he replied "I do not remember who I thought was your commander in chief at that time; there was at the time some estimate but I do not remember. " He said he did not know about kamikaze plans until "The first time I heard of Kamikaze attacks was when Kyrita's fleet went through San Bernadino Strait. I knew that Kamikaze attack was coming from Manila Area [i.e., land-based air under Mizawa, Ohnishi and Fukodome] to oppose the Leyte landing. "[18]
First Striking Force
Vice Admiral Takeo Kurita, was in overall command of the First Striking Force. It was based in Lingga Roads, near Singapore, to be near its fuel supply. Coincidentally, Lingga Roads was closer to India, and the British interpreted this as a threat to it, which led them to hold forces there. [19] Whether this really kept British contributions out of the U.S. Pacific Fleet is debatable, since Admiral Ernest King, U.S. Chief of Naval Operations, was anti-British and was reluctant to include their forces under any conditions.
Interrogated by the U.S. Strategic Bombing Survey in 1945, Kurita was described as "somewhat on the defensive, giving only the briefest of replies prior to the discussion of [the Leyte campaign actions]. In some instances his memory for details such as times, cruising dispositions, etc. appeared to be inaccurate." [20] In a 1977 interview, however, he said he chose not to pass through San Bernadino Strait and attack the transports.
What had we come this far for? Bringing so many ships, and also losing so many ships - wasn't it in order to win a victory at Leyte? I thought that, if the reported task force was 30 miles north east of us, we could definitely catch it. I thought it went without saying to steer towards the enemy force that was stronger.... After all, what lay to the south of us was just a collection of soldiers.... Naval war consists of warships sinking warships. Transport shipping is an opponent for land forces to deal with, isn't it? [21]
Vice Admiral Shigeo Nishimura, commanding Force C of the First Striking Force, was a respected "sea dog", unusual in never having served in a shore command and having passed the exams, but not taken the Staff College course. [22]
Second Striking Force mission
The Second Striking Force was made up of cruisers and destroyers, under VADM Kiyohido Shima. As opposed to Nishimura, Shima had spent much of his career in administrative posts. Thomas Cutler speculates that one reason not to merge the forces was that the less combat-experienced Shima was senior to Nishimura.[23] Shima and Mizawa fought over authority. [24]
Land-based aviation
Japanese aviation in the Phillippines had both Navy and Army components. Morison describes it as coordinated loosely by Vice Admiral Gunichi Mizawa,[25] who was relieved, for reasons of health, by Vice Admiral Denshichi Okochi in November 1942, after the Battle of Leyte proper.
Fifth Base Air Force, commanded by Vice Admiral Heigo Tominaga and then Vice Admiral Takijiro Ohnishi, was the Naval aviation organization specifically responsible for the Phillipines. Its Army counterpart was Fourth Air Army, led by Lieutenant General Kiyoji Tominaga. All were headquartered in Manila. Sixth Base Air Force, under Vice Admiral Fukudome, was responsibble for southern Kyushu, the Ryukyus, and Formosa. It had a primarily reinforcing role.
Fukudome was senior to Ohnishi so took control of their merged organization. [26]
As the battle developed, the role of the kamikaze, of which Vice Admiral Ohnishi was the chief advocate, was increasingly important.
Submarines
The battle
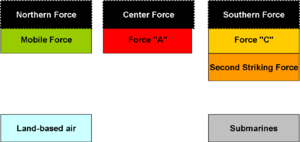
By the time landings had started, the most crucial Japanese objective was to attack the transports and other Seventh Fleet ships. They planned a two-pronged attack, through Surigao Strait and through San Bernadino Strait; the latter passes Samar. Their main body was Kurita's Force A within the First Striking Force. Two uncoordinated forces were to try to approach through Surigao Strait, Nishimura's Force C and Shima's Second Striking Force. Meanwhile, Ozawa was to continue acting as a decoy to divert Third Fleet away from the Japanese attack forces.
While the term operational art, or actions intended to specify where battle will take place, was not yet in wide use, it was at the operational level where some of the worst decisionmaking took place. [27] Examples include Halsey leaving San Bernadino Strait unguarded while Kinkaid assumed that he had it protected, Kurita choosing not to break through at Samar. Ozawa's decoying of Halsey was an example of successful operational art.
At the strategic level, the U.S. objective was the capture of Leyte. The Japanese objective was to repel it. Operationally, however, some of the strongest forces of each side had the enemy's carriers as a center of gravity. The Emperor said,
Contrary to the views of the Army and Navy General Staffs, I agreed to the showdown battle of Leyte thinking that if we attacked at Leyte and America flinched, then we would probably find room to negotiate. [28]
It is unclear what the Japanese would have done had the pincer against the invasion transports worked, when they still considered Third Fleet a primary objective. [29] Robinson mentions Morison's observation that it was unclear what they would have done had they successfully decoyed Halsey from the invasion beaches. They did not have the land-based air strength to attack Third Fleet. [30] Possibly, they saw kamikaze tactics as sufficient to defeat Third Fleet.
Japanese scouting
American forces shot down a Japanese scout plane on the 20th. Unknown to the U.S., it was looking for kamikaze targets, but probably due to poor communications, the Japanese did not start coordinated kamikaze operations. They managed a single attack on the 21st, damaging the cruiser HMAS Australia.[31]
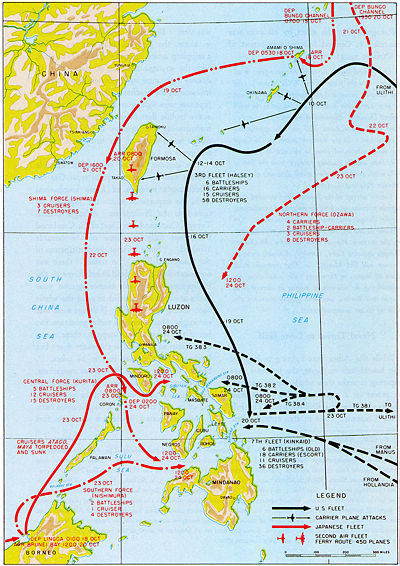
Palawan Passage
On 23 October, Japanese Center Force was sighted by U.S. patrol submarines, USS Darter and USS Dace, in Palawan Passage. After reporting it to higher headquarters, USS Darter and USS Dace torpedoed three heavy cruisers, sinking two and damaging a third such that it had no additional role in the war. The first, IJN Atago, was Admiral Kurita's flagship; Rear Admiral Ugaki took temporary command until Kurita was rescued by a destroyer, [32]
This was the first of several shocks to Kurita, which may have affected his later judgment. It was also a key intelligence datum to the U.S. command.
Battle of the Sibuyan Sea
Vice Admiral Willis Lee was Commander, Battleships, Pacific Fleet, and wore the "second hat" of commanding Task Force 34 (battleships) of Third Fleet. TF 34, however, never operated independently; Lee's reports collated information from battleships and other heavy surface combatants operating with the fast carrier groups. They reported finding a Japanese force on the morning of the 24th.[33]
In this action, Third Fleet indeed sank the superbattleship IJN Musashi.
Battle of Surigao Strait
Equipped with superb optics, the Japanese began the war ruling night action. The Allied development of radar, however, neutralized this advantage, but the Japanese often still preferred stealth by night. This battle actually consists of two separate engagements, in which a U.S. force built around the Seventh Fleet Gunfire Support Unit defeated, successively, Force C of the First Striking Force under Vice Admiral Nishimura and the the Second Striking Force under Vice Admiral Shima. It was the last engagement in which battleships fought directly, although much of the damage was done by torpedoes from destroyers.
The Japanese forces under Admirals Nishimura and Shima had no common command, minimal coordination, and were too far apart for mutual suport. Nishimura's stronger force came first, and all but one destroyer, IJN Shigure, sunk. Forces in Surigao Strait were an afterthought. "Admiral Shima's fleet happened to be there at the same time. In order to get to Leyte they decided to combine. It was not originally planned that Admiral Shima's force should take part in this southern action. It happened only by a series of coincidences that he was first ordered to Okinawa, then to Manila by Bako to attack your force but found it impossible; and so while en route to Manila he was given orders to follow Admiral Nishimura's force in an attempt on Leyte Gulf. This was truly an appendix to our plan."[16]
Action off Samar
Sometimes called the Battle of San Bernadino Strait, the Action off Samar describes the improvised and successful American defense against Kurita's Force A, which was attempting to break into Leyte Gulf. While his Force A had lost combat power in the preliminaries and the Battle of the Sibuyan Sea, it was still an immensely powerful gunfire force that could devastate the transports and support vessels in Leyte Gulf.
Until an antisubmarine patrol aircraft sighted the Japanese force, Admiral Kinkaid, commanding Seventh Fleet assumed/ that Third Fleet forces were guarding the San Bernardino Straits in position to intercept and destroy any enemy forces attempting to come through. "To confirm this assumption, Commander Seventh Fleet had sent a dispatch to the Commander Third Fleet asking if he was guarding the San Bernardino Straits. Reply was not received until after the enemy surface forces were attacking our Northern CVE Group. "[34]
Organized Kamikaze operations
Leyte Gulf was the first place at which the Japanese used large kamikaze forces, starting operations on the 25th. According to Fukudome's operations officer, Ohnishi, who committed seppuku at the end of the war, had planned these operations a month earlier. [35] These attacks continued well after the main Battle of Leyte, including operations against convoys supporting U.S. land forces.
VADM Fukudome said
After the two air fleets were combined to form the Combined Base Air Force, I, being the senior officer took command with Admiral Ohnishi as Chief of Staff. Throughout, the Kamikaze or Special Attack planes constituted the nucleus of my air force. The targets varied from time to time and were selected from a standpoint of obtaining greatest advantage to our forces. Principal targets were perhaps carriers, sometimes cruisers were selected, and again, especially when your destroyers came in large numbers against the forces that we had landed in Leyte, they were designated as principal targets. The Kamikaze confined its operations to naval vessels (sea units). In the operations against land targets, we used principally medium type, land attack planes and ordinary attack lanes and bombers, but used horizontal-bombing and not dive-bombing against land targets. In addition, we used seaplanes for attacking torpedo boats.[26]
When asked "What was the reason, throughout this period, that loaded transports were not a primary target of the Special Attack Force?" He said, "I wish to correct myself on an earlier statement. Loaded transports were looked upon as at least of equal importance with carriers, perhaps even a little higher than carriers, as targets." Rear Admiral Ralph Oftsie, his principal interrogator, said "In fact, however, no loaded transports were ever hit, and for that reason I assumed that such orders were never issued," to which Fukudome responded, " On one occasion loaded transports were made the principal targets, some 300 miles east-southeast of Leyte; and on another occasion, in an area very close to Leyte, our Kamikaze were sent out to attack what we supposed were loaded transports, but, by some error, the attack was made against small landing craft."
Battle of Cape Engano
On the 24th, Ozawa launched an air strike against Halsey, more to get his attention than expecting to do serious damage. After the survivors returned, he formed a surface Advanced Guard under RADM Masuda, to "divert the enemy" in support of Kurita's main effort. Initially delighted when he intercepted messages from U.S. search planes, he thought he finally had attracted Halsey.
On learning that Kurita had reversed course after the Action off Samar, Ozawa concluded that Operation SHO-GO had failed, and turned north to save what he could. An hour later, Combined Fleet ordered Ozawa to resume his attack. He recalled Masuda to join his main force.[36]
Halsey, who believed the Japanese carriers were the principal Third Fleet objective, brought them under attack on October 25 and 26.
After the major naval battles discussed here, Japan still tried to get reinforcements to their troops, in what were called TA operations by escorted naval transports. Admiral Okochi commanded after Admiral Mizawa became too ill to do so.[37]
They also tried stop U.S. convoys supporting land warfare, principally using kamikazes.
Outcome
After the Battle of Pearl Harbor and certainly by 1944, it was obvious that aircraft and the aircraft carrier had replaced the battleship as the decisive factor in major naval combat. At the Battle of the Philippine Sea, fought before Leyte Gulf, Japanese naval aviation was essentially destroyed—aircraft carriers without pilots are useless.
Leyte Gulf, however, effectively destroyed the Imperial Japanese Navy as a surface force. Of the 282 warships engaged (216 American, 2 Australian, and 64 Japanese), the Japanese lost 4 carriers, 3 battleships, 10 cruisers, and 11 destroyers. American losses totaled one light carrier, two escort carriers, and three destroyers.
Halsey always defended his decision to abandon the San Bernadino Strait and the beachhead, arguing that its defense was Kinkaid's job and his mission was strategic. Morison suggested it was not an "either-or" decision and that three of his carrier groups could have destroyed Ozawa's foce while one group, and possibly TF 34 formed into Battle Line, could have covered the Strait.[38]
Japan did not effectively defend the Phillipines. It has been reported that Emperor Hirohito refused the operational decision of the able field commander, General Tomiyuki Yamashita, who had wanted to make his stand on Luzon, not Leyte.
References
- ↑ Samuel Eliot Morison (1970), History of United States Naval Operations in World War II, vol. Volume XII: Leyte, June 1944-January 1945, Atlantic Monthly/Little, Brown, p. 4
- ↑ Morison, pp. 5-7
- ↑ Courtney Whitney, MacArthur, His Rendevous with History, 1966, quoted in Morison, p. 7
- ↑ , CHAPTER VII--THE PHILIPPINES: STRATEGIC OBJECTIVE, Reports of General MacArthur, Office of the Chief of Military History, U.S. Army, 1966
- ↑ Morison, pp. 8-11
- ↑ , Chapter VIII, The Leyte Operation, Reports of General MacArthur: The Campaigns of MacArthur in the Pacific, Office of the Chief of Military History, U.S. Army, 1966
- ↑ Morison, p. 57
- ↑ MUSKETEER/KING V CANF SWPA - OPERATION PLAN 13-44, U.S. Navy, 26 December 1944
- ↑ Kenneth I. Friedman (2001), Afternoon of the Rising Sun: the Battle of Leyte Gulf, Presidio Press, ISBN 08911417567, p. 22
- ↑ carrier-to-target-to-land
- ↑ Potter, Bull Halsey, p. 279, quoted by Friedman, p. 22
- ↑ The Battle of Leyte Gulf: 23-26 October 1944 (Bluejacket Books) by Thomas J. Cutler, p. 61. quoted by Friedman, p. 23
- ↑ Com Third Fleet Operation Order 21-44 of 3 Oct., quoted by Morison, p. 58
- ↑ Kent S. Coleman (2006), Thesis Title: Halsey at Leyte Gulf: Command Decision and Disunity of Effort, U.S. Army Command and General Staff College
- ↑ William F. Halsey with J. Bryan, Admiral Halsey's Story (1947) pp. 220-1
- ↑ 16.0 16.1 "Interrogation of: Rear Admiral TAKATA, Toshitane,IJN; attached successively to the Staff of the Third Fleet, the Combined Fleet, and the Naval General Staff.", U.S. Strategic Bombing Survey, 1 November 1945, INTERROGATION NAV NO. 64/USSBS NO. 258 (Japanese Naval Planning after Midway)
- ↑ Morison, p. 74
- ↑ "Interrogation of Admiral Ozawa, Jisaburo, task force commander in the Leyte operation", U.S. Strategic Bombing Survey, 30 October 1945, Interrogation No. 55
- ↑ Morison, p. 5
- ↑ "KURITA, Takeo, Vice Admiral, I.J.N.", U.S. Strategic Bombing Survey Interrogation of Japanese Officials, Interrogation No. 90
- ↑ C. Peter Chen, "Takeo Kurita", World War II database
- ↑ Anthony P. Tully (2009), Battle of Surigao Strait, Indiana University Press, pp. 30-34
- ↑ Thomas J. Cutler (2001), The Battle of Leyte Gulf: 23-26 October 1944, Naval Institute Press, pp. 95-96
- ↑ Tully, pp. 20-21
- ↑ Morison, pp. 68-69
- ↑ 26.0 26.1 Interrogation of: Vice Admiral FUKUDOME, Shigeru, IJN, U.S. Strategic Bombing Survey, 9-12 December 1945, INTERROGATION NAV NO. 115/USSBS NO. 503
- ↑ D. C. Robinson (10 March 1993), Operations Analysis: the Battle for Leyte Gulf, U.S. Naval War College, pp. 10-11
- ↑ Herbert Bix (2000), Hirohito and the Making of Modern Japan, HarperCollins, ISBN 006019314X, pp. 481-482
- ↑ Robinson, p. 19
- ↑ Morison, p. 167
- ↑ Edward P. Hoyt (1983), The Kamikazes, Burford Books, ISBN 1580800319, pp. 59-64
- ↑ Morison, pp. 169-174
- ↑ Willis Lee (14 December 1944), Report of Operations of Task Force THIRTY-FOUR During the Period 6 October 1944 to 3 December 1944., U.S. Navy
- ↑ Thomas Kinkaid, commanding Task Force 77 (18 November 1944), Preliminary Action Report of Engagements in Leyte Gulf and off Samar Island on 25 October, 1944, Hyperwar Foundation
- ↑ "Interrogation of: Commander YAMAGUCHI, Moriyoshi; from August 1944 to January 1945 Operations Officer on the Staff of Vice Admiral FUKUDOME, CinC Second Air Fleet (FORMOSA), and after 23 October CinC First Combined Base Air Force (LUZON).", U.S. Strategic Bombing Survey, 26 October 1945, INTERROGATION NAV NO. 44/USSBS NO. 193
- ↑ Morison, pp. 317-321
- ↑ Allyn D. Nevitt, The TA Operations to Leyte, Part I, CombinedFleet.com
- ↑ Morison, 193-196.
- Pages using ISBN magic links
- CZ Live
- History Workgroup
- Military Workgroup
- World War II Subgroup
- Pacific War Subgroup
- United States Navy Subgroup
- Articles written in American English
- Advanced Articles written in American English
- All Content
- History Content
- Military Content
- History tag
- Military tag
- World War II tag
- Pacific War tag
- United States Navy tag