Battle of Leyte Gulf: Difference between revisions
imported>Howard C. Berkowitz No edit summary |
imported>Howard C. Berkowitz |
||
| Line 76: | Line 76: | ||
===Action off Samar=== | ===Action off Samar=== | ||
{{main|Action off Samar}} | {{main|Action off Samar}} | ||
===Organized Kamikaze operations=== | ===Organized Kamikaze operations=== | ||
Revision as of 00:40, 16 June 2010
The Battle of Leyte Gulf in October 23-26, 1944, was the largest naval battle in world history, in terms of total combatant personnel and firepower. It was fought in the seas around and to the east of the Philippine Islands between the Japanese Imperial Navy and Allied naval forces. The bulk of naval combat took place after the initial troop landings on the island of Leyte.
Both sides suffered from divided command. The only joint commanders were in Washington and Tokyo.
American situation
U.S. Pacific strategy derived from Joint Chiefs of Staff decisions at the Cairo Conference (1943), to obtain "bases from which the unconditional surrender of Japan can be forced."[1] There was, however, little clarity and much argument among the JCS and the two theater commanders, Douglas MacArthur for the Southwest Pacific Area and Chester Nimitz for the [Central] Pacific and Pacific Ocean Areas. JCS guidance to Nimitz and MacArthur, dated 12 March 1944, reflected what was to become an obsolete concept: "The JCS has decided that the most feasible approach to Formosa, Luzon and China is by way of the Marianas, Luzon and China."
Events were to make Formosa, Luzon and China infeasible as the final bases for attacks on the Japanese home islands.
Concept of operations
MacArthur had a deep emotional bond to the Phillipines, and both believed the honor of the United States required their liberation and that such an approach was strategically sound.
Command structure
United States Third Fleet under Admiral William Halsey reported to Admiral Chester Nimitz, and had the roles of defeating the major Japanese fleet and taking the islands of the Central Pacific. To increase the tempo of operations, the same ships were Third Fleet when under Halsey and his staff, and Fifth Fleet when under Admiral Raymond Spruance. Spruance and Halsey, without friction, alternated in planning and executing operations.
The Joint Chiefs in Washington had never been able to agree on a single commander for the Pacific. Nevertheless, the Third and Seventh Fleets were standing organizations that had reasonable internal communications.
Seventh Fleet mission
Under MacArthur, the Seventh Fleet, commanded by Vice Admiral Thomas Kinkaid (commander, Allied Naval Forces, Southwest Pacific Area) had the mission of landing and supporting the landing force. [2]
Third Fleet mission
There was much more ambiguity in the mission of Vice Admiral William Halsey's Third Fleet.
Japanese situation
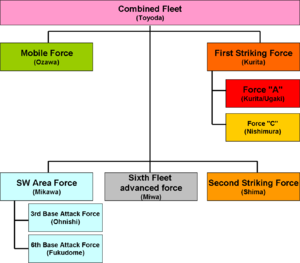
As with the U.S. forces, the only common command was at the national capital. Admiral Toyoda directed a number of units, which had extremely poor coordination — even rivalry — with one another.
Concept of operations
Command structure
Mobile Fleet
First Striking Force
Second Striking Force mission
Land-based aviation
Submarines
The battle
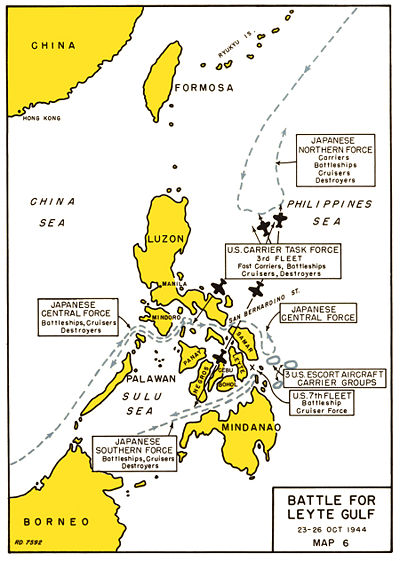
To reach the Leyte beaches, Japanese forces would have to come through either San Bernardino Strait to the north, covered by Halsey, or Surigao Strait to the south, covered by Oldendorf.
Japanese scouting
American forces shot down a Japanese scout plane on the 20th. Unknown to the U.S., it was looking for kamikaze targets, but probably due to poor communications, the Japanese did not start coordinated kamikaze operations. They managed a single attack on the 21st, damaging the cruiser HMAS Australia.[3]
The Fight in Palawan Passage
On 23 October, Japanese Center Force was sighted by U.S. patrol submarines, USS Darter and USS Dace, in Palawan Passage. After reporting it to higher headquarters, USS Darter and USS Dace torpedoed three heavy cruisers, sinking two and damaging a third such that it had no additional role in the war. The first, IJN Atago, was Admiral Kurita's flagship; Rear Admiral Ugaki took temporary command until Kurita was rescued by a destroyer, [4]
This was the first of several shocks to Kurita, which may have affected his later judgment. It was also a key intelligence datum to the U.S. command.
Battle of the Sibuyan Sea
Vice Admiral Willis Lee, commanding Task Force 34 (battleships) of Third Fleet, reported finding a Japanese force on the morning of the 24th.[5]
Halsey's planes blasted away at Kurita's Center Force, who finally turned tail and retreated. So overconfident were the Yanks that they reported far more damage than they actually inflicted. Halsey was an aviator who thought battleships were obsolete dinosaurs, so he wrote Kurita's force off--and refused to listen to aides who had doubts.
In this action, Third Fleet indeed sank the superbattleship IJN Musashi.
Battle of Surigao Strait
Equipped with superb optics, the Japanese began the war ruling night action. The Allied development of radar, however, neutralized this advantage, but the Japanese often still preferred stealth by night.
October 24 Admiral Kurita headed toward San Bernardino, and Admiral Nishimura headed for Surigao. Oldendorf demonstrated a textbook exercise in how to sink an enemy fleet. His ships steamed back and forth across the top of a "T" while Nishimura's ships came up the stem of the "T" one by one and were sunk. Only one escaped.
Late on the night of the 24th Halsey was puzzled about the Japanese carriers--they must be somewhere, but he could not find them. They were his main objective, according to Mahanian doctrine of great fleet battles. In fact Ozawa with his nearly empty carriers was making smoke, breaking radio silence on various frequencies, and sending escorts out ahead--his fleet was the decoy and its mission was to be spotted.
Action off Samar
Organized Kamikaze operations
Battle of Cape Engano
Outcome
In the greatest and most complex naval battle ever fought, half the Japanese Navy went to the bottom; US losses were light, and the troops on the beaches were untouched. Of the 282 warships engaged (216 American, 2 Australian, and 64 Japanese), the Japanese lost 4 carriers, 3 battleships, 10 cruisers, and 11 destroyers. American losses totaled one light carrier, two escort carriers, and three destroyers.
Halsey always defended his decision to abandon Leyte; its defense was Kinkaid's job and his mission was strategic. The overwhelming weight of opinion has been that Ozawa outfoxed Halsey, who clung too tenaciously to his carrier doctrine, and who failed to gather and act on the information that was available to him. Halsey's blunder might have cost tens of thousands of lives, or at least delayed the invasion of the Philippines for months, but his luck made him the victor in the biggest naval battle of all time.
Although the Japanese came surprising close to inflicting a major defeat on the Americans, at the last minute the tide turned and the U.S. Navy sank virtually all of Japan's naval power. Part of World War II in the Pacific it involved a complex overlapping series of engagements fought off the Philippine island of Leyte, which the U.S. Army had just invaded. The army forces were highly vulnerable to naval attack, and the Japanese goal was to inflict massive destruction on them. Two American fleets were involved, the Seventh and Third, but they were independent and did not communicate well. The Japanese communication system was even worse, and the Japanese army and navy did not cooperate.
References
- ↑ Samuel Eliot Morison (1970), History of United States Naval Operations in World War II, vol. Volume XII: Leyte, June 1944-January 1945, Atlantic Monthly/Little, Brown, p. 4
- ↑ MUSKETEER/KING V CANF SWPA - OPERATION PLAN 13-44, U.S. Navy, 26 December 1944
- ↑ Edward P. Hoyt (1983), The Kamikazes, Burford Books, ISBN 1580800319, pp. 59-64
- ↑ Morison, pp. 169-174
- ↑ Willis Lee (14 December 1944), Report of Operations of Task Force THIRTY-FOUR During the Period 6 October 1944 to 3 December 1944., U.S. Navy
- Pages using ISBN magic links
- CZ Live
- History Workgroup
- Military Workgroup
- World War II Subgroup
- Pacific War Subgroup
- United States Navy Subgroup
- Articles written in American English
- Advanced Articles written in American English
- All Content
- History Content
- Military Content
- History tag
- Military tag
- World War II tag
- Pacific War tag
- United States Navy tag