Exponential function: Difference between revisions
imported>Dmitrii Kouznetsov m (→References: formating) |
imported>Dmitrii Kouznetsov m (→Generalization of exponential: misprint) |
||
| Line 73: | Line 73: | ||
At non-integer values of <math>c</math>, the [[fixed point]]s of logarithm | At non-integer values of <math>c</math>, the [[fixed point]]s of logarithm | ||
<math>L\approx 0.31813150520476413 \pm 1.3372357014306895~ \mathrm{i}</math> are [[branch point]]s of function < | <math>L\approx 0.31813150520476413 \pm 1.3372357014306895~ \mathrm{i}</math> are [[branch point]]s of function <math>\exp^c</math>; in figure, the cut is placed parallel to the real axis. | ||
At <math>c<0</math> there is an additional cut which goes along the negative part of the real axis. In the figure, these cuts are marked with pink. | At <math>c<0</math> there is an additional cut which goes along the negative part of the real axis. In the figure, these cuts are marked with pink. | ||
Revision as of 02:27, 29 October 2008
Exponential function or exp, can be defined as solution of differential equation
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \exp^{\prime}(z)=\exp(z)}
with the additional condition
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \exp(0)=1 }
The study of the exponential function began with Leonhard Euler around 1730[1] Since that time, it has had widely applications in technology and science; in particular, exponential growth is described with such functions.
Properties
The exponential is an entire function.
For any complex Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle p} and Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle q} , the basic property holds:
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \exp(a)~\exp(b)=\exp(a+b) }
The definition allows to calculate all the derivatives at zero; so, the Taylor expansion has the form
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \exp(z)=\sum_{n=0}^\infty \frac{z^n}{n!} ~ ~ \forall z\in \mathbb{C} }
where Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mathbb{C}} means the set of complex numbers. The series converges for any complex Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle z} . In particular, the series converges for any real value of the argument.
Inverse function
The inverse function of the exponential is the logarithm; for any complex Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle z\ne 0} , the relation holds:
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \exp(\log(z))=z ~ \forall z\in \mathbb{C} }
Exponential also can be considered as inverse of logarithm, while the imaginary part of the argument is smaller than Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \pi} :
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \log(\exp(z))=z ~ \forall z\in \mathbb{C} ~ \mathrm{~ such ~ that ~ } |\Im(z)|<\pi }
When the logarithm has a cut along the negative part of the real axis, exp can be considered.
Number e
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mathrm {e} = \exp(1)} is widely used in applications; this notation is commonly accepted. Its approximate value is
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle {\rm e}=\exp(1) \approx 2.71828 18284 59045 23536}
Relation with sin and cos functions
The exponential is related to the trigonometric functions sine and cosine by de Moivre's formula:
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \exp(\mathrm{i} z) = \cos(z)+\mathrm{i} \sin(z) ~ \forall z\in \mathbb{C} }
Generalization of exponential
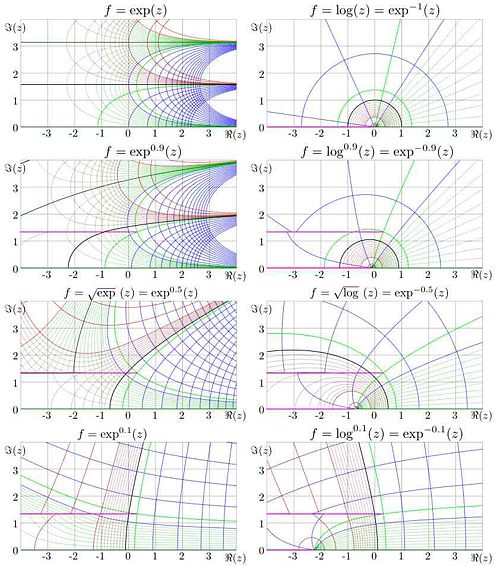
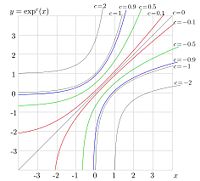
The notation Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \exp_b} is used for the exponential with scaled argument;
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \exp_b(z)=b^z=\exp(\log(b) z)}
Notation Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \exp_b^c} is used for the iterated exponential:
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \exp_b^0(z) =z }
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \exp_b^1(z) =\exp_b(z) }
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \exp_b^2(z) =\exp_b(\exp_b(z) }
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \exp_b^{c+1}(z) =\exp_b(\exp_b^c(z) }
For non-integer values of Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle c} , the iterated exponential can be defined as
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \exp_b^c(z) = \mathrm{sexp}_b\Big(c+ {\mathrm{sexp}_b}^{-1}(z)\Big) }
where Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mathrm{sexp}_b(z) } is function Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle F} satisfying conditions
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle F(z+1)=\exp_b(F(z))}
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle F(0)=1}
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle F(z)~ \mathrm{ ~is~ holomorphic~ and~ bounded~ at}~ |\Re(z)|<1}
The inverse function is defined with condition
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle F\Big(F^{-1}(z)\Big)=z}
and, within some range of values of Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle z}
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle F^{-1}\Big (F(z)\Big)=z}
If in the notation Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \exp_b^c} the superscript is omitted, it is assumed to be unity; for example Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \exp_b^1=\exp_b} . If the suberscript is omitted, it is assumed to be Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mathrm{e}} , id est, Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \exp^c=\exp_\mathrm{e}^c}
At non-integer values of Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle c} , the fixed points of logarithm Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle L\approx 0.31813150520476413 \pm 1.3372357014306895~ \mathrm{i}} are branch points of function Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \exp^c} ; in figure, the cut is placed parallel to the real axis. At Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle c<0} there is an additional cut which goes along the negative part of the real axis. In the figure, these cuts are marked with pink.
References
- ↑ William Dunham, Euler, the Master of us all, MAA (1999) ISBN 0-8835-328-0. Pp.17-37.
- Ahlfors, Lars V. (1953). Complex analysis. McGraw-Hill Book Company, Inc..
- H.Kneser. ``Reelle analytische Losungen der Gleichung Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \varphi(\varphi(x))=\mathrm{e}^{x}} und verwandter Funktionalgleichungen. Journal fur die reine und angewandte Mathematik, 187 (1950), 56-67.