Battle of Leyte Gulf: Difference between revisions
imported>Howard C. Berkowitz |
imported>Howard C. Berkowitz |
||
| Line 44: | Line 44: | ||
In this action, Third Fleet indeed sank the superbattleship ''IJN Musashi''. | In this action, Third Fleet indeed sank the superbattleship ''IJN Musashi''. | ||
===Battle of Surigao Strait=== | ===Battle of Surigao Strait=== | ||
{{main|Battle of Surigao Strait}} | |||
Equipped with superb optics, the Japanese began the war ruling night action. The Allied development of [[radar]], however, neutralized this advantage, but the Japanese often still preferred stealth by night. | Equipped with superb optics, the Japanese began the war ruling night action. The Allied development of [[radar]], however, neutralized this advantage, but the Japanese often still preferred stealth by night. | ||
October 24 Admiral Kurita headed toward San Bernardino, and Admiral Nishimura headed for Surigao. Oldendorf demonstrated a textbook exercise in how to sink an enemy fleet. His ships steamed back and forth across the top of a "T" while Nishimura's ships came up the stem of the "T" one by one and were sunk. Only one escaped. | October 24 Admiral Kurita headed toward San Bernardino, and Admiral Nishimura headed for Surigao. Oldendorf demonstrated a textbook exercise in how to sink an enemy fleet. His ships steamed back and forth across the top of a "T" while Nishimura's ships came up the stem of the "T" one by one and were sunk. Only one escaped. | ||
Late on the night of the 24th Halsey was puzzled about the Japanese carriers--they must be somewhere, but he could not find them. They were his main objective, according to Mahanian doctrine of great fleet battles. In fact Ozawa with his nearly empty carriers was making smoke, breaking radio silence on various frequencies, and sending escorts out ahead--his fleet was the decoy and its mission was to be spotted. | Late on the night of the 24th Halsey was puzzled about the Japanese carriers--they must be somewhere, but he could not find them. They were his main objective, according to Mahanian doctrine of great fleet battles. In fact Ozawa with his nearly empty carriers was making smoke, breaking radio silence on various frequencies, and sending escorts out ahead--his fleet was the decoy and its mission was to be spotted. | ||
===Action off Samar=== | ===Action off Samar=== | ||
{{main|Action off Samar}} | {{main|Action off Samar}} | ||
Revision as of 09:12, 2 June 2010
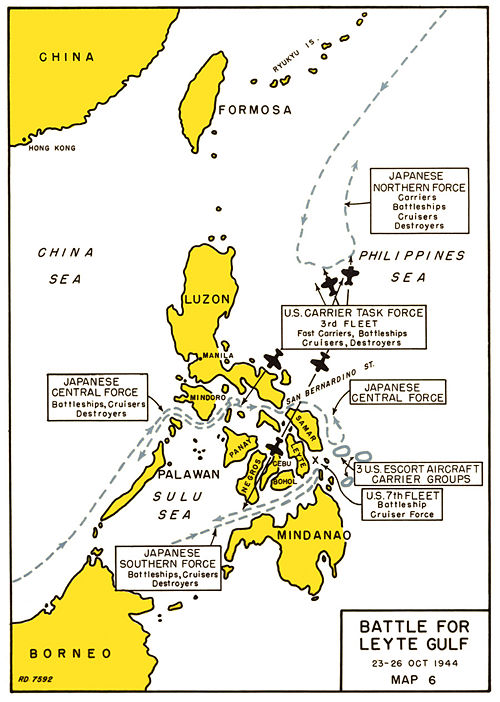
The Battle of Leyte Gulf in October 23-26, 1944, was the largest naval battle in world history. It was fought in the seas around and to the east of the Philippine Islands between the Japanese Imperial Navy and Allied naval forces. The American Fleet was landing troops on the island of Leyte and the Japanese were attempting to interdict and crush that invasion with an elaborate battle plan.
Both sides suffered from divided command. The only joint commanders were in Washington and Tokyo.
By late 1944, the divided American offensives in the Pacific were converging. U.S. Central Pacific command under Admiral Chester W. Nimitz jumped from island to island across the central Pacific, leapfrogging over the strongest Japanese holdings. General Douglas MacArthur's army troops were simultaneously approaching Japan from the south. The ultimate goal was to invade the home islands, but to get within range the Philippines first had to be reconquered. Wading through the surf at the island of Leyte--with 174,000 soldiers--MacArthur had returned as promised.
American situation
The Phillipines were in the Southwest Pacific Area, under GEN Douglas MacArthur, to whom United States Seventh Fleet reported. Its focus was on the recapture of the Phillipines.
United States Third Fleet under Admiral William Halsey reported to Admiral Chester Nimitz, and had the roles of defeating the major Japanese fleet and taking the islands of the Central Pacific. To increase the tempo of operations, the same ships were Third Fleet when under Halsey and his staff, and Fifth Fleet when under Admiral Raymond Spruance. Spruance and Halsey, without friction, alternated in planning and executing operations.
The Joint Chiefs in Washington had never been able to agree on a single commander for the Pacific. Nevertheless, the Third and Seventh Fleets were standing organizations that had reasonable internal communications.
Japanese situation
Admiral Toyoda (Commander in Chief of the remaining fleets) had to defend the Philippines, but he knew his navy was hopelessly outclassed, outgunned and outnumbered by more than 3 to 1. Fuel oil was running short, and carrier aviation had almost ceased to exist. But he and Admiral Ozawa drew up an ingenious plan that exactly identified the Yankee weak point and could exploit it with a smashing defeat that might force Washington to negotiate peace terms. The Navy wanted Nimitz; the Army insisted on MacArthur. Japan's plan: send in three fleets--two to lure away the uncoordinated guards, the third to sink the transports, support ships and massacre the invaders on the beaches.
Background
Admiral William "Bull" Halsey commanded the massive Third Fleet, and he believed fervently in the carrier doctrine. He proved to be as aggressive as Spruance was cautious--his goal was to destroy the Japanese strategic forces, that is their carriers. Admiral Thomas Kinkaid's Seventh fleet (reporting to MacArthur) comprised TF (Taffy) 1, 2 and 3, with 16 small, slow, unarmored escort carriers designed as platforms for close ground support, plus 9 small destroyers. Under Kinkaid, Admiral Jesse Oldendorf had 6 old battleships (some resurrected from Pearl Harbor), plus 9 cruisers and 66 destroyers; Oldendorf's armada was designed for bombarding beaches, not for fighting an enemy fleet.
The battle
To reach the Leyte beaches, Japanese forces would have to come through either San Bernardino Strait to the north, covered by Halsey, or Surigao Strait to the south, covered by Oldendorf.
Preliminaries and Palawan Passage
American forces shot down a Japanese scout plane on the 20th. Unknown to the U.S., it was looking for kamikaze targets, but probably due to poor communications, the Japanese did not start coordinated kamikaze operations. They managed a single attack on the 21st, damaging the cruiser HMAS Australia.[1]
The Japanese Center Force was sighted by U.S. patrol submarines in Palawan Passage. After reporting it to higher headquarters, USS Darter and USS Dace torpedoed three heavy cruisers, sinking two and damaging a third such that it had no additional role in the war.
Battle of the Sibuyan Sea
Vice Admiral Willis Lee, commanding Task Force 34 (battleships) of Third Fleet, reported finding a Japanese force on the morning of the 24th.[2]
Halsey's planes blasted away at Kurita's Center Force, who finally turned tail and retreated. So overconfident were the Yanks that they reported far more damage than they actually inflicted. Halsey was an aviator who thought battleships were obsolete dinosaurs, so he wrote Kurita's force off--and refused to listen to aides who had doubts.
In this action, Third Fleet indeed sank the superbattleship IJN Musashi.
Battle of Surigao Strait
Equipped with superb optics, the Japanese began the war ruling night action. The Allied development of radar, however, neutralized this advantage, but the Japanese often still preferred stealth by night.
October 24 Admiral Kurita headed toward San Bernardino, and Admiral Nishimura headed for Surigao. Oldendorf demonstrated a textbook exercise in how to sink an enemy fleet. His ships steamed back and forth across the top of a "T" while Nishimura's ships came up the stem of the "T" one by one and were sunk. Only one escaped.
Late on the night of the 24th Halsey was puzzled about the Japanese carriers--they must be somewhere, but he could not find them. They were his main objective, according to Mahanian doctrine of great fleet battles. In fact Ozawa with his nearly empty carriers was making smoke, breaking radio silence on various frequencies, and sending escorts out ahead--his fleet was the decoy and its mission was to be spotted.
Action off Samar
When Kinkaid finally bothered to check to be sure Halsey was still covering the San Bernardino Strait, he was dumbfounded to be told "no"--Halsey was out chasing carriers. In fact Kurita had circled about and was now roaring though San Bernardino Strait with four battleships, eight cruisers and eleven destroyers, all headed straight toward MacArthur's defenseless troops and transports on the Leyte beaches. Kinkaid desperately called for help; Halsey said he was busy, use Oldendorf's battleships. But they're too far away and low on ammunition! Suddenly, Nimitz, who had been eavesdropping from Pearl Harbor intervened. Humiliated, Halsey sent half his powerful force back, but it was too late.
Kurita misjudged the situation. Instead of concentrating on his main mission of attacking the beaches, and detailing a few cruisers to finish off Sprague, he decided Taffy 3 was the main enemy and launched all his warships in uncoordinated pell mell attacks. Then in the strangest move of the strangest battle of the 20th century, Kurita panicked. Japanese radio gear was so poor he had not received Ozawa's message that Halsey had been successfully decoyed out of action, but he did hear Kinkaid's uncoded yells for help. Kurita assumed he would soon be surrounded by Halsey's huge fleet. The Americans appeared ten feet tall--the little Yankee destroyers were reported to be large cruisers. Despite his vastly overwhelming firepower and speed, Kurita had ordered defensive zigzagging, which nullified his advantages. When he failed to gain on the slow CVEs, he assumed they must be Halsey's fast carriers. With his big battleships closing at point blank range against the overwhelmed Yankees, with a stunning victory almost in his grasp, Kurita suddenly ordered retreat; he turned and escaped back through San Bernardino Strait. By assuming the worst about the enemy instead of concentrating on his own capabilities, he failed the test of battle. A more subtle explanation is that Kurita accepted the new doctrine that his battleships were obsolete and could not defeat fleet carriers of the sort he mistakenly perceived in front of him; therefore he might as well quit. He did not realize that no big carriers were around. The old doctrine of the power of big guns had been reaffirmed by Oldendorf's smashing victory, and might also have been reaffirmed by Kurita's battleships if only he had followed the original plan and not succumbed to defeatism.
Organized Kamikaze operations
Battle of Cape Engano
Outcome
In the greatest and most complex naval battle ever fought, half the Japanese Navy went to the bottom; US losses were light, and the troops on the beaches were untouched. Of the 282 warships engaged (216 American, 2 Australian, and 64 Japanese), the Japanese lost 4 carriers, 3 battleships, 10 cruisers, and 11 destroyers. American losses totaled one light carrier, two escort carriers, and three destroyers.
Halsey always defended his decision to abandon Leyte; its defense was Kinkaid's job and his mission was strategic. The overwhelming weight of opinion has been that Ozawa outfoxed Halsey, who clung too tenaciously to his carrier doctrine, and who failed to gather and act on the information that was available to him. Halsey's blunder might have cost tens of thousands of lives, or at least delayed the invasion of the Philippines for months, but his luck made him the victor in the biggest naval battle of all time.
Although the Japanese came surprising close to inflicting a major defeat on the Americans, at the last minute the tide turned and the U.S. Navy sank virtually all of Japan's naval power. Part of World War II in the Pacific it involved a complex overlapping series of engagements fought off the Philippine island of Leyte, which the U.S. Army had just invaded. The army forces were highly vulnerable to naval attack, and the Japanese goal was to inflict massive destruction on them. Two American fleets were involved, the Seventh and Third, but they were independent and did not communicate well. The Japanese communication system was even worse, and the Japanese army and navy did not cooperate.
References
- ↑ Edward P. Hoyt (1983), The Kamikazes, Burford Books, ISBN 1580800319, pp. 59-64
- ↑ Willis Lee (14 December 1944), Report of Operations of Task Force THIRTY-FOUR During the Period 6 October 1944 to 3 December 1944., U.S. Navy
- Pages using ISBN magic links
- CZ Live
- History Workgroup
- Military Workgroup
- World War II Subgroup
- Pacific War Subgroup
- United States Navy Subgroup
- Articles written in American English
- Advanced Articles written in American English
- All Content
- History Content
- Military Content
- History tag
- Military tag
- World War II tag
- Pacific War tag
- United States Navy tag