Cefonicid: Difference between revisions
imported>David E. Volk (New page: {{subpages}} {{Chem infobox |align=right |image=center|thumb|250px|{{#ifexist:Template:Cefadroxil.jpg/credit|{{Cefadroxil.jpg/credit}}<br/>|}} |width=250px |molnam...) |
mNo edit summary |
||
| Line 26: | Line 26: | ||
== References == | == References == | ||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
{{CZMed}} | {{CZMed}}[[Category:Suggestion Bot Tag]] | ||
Latest revision as of 06:00, 26 July 2024
|
| |||||||
| cefonicid | |||||||
| |||||||
| Uses: | antibiotic drug | ||||||
| Properties: | beta-lactam | ||||||
| Hazards: | see drug interactions | ||||||
| |||||||
Cefonicid, also known as cefonicido and cefonicidum, is a second-generation cephalosporin type of antibiotic medication. It antibacterial activity is due to the core beta-lactam structure which interacts with penicillin-binding proteins within bacteria, thus distruption bacterial cell wall synthesis. It is sold under the brand names Monocid and Praticef. It is administered intravenously or intramuscularly for treatment of urinary tract infections, lower respiratory tract infections, and soft tissue and bone infections.
Chemistry
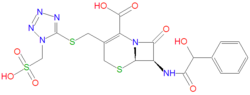
The IUPAC name of cefonicid is (6R,7R)-7-[(2-hydroxy-2-phenylacetyl)amino]-8-oxo-3-[[1-(sulfomethyl)tetrazol-5-yl]sulfanylmethyl]-5-thia-1-azabicyclo[4.2.0]oct-2-ene-2-carboxylic acid. Its chemical formula, C18H18N6O8S3, gives it a molecule mass of 542.5660 grams/mole. Like penicillins and other cephalosporins, cefonicid's antibacterial activity is due to the presence of a beta-lactam, which can react with penicillin-binding proteins through an acylation reaction.
References
The most up-to-date information about Cefonicid and other drugs can be found at the following sites.
- Cefonicid - FDA approved drug information (drug label) from DailyMed (U.S. National Library of Medicine).
- Cefonicid - Drug information for consumers from MedlinePlus (U.S. National Library of Medicine).
- Cefonicid - Detailed information from DrugBank.