Tetration: Difference between revisions
imported>Dmitrii Kouznetsov |
imported>Dmitrii Kouznetsov |
||
| Line 73: | Line 73: | ||
==Asymptotic behavior of tetration== | ==Asymptotic behavior of tetration== | ||
The analytic extension of tetration <math>~F(z)</math> is supposed to grow | |||
fast along the real axis of the complex <math>z</math>-plane, | |||
at least for some values of base <math>b</math>. | |||
However, it has no need to grow infinitely in the direction of imaginary axis. For mathematics of computation, it would be better, if <math>F(x+{\rm i} y)</math> remains bounded at <math>y\rightarrow +\infty</math>. Consider this possibility. | |||
Assume, there exist solution <math>F(z)</math> of equations | |||
(10), (11), analytic in the <math>\Re(z) \ge 0</math>, with, probably, countable number of cuts and singularities at <math>\Re(z)<0</math>, | |||
with exponential asymptotic behavior | |||
(12) <math> F(z)=L+\varepsilon(z) + o \big(\varepsilon(z)^{2}\big) </math> | |||
within some range,<!-- between cuts, $\Im(z)>0$, !--> | |||
where | |||
(13) <math> \varepsilon(z)=\exp(Qz+r) </math>, | |||
<math>Q</math> and <math>r</math> are fixed complex numbers, | |||
and <math>L</math> is eigenvalue of logarithm, solution of equation | |||
(14) <math> x=\log_{b}(x)</math>. | |||
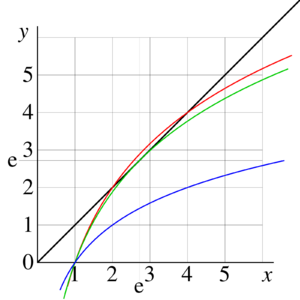
[[Image:ExampleEquationLog01.png|300px|right|thumb|FIg.1. Example of graphic solution of equation | |||
<math>x=\log_b(x)</math> for | |||
<math>b=\sqrt{2}</math> (two real solutions, <math>x=2</math> and <math>x=4</math>), | |||
<math>b=\exp(1/\rm e)</math> (one real solution <math>x=\rm e</math>) | |||
<math>b=2</math> (no real solutions).]] | |||
Solutions of equation (14) are called [[fixed point]]s of logarithm. | |||
Three examples of graphical solution of equation (14) are shown in figure 1 for | |||
<math>b=\sqrt{2}</math>, | |||
<math>b=\exp(1/\rm e)</math>, and | |||
<math>b=2</math>. | |||
The black line shows function <math> y=x</math> in the <math>x,y</math> plane. | |||
The colored curves show function <math> y=\log_b(x)</math> for cases | |||
<math>b=\sqrt{2}</math> (red), | |||
<math>b=\exp(1/\rm e)</math> (green), and | |||
<math>b=2</math> (blue). | |||
At | |||
<math>b=\sqrt{2}</math>, there exist 2 solutions, | |||
<math>x=2</math> and | |||
<math>x=4</math>. | |||
At | |||
<math>b=\exp(1/\rm e)</math> there exist one solution | |||
<math>x=\rm e</math>. | |||
and <math>b=2</math>, there are no real solutions.<br> | |||
In general, | |||
*at <math>b<\exp(1/\rm e)</math> there are two real solutions | |||
*at <math>b=\exp(1/\rm e)</math>, there is one soluition, and | |||
*at <math>b>\exp(1/\rm e)</math> there esist two solutions, but they are complex. | |||
In particular, | |||
at | |||
<math> b=\sqrt{2}</math>, the solutions are <br> | |||
<math>x=L_{\sqrt{2},1}=2</math> and | |||
<math>x=L_{\sqrt{2},2}=4 </math> <br>. | |||
At | |||
<math> b=2</math>, the solutions are <br> | |||
<math>x=L_2 \approx 0.824678546142074222314065+1.56743212384964786105857 \!~\rm i </math> and<br> | |||
<math>x=L_2^*\approx 0.824678546142074222314065-1.56743212384964786105857 \!~\rm i </math>. | |||
At <math> b=\rm e</math>, the solutions are<br> | |||
<math>x=L_{\rm e} \approx 0.318131505204764135312654+1.33723570143068940890116 \!~\rm i</math> | |||
and<br> | |||
<math>x=L_{\rm e}^* \approx 0.318131505204764135312654-1.33723570143068940890116 \!~\rm i</math>. | |||
Few hundred straightforward iterations of equation (14) are sufficient to get the error smaller than the last decimal digit in the approximations above. | |||
The solutions | |||
<math>x=L_1 </math> and | |||
<math>x=L_2 </math> of equation (14) are plotted in figure 2 versus | |||
<math>\beta=\ln(b)</math> with thin black lines. Let | |||
<math>L_1<L_2 </math>, and only at | |||
<math>\ln(b)=1/e </math>, the equality | |||
<math>L_1=L_2 </math> takes place. | |||
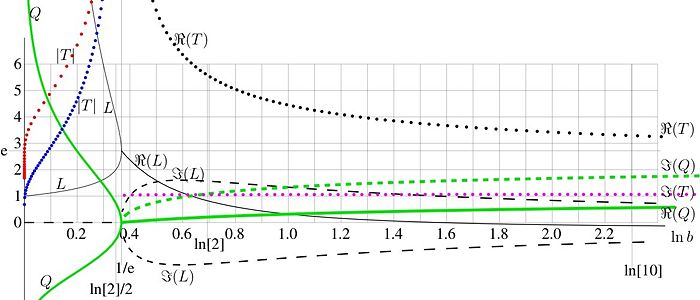
[[Image:TetrationAsymptoticParameters01.jpg|700px|right|thumb|FIg.2. parameters of asymptotic of tetration versus logarithm of the base]] | |||
The thin black solid curve at | |||
<math> \beta \ge 1/\rm e</math> represents the real part of the solutions | |||
<math>L </math> and | |||
<math>L^* </math> of (14); the thin black dashed curve represents the two options for the imaginary part; the two solutions are complex conjugaitons of each other. Let | |||
<math>\Re(L)>0</math>. | |||
==Evaluation of tetration== | ==Evaluation of tetration== | ||
Revision as of 07:54, 29 October 2008
This article is currently under construction. While, use article from wikipedia http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tetration
Tetration is fastly growing mathematical function, which was introduced in XX century and suggested for representation of huge numbers in mathematics of computation. However, up to year 2008, this function is not considered as elementary function, it is not implemented in programming languages and it is not used for the internal representation of data, at least in the commercial software.
Definiton
For real , Tetration on the base is function of complex variable, which is holomorphic at least in the range , bounded in the range , and satisfies conditions
at least within range .
Etymology
Creation of word tetration is attributed to Englidh mathematician Reuben Louis Goodstein [1] [2]. This name indicates, that this operation is fourth (id est, tetra) in the hierarchy of operations after summation, multiplication, and exponentiation. In principle, one can define "pentation", "sexation", "septation" in the simlar manner, although tetration, perhaps, already has growth fast enough for the requests of XXI century.
Real values of the arguments
Examples of behavior of this function at the real axis are shown in figure 1 for values , , , and for . It has logarithmic singularity at , and it is monotonously increasing function.
At tetration approaches its limiting value as , and .
Fast growth
At tetration grows faster than any exponential function. For this reason the tetration is suggested for the representation of huge numbers in mathematics of computation. A number, that cannot be stored as floating point, could be represented as for some standard value of (for example, or ) and relatively moderate value of . The analytic properties of tetration could be used for the implementation of arithmetic operations with huge numbers without to convert them to the floating point representation.
Integer values of the argument
For integer , tetration can be interpreted as iterated exponential:
and so on; then, the argument of tetration can be interpreted as number of exponentiations of unity. From definition it follows, that
and
Relation with the Ackermann function
At base , tetration is related to the Ackermann function:
where Ackermann function is defined for the non-negative integer values of its arguments with equations
Asymptotic behavior of tetration
The analytic extension of tetration is supposed to grow fast along the real axis of the complex -plane, at least for some values of base . However, it has no need to grow infinitely in the direction of imaginary axis. For mathematics of computation, it would be better, if remains bounded at . Consider this possibility.
Assume, there exist solution of equations (10), (11), analytic in the , with, probably, countable number of cuts and singularities at , with exponential asymptotic behavior
(12)
within some range, where
(13) ,
and are fixed complex numbers, and is eigenvalue of logarithm, solution of equation
(14) .
Solutions of equation (14) are called fixed points of logarithm. Three examples of graphical solution of equation (14) are shown in figure 1 for , , and .
The black line shows function in the plane. The colored curves show function for cases (red), (green), and (blue).
At , there exist 2 solutions, and .
At there exist one solution .
and , there are no real solutions.
In general,
- at there are two real solutions
- at , there is one soluition, and
- at there esist two solutions, but they are complex.
In particular,
at
, the solutions are
and
.
At
, the solutions are
and
.
At , the solutions are
and
.
Few hundred straightforward iterations of equation (14) are sufficient to get the error smaller than the last decimal digit in the approximations above.
The solutions and of equation (14) are plotted in figure 2 versus with thin black lines. Let , and only at , the equality takes place.
The thin black solid curve at represents the real part of the solutions and of (14); the thin black dashed curve represents the two options for the imaginary part; the two solutions are complex conjugaitons of each other. Let .
Evaluation of tetration
As the asymptoric of tetration is crutually depend of base in ficinity of value , the evaluation procidure is different foe the cases , , and , and should be considered intependently.
Case
Case
Case
Existence and uniqueness of tetration
If you plan to contribute here, look at draft at User:Dmitrii Kouznetsov/Analytic Tetration.
Inverse of tetration
Iterated exponential and
Especially interesting, and in particular, for the qualitative breakthrough, is the case of iteration of natural exponential, id est, . Existence of the fractional iteration, and, in particular, existence of operation was demonstrated in 1950 by H.Kneser. [3]. However, that time, there was no computer facility for the evlauation of such an exotic function that ; perhaps, just absence of an apropriate plotter did not allow Kneser to plot the distribution of fractal exponential function in the complex plane for various values of .
See also
References
- ↑ "TETRATION, a term for repeated exponentiation, was introduced by Reuben Louis Goodstein". Earliest Known Uses of Some of the Words of Mathematics, http://members.aol.com/jeff570/t.html
- ↑ R.L.Goodstein (1947). "Transfinite ordinals in recursive number theory". Journal of Symbolic Logic 12.
- ↑ Kneser
Free online sources
- http://reglos.de/lars/ffx.html , Lars Kindermann. References about Iterative Roots and Fractional Iteration.
- http://math.eretrandre.org/tetrationforum/index.php , Discussion about tetration
- http://tetration.itgo.com/ Tetration site by Andrew Robbins
- http://www.tetration.org/ Tetration site by Daniel Geisler