Montana (U.S. state): Difference between revisions
(start bibliography) |
mNo edit summary |
||
| (10 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{subpages}} | {{subpages}} | ||
{{dambigbox|Montana (U.S. state)|Montana}} | |||
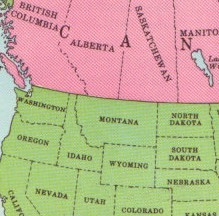
[[Image:NW USA.jpg|right|275px]] | [[Image:NW USA.jpg|right|275px]] | ||
'''Montana''' is one of the states | '''Montana''' is one of the constituent states of the [[United States of America]]. Montana has an area of 147,046 square miles (380,848 square kilometers) and a population of 1,084.225 (2020 census). It joined the Union on November 8, 1889 as the 41st state. It's capital is [[Helena]]. | ||
Montana | ==Physiography== | ||
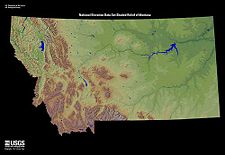
{{Image|Montana.jpg|right|225px|USGS shaded relief map of Montana}} | |||
Montana straddles the [[Great Plains]] in the eastern portion of the state and the [[Rocky Mountains]] to the west. The [[Continental Divide]] runs north to south through the western Rockies. The principle rivers are the [[Missouri River]] which ultimately empties into the [[Gulf of Mexico]] and the [[Yellowstone River]] which is a tributary of the Missouri. | |||
==Climate== | |||
Overall Montana has a dry continental climate due to its isolation from the mitigating influence of any large bodies of water. Within the state, there are two main climate regions. | |||
The eastern, or [[Great Plains]], part of the state, the climate is semiarid with very cold winters and warm summers, occassionally punctuated by Chinook winds coming off the eastern slopes of the [[Rocky Mountains]]. | |||
== | |||
The western, [[Rocky Mountain]] portion of the state exhibits several climate zones, stratified by elevation. The dry valley bottoms are much like eastern Montana, while the Rockies become wetter, snowier, and cooler with increasing altitude. | |||
==Economy== | |||
Montana's economy is mainly based on primary sector activities of | |||
forestry, mining, and energy production supplemented by tourism and recreation. | |||
Agricultural is pursued in the dry valleys of the Rockies and on the Great Plains, the latter featuring cattle and sheep grazing. The eastern part of the state also features oil and coal mining, with coal-fired electricity plants in the Rockies. In northwest Montana, there are numerous dams producing hydropower. Forestry in the forested western part of the state includes lumbering, plywood and other board lumber, and pulp and paper. | |||
Finally, tourism (recreational hiking and camping, skiing) is a major industry in the Rocky Mountains of western Montana. In addition, the state features [[Glacier National Park]] and [[Little Bighorn National Monument]], the site of Custer's Last Stand. | |||
==See also== | |||
[[United States of America/Catalogs/States and Territories|U.S. States and Territories]][[Category:Suggestion Bot Tag]] | |||
Latest revision as of 06:00, 21 September 2024
Montana is one of the constituent states of the United States of America. Montana has an area of 147,046 square miles (380,848 square kilometers) and a population of 1,084.225 (2020 census). It joined the Union on November 8, 1889 as the 41st state. It's capital is Helena.
Physiography
Montana straddles the Great Plains in the eastern portion of the state and the Rocky Mountains to the west. The Continental Divide runs north to south through the western Rockies. The principle rivers are the Missouri River which ultimately empties into the Gulf of Mexico and the Yellowstone River which is a tributary of the Missouri.
Climate
Overall Montana has a dry continental climate due to its isolation from the mitigating influence of any large bodies of water. Within the state, there are two main climate regions.
The eastern, or Great Plains, part of the state, the climate is semiarid with very cold winters and warm summers, occassionally punctuated by Chinook winds coming off the eastern slopes of the Rocky Mountains.
The western, Rocky Mountain portion of the state exhibits several climate zones, stratified by elevation. The dry valley bottoms are much like eastern Montana, while the Rockies become wetter, snowier, and cooler with increasing altitude.
Economy
Montana's economy is mainly based on primary sector activities of forestry, mining, and energy production supplemented by tourism and recreation.
Agricultural is pursued in the dry valleys of the Rockies and on the Great Plains, the latter featuring cattle and sheep grazing. The eastern part of the state also features oil and coal mining, with coal-fired electricity plants in the Rockies. In northwest Montana, there are numerous dams producing hydropower. Forestry in the forested western part of the state includes lumbering, plywood and other board lumber, and pulp and paper.
Finally, tourism (recreational hiking and camping, skiing) is a major industry in the Rocky Mountains of western Montana. In addition, the state features Glacier National Park and Little Bighorn National Monument, the site of Custer's Last Stand.