User:John R. Brews/WP Import: Difference between revisions
imported>John R. Brews |
No edit summary |
||
| (79 intermediate revisions by one other user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{AccountNotLive}} | |||
{{TOC|right}} | {{TOC|right}} | ||
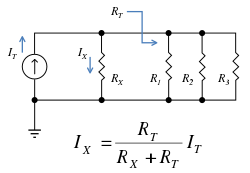
[[Image:Current division example.svg|thumbnail|250px|Figure 1: Schematic of an electrical circuit illustrating current division. Notation ''R<sub>T<sub>.</sub></sub>'' refers to the ''total'' resistance of the circuit to the right of resistor ''R<sub>X</sub>''.]] | |||
In [[electronics]], a '''current divider ''' is a simple [[linear]] [[Electrical network|circuit]] that produces an output [[Electric current|current]] (''I''<sub>X</sub>) that is a fraction of its input current (''I''<sub>T</sub>). The splitting of current between the branches of the divider is called '''current division'''. The currents in the various branches of such a circuit divide in such a way as to minimize the total energy expended. | |||
The formula describing a current divider is similar in form to that for the [[voltage divider]]. However, the ratio describing current division places the impedance of the unconsidered branches in the [[numerator]], unlike voltage division where the considered impedance is in the numerator. To be specific, if two or more [[Electrical impedance|impedance]]s are in parallel, the current that enters the combination will be split between them in inverse proportion to their impedances (according to [[Ohm's law]]). It also follows that if the impedances have the same value the current is split equally. | |||
A | ==Resistive divider== | ||
A general formula for the current ''I<sub>X</sub>'' in a resistor ''R<sub>X</sub>'' that is in parallel with a combination of other resistors of total resistance ''R<sub>T</sub>'' is (see Figure 1): | |||
:<math>I_X = \frac{R_T}{R_X+R_T}I_T \ </math> | |||
where ''I<sub>T</sub>'' is the total current entering the combined network of ''R<sub>X</sub>'' in parallel with ''R<sub>T</sub>''. Notice that when ''R<sub>T</sub>'' is composed of a [[Series_and_parallel_circuits#Parallel_circuits|parallel combination]] of resistors, say ''R<sub>1</sub>'', ''R<sub>2</sub>'', ... ''etc.'', then the reciprocal of each resistor must be added to find the total resistance ''R<sub>T</sub>'': | |||
:<math> \frac {1}{R_T} = \frac {1} {R_1} + \frac {1} {R_2} + \frac {1}{R_3} + ... \ . </math> | |||
==General case== | |||
Although the resistive divider is most common, the current divider may be made of frequency dependent [[Electrical impedance|impedance]]s. In the general case the current I<sub>X</sub> is given by: | |||
:<math>I_X = \frac{Z_T} {Z_X+Z_T}I_T \ ,</math> | |||
==Using Admittance== | |||
Instead of using [[Electrical impedance|impedance]]s, the current divider rule can be applied just like the [[voltage divider]] rule if [[admittance]] (the inverse of impedance) is used. | |||
:<math>I_X = \frac{Y_X} {Y_{Total}}I_T</math> | |||
Take care to note that Y<sub>Total</sub> is a straightforward addition, not the sum of the inverses inverted (as you would do for a standard parallel resistive network). For Figure 1, the current I<sub>X</sub> would be | |||
:<math>I_X = \frac{Y_X} {Y_{Total}}I_T = \frac{\frac{1}{R_X}} {\frac{1}{R_X} + \frac{1}{R_1} + \frac{1}{R_2} + \frac{1}{R_3}}I_T</math> | |||
=== | ===Example: RC combination=== | ||
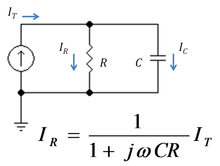
[[Image:Low pass RC filter.PNG|thumbnail|220px|Figure 2: A low pass RC current divider]] | |||
Figure 2 shows a simple current divider made up of a [[capacitor]] and a resistor. Using the formula above, the current in the resistor is given by: | |||
= | ::<math> I_R = \frac {\frac{1}{j \omega C}} {R + \frac{1}{j \omega C} }I_T </math> | ||
:::<math> = \frac {1} {1+j \omega CR} I_T \ , </math> | |||
: | where ''Z<sub>C</sub> = 1/(jωC) '' is the impedance of the capacitor. | ||
The | The product ''τ = CR'' is known as the [[time constant]] of the circuit, and the frequency for which ωCR = 1 is called the [[corner frequency]] of the circuit. Because the capacitor has zero impedance at high frequencies and infinite impedance at low frequencies, the current in the resistor remains at its DC value ''I<sub>T</sub>'' for frequencies up to the corner frequency, whereupon it drops toward zero for higher frequencies as the capacitor effectively [[short-circuit]]s the resistor. In other words, the current divider is a [[low pass filter]] for current in the resistor. | ||
== | ==Loading effect== | ||
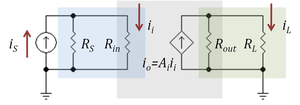
[[Image: | [[Image:Current division.PNG|thumbnail|300px|Figure 3: A current amplifier (gray box) driven by a Norton source (''i<sub>S</sub>'', ''R<sub>S</sub>'') and with a resistor load ''R<sub>L</sub>''. Current divider in blue box at input (''R<sub>S</sub>'',''R<sub>in</sub>'') reduces the current gain, as does the current divider in green box at the output (''R<sub>out</sub>'',''R<sub>L</sub>'')]] | ||
The gain of an amplifier generally depends on its source and load terminations. Current amplifiers and transconductance amplifiers are characterized by a short-circuit output condition, and current amplifiers and transresistance amplifiers are characterized using ideal infinite impedance current sources. When an amplifier is terminated by a finite, non-zero termination, and/or driven by a non-ideal source, the effective gain is reduced due to the '''loading effect''' at the output and/or the input, which can be understood in terms of current division. | |||
Figure 3 shows a current amplifier example. The amplifier (gray box) has input resistance ''R<sub>in</sub>'' and output resistance ''R<sub>out</sub>'' and an ideal current gain ''A<sub>i</sub>''. With an ideal current driver (infinite Norton resistance) all the source current ''i<sub>S</sub>'' becomes input current to the amplifier. However, for a [[Norton's theorem|Norton driver]] a current divider is formed at the input that reduces the input current to | |||
::<math>i_{i} = \frac {R_S} {R_S+R_{in}} i_S \ , </math> | |||
which clearly is less than ''i<sub>S</sub>''. Likewise, for a short circuit at the output, the amplifier delivers an output current ''i<sub>o</sub>'' = ''A<sub>i</sub> i<sub>i</sub>'' to the short-circuit. However, when the load is a non-zero resistor ''R<sub>L</sub>'', the current delivered to the load is reduced by current division to the value: | |||
::<math>i_L = \frac {R_{out}} {R_{out}+R_{L}} A_i i_{i} \ . </math> | |||
Combining these results, the ideal current gain ''A<sub>i</sub>'' realized with an ideal driver and a short-circuit load is reduced to the '''loaded gain''' ''A<sub>loaded</sub>'': | |||
::<math>A_{loaded} =\frac {i_L} {i_S} = \frac {R_S} {R_S+R_{in}}</math> <math> \frac {R_{out}} {R_{out}+R_{L}} A_i \ . </math> | |||
The resistor ratios in the above expression are called the '''loading factors'''. For more discussion of loading in other amplifier types, see [[Voltage division#Loading effect|loading effect]]. | |||
===Unilateral versus bilateral amplifiers=== | |||
[[Image:H-parameter current amplifier.PNG|thumbnail|300px|Figure 4: Current amplifier as a bilateral two-port network; feedback through dependent voltage source of gain β V/V]] | |||
Figure 3 and the associated discussion refers to a [[Electronic amplifier#Unilateral or bilateral|unilateral]] amplifier. In a more general case where the amplifier is represented by a [[two-port network|two port]], the input resistance of the amplifier depends on its load, and the output resistance on the source impedance. The loading factors in these cases must employ the true amplifier impedances including these bilateral effects. For example, taking the unilateral current amplifier of Figure 3, the corresponding bilateral two-port network is shown in Figure 4 based upon [[Two-port network#Hybrid parameters (h-parameters)| h-parameters]].<ref name=H_port/> Carrying out the analysis for this circuit, the current gain with feedback ''A<sub>fb</sub>'' is found to be | |||
::<math> A_{fb} = \frac {i_L}{i_S} = \frac {A_{loaded}} {1+ {\beta}(R_L/R_S) A_{loaded}} \ . </math> | |||
That is, the ideal current gain ''A<sub>i</sub>'' is reduced not only by the loading factors, but due to the bilateral nature of the two-port by an additional factor<ref>Often called the ''improvement factor'' or the ''desensitivity factor''.</ref> ( 1 + β (R<sub>L</sub> / R<sub>S</sub> ) A<sub>loaded</sub> ), which is typical of [[negative feedback amplifier]] circuits. The factor β (R<sub>L</sub> / R<sub>S</sub> ) is the current feedback provided by the voltage feedback source of voltage gain β V/V. For instance, for an ideal current source with ''R<sub>S</sub>'' = ∞ Ω, the voltage feedback has no influence, and for ''R<sub>L</sub>'' = 0 Ω, there is zero load voltage, again disabling the feedback. | |||
==References and notes== | ==References and notes== | ||
{{reflist|refs= | |||
<ref name=H_port>>The [[Two-port network#Hybrid parameters (h-parameters)|h-parameter two port]] is the only two-port among the four standard choices that has a current-controlled current source on the output side.</ref> | |||
<ref name= | |||
| | |||
</ref> | |||
}} | }} | ||
Latest revision as of 03:07, 22 November 2023
The account of this former contributor was not re-activated after the server upgrade of March 2022.
In electronics, a current divider is a simple linear circuit that produces an output current (IX) that is a fraction of its input current (IT). The splitting of current between the branches of the divider is called current division. The currents in the various branches of such a circuit divide in such a way as to minimize the total energy expended.
The formula describing a current divider is similar in form to that for the voltage divider. However, the ratio describing current division places the impedance of the unconsidered branches in the numerator, unlike voltage division where the considered impedance is in the numerator. To be specific, if two or more impedances are in parallel, the current that enters the combination will be split between them in inverse proportion to their impedances (according to Ohm's law). It also follows that if the impedances have the same value the current is split equally.
Resistive divider
A general formula for the current IX in a resistor RX that is in parallel with a combination of other resistors of total resistance RT is (see Figure 1):
where IT is the total current entering the combined network of RX in parallel with RT. Notice that when RT is composed of a parallel combination of resistors, say R1, R2, ... etc., then the reciprocal of each resistor must be added to find the total resistance RT:
General case
Although the resistive divider is most common, the current divider may be made of frequency dependent impedances. In the general case the current IX is given by:
Using Admittance
Instead of using impedances, the current divider rule can be applied just like the voltage divider rule if admittance (the inverse of impedance) is used.
Take care to note that YTotal is a straightforward addition, not the sum of the inverses inverted (as you would do for a standard parallel resistive network). For Figure 1, the current IX would be
Example: RC combination
Figure 2 shows a simple current divider made up of a capacitor and a resistor. Using the formula above, the current in the resistor is given by:
where ZC = 1/(jωC) is the impedance of the capacitor.
The product τ = CR is known as the time constant of the circuit, and the frequency for which ωCR = 1 is called the corner frequency of the circuit. Because the capacitor has zero impedance at high frequencies and infinite impedance at low frequencies, the current in the resistor remains at its DC value IT for frequencies up to the corner frequency, whereupon it drops toward zero for higher frequencies as the capacitor effectively short-circuits the resistor. In other words, the current divider is a low pass filter for current in the resistor.
Loading effect
The gain of an amplifier generally depends on its source and load terminations. Current amplifiers and transconductance amplifiers are characterized by a short-circuit output condition, and current amplifiers and transresistance amplifiers are characterized using ideal infinite impedance current sources. When an amplifier is terminated by a finite, non-zero termination, and/or driven by a non-ideal source, the effective gain is reduced due to the loading effect at the output and/or the input, which can be understood in terms of current division.
Figure 3 shows a current amplifier example. The amplifier (gray box) has input resistance Rin and output resistance Rout and an ideal current gain Ai. With an ideal current driver (infinite Norton resistance) all the source current iS becomes input current to the amplifier. However, for a Norton driver a current divider is formed at the input that reduces the input current to
which clearly is less than iS. Likewise, for a short circuit at the output, the amplifier delivers an output current io = Ai ii to the short-circuit. However, when the load is a non-zero resistor RL, the current delivered to the load is reduced by current division to the value:
Combining these results, the ideal current gain Ai realized with an ideal driver and a short-circuit load is reduced to the loaded gain Aloaded:
The resistor ratios in the above expression are called the loading factors. For more discussion of loading in other amplifier types, see loading effect.
Unilateral versus bilateral amplifiers
Figure 3 and the associated discussion refers to a unilateral amplifier. In a more general case where the amplifier is represented by a two port, the input resistance of the amplifier depends on its load, and the output resistance on the source impedance. The loading factors in these cases must employ the true amplifier impedances including these bilateral effects. For example, taking the unilateral current amplifier of Figure 3, the corresponding bilateral two-port network is shown in Figure 4 based upon h-parameters.[1] Carrying out the analysis for this circuit, the current gain with feedback Afb is found to be
That is, the ideal current gain Ai is reduced not only by the loading factors, but due to the bilateral nature of the two-port by an additional factor[2] ( 1 + β (RL / RS ) Aloaded ), which is typical of negative feedback amplifier circuits. The factor β (RL / RS ) is the current feedback provided by the voltage feedback source of voltage gain β V/V. For instance, for an ideal current source with RS = ∞ Ω, the voltage feedback has no influence, and for RL = 0 Ω, there is zero load voltage, again disabling the feedback.
References and notes
- ↑ >The h-parameter two port is the only two-port among the four standard choices that has a current-controlled current source on the output side.
- ↑ Often called the improvement factor or the desensitivity factor.