User talk:Alexa Arena/sandbox: Difference between revisions
imported>Alexa Arena |
Pat Palmer (talk | contribs) m (Text replacement - "United States" to "United States") |
||
| (14 intermediate revisions by one other user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
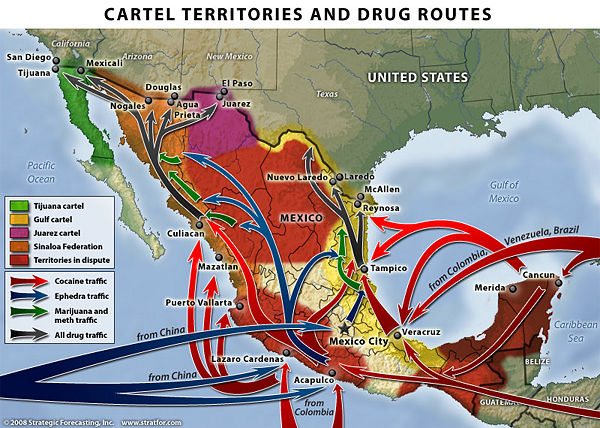
The '''Mexican Drug War''' is an ongoing conflict between criminal groups that operate within the Mexican drug trade. These groups are commonly referred to as drug cartels or drug trafficking organizations (DTOs).<ref>Seelke, C. R. (2010). Mexico-U.S. Relations: Issues for Congress, Congressional Research Service: 38 </ref> Rival drug cartels fight over control of “areas of influence,”<ref>Ray Walser, P. D. (2008) Mexico, Drug Cartels, and the Merida Initiative: A Fight We Cannot Afford to Lose. Executive Summary, Backgrounder No. 2163, 12</ref> strategic strongholds for the drug business. The majority of these areas are pockets along the 200-mile long Mexican border with the [[United States]]. | The '''Mexican Drug War''' is an ongoing conflict between criminal groups that operate within the Mexican drug trade. These groups are commonly referred to as drug cartels or drug trafficking organizations (DTOs).<ref name=Seelke>Seelke, C. R. (2010). Mexico-U.S. Relations: Issues for Congress, Congressional Research Service: 38 </ref> Rival drug cartels fight over control of “areas of influence,”<ref name=Ray>Ray Walser, P. D. (2008) Mexico, Drug Cartels, and the Merida Initiative: A Fight We Cannot Afford to Lose. Executive Summary, Backgrounder No. 2163, 12</ref> strategic strongholds for the drug business. The majority of these areas are pockets along the 200-mile long Mexican border with the [[United States of America|United States]]. | ||
{{Image|STRATFOR Mexican Drug Cartels Map.jpg|right|600px|Cartel Territories and Drug Routes.}} | |||
== Origins == | == Origins == | ||
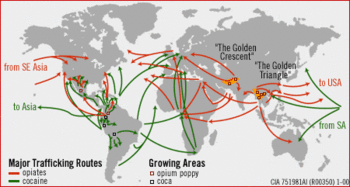
The drugs that circulate through [[Mexico]] originate primarily from the [[South America | South American]] countries of [[Colombia]], [[Venezuela]], and [[Brazil]]. | The drugs that circulate through [[Mexico]] originate primarily from the [[South America | South American]] countries of [[Colombia]], [[Venezuela]], and [[Brazil]].<ref name=Ray>Ray Walser, P. D. (2008) Mexico, Drug Cartels, and the Merida Initiative: A Fight We Cannot Afford to Lose. Executive Summary, Backgrounder No. 2163, 12</ref> Drugs, namely marijuana, cocaine, and opiates, travel to Mexico as part of the global [[illegal drug trade]]. Mexico serves as the south-to-north transit route from South America to the United States. {{Image|Drugroutemap.gif|right|350px|International Drug Routes}} | ||
=== Cultural Influence === | === Cultural Influence === | ||
In [[Latin America|Latin American]] culture, | In [[Latin America|Latin American]] culture, the extended family maintains a tight knit relationship and Mexican drug cartels act along familial and kinship lines. Feuds between Mexican drug cartels have been known to last for months, years, and even decades as a result of their inherent allegiance to family. | ||
Machismo, masculine pride, plays a large role in Mexican culture. | Machismo, masculine pride, plays a large role in Mexican culture. Many drug-related killings revolve around personal disputes rather than business conflicts.<ref name=Williams>Williams, P. (2009). "Illicit markets, weak states and violence: Iraq and Mexico." Crime, Law and Social Change 52(3): 323-336.</ref> Just as cartels are established along familial lines, they fight as familial units against other cartels that threaten their hold on drug routes and markets. | ||
== Effects on the Mexican Population == | == Effects on the Mexican Population == | ||
In recent years, the effects of the Mexican Drug War have increased in scale. Cartel violence formerly affected innocent civilians. As of late, it has escalated to affect whole towns. Some communities have experienced systematic occupation by drug cartels, whom have taken over such institutions as public offices and police departments.<ref name=Ray>Ray Walser, P. D. (2008) Mexico, Drug Cartels, and the Merida Initiative: A Fight We Cannot Afford to Lose. Executive Summary, Backgrounder No. 2163, 12</ref> | |||
Drug War escalation has exposed widespread corruption in Mexico. Numerous police and military officials have been discovered to be working with drug traffickers. The lack of just authority destabilizes the affected areas of Mexico and perpetuates the Drug War by infiltrating everyday life. | |||
== Violence == | == Violence == | ||
| Line 28: | Line 26: | ||
The violence in Mexico that has ensued as part of the drug trade is a consequence of the culture, geographic location, and history of Mexico. Mexican drug cartels have proven to be indiscriminate in their acts of violence. The only rationale which experts have been able to discern is that these acts of violence aim to make a statement, to inflict collateral damage. 3 | The violence in Mexico that has ensued as part of the drug trade is a consequence of the culture, geographic location, and history of Mexico. Mexican drug cartels have proven to be indiscriminate in their acts of violence. The only rationale which experts have been able to discern is that these acts of violence aim to make a statement, to inflict collateral damage.<ref name=Williams>Williams, P. (2009). "Illicit markets, weak states and violence: Iraq and Mexico." Crime, Law and Social Change 52(3): 323-336.</ref> | ||
=== Escalation of Violence === | === Escalation of Violence === | ||
The violence in Mexico has escalated at alarming rates in recent years. Between December 2006 and July 2010 an estimated 28,000 people were killed in drug-trafficking related violence. | The violence in Mexico has escalated at alarming rates in recent years. Between December 2006 and July 2010 an estimated 28,000 people were killed in drug-trafficking related violence.<ref name=Seelke>Seelke, C. R. (2010). Mexico-U.S. Relations: Issues for Congress, Congressional Research Service: 38 </ref> | ||
In response to the Mexican government’s attempts at interdiction, drug cartels have enacted more violence. Reactionary violence asserts the DTOs’ power and expresses their refusal to accede to laws, regulations, and norms. The escalation of violence has caused major setbacks for the government and its efforts to combat the Mexican Drug War. | |||
== US Involvement in the Mexican Drug Trade == | == US Involvement in the Mexican Drug Trade == | ||
| Line 42: | Line 38: | ||
=== Arms === | === Arms === | ||
A significant number of weapons used in the conflicts in Mexico originate in the United States.3 These weapons travel to Mexico through the [[illegal arms trade]]. Illicit arms trafficking from the United States to Mexico has been made easier by the formation of trade blocs between Mexico, the United States, and Canada. One example of this is the 1994 [[North Atlantic Free Trade Agreement]] (NAFTA). | A significant number of weapons used in the conflicts in Mexico originate in the United States.<ref name=Williams>Williams, P. (2009). "Illicit markets, weak states and violence: Iraq and Mexico." Crime, Law and Social Change 52(3): 323-336.</ref> These weapons travel to Mexico through the [[illegal arms trade]]. Illicit arms trafficking from the United States to Mexico has been made easier by the formation of trade blocs between Mexico, the United States, and Canada. One example of this is the 1994 [[North Atlantic Free Trade Agreement]] (NAFTA). | ||
=== Military Personnel === | === Military Personnel === | ||
A great proportion of the men involved in the Mexican drug cartels are experienced in violence and crime. An estimated one in three drug traffickers in Mexico has received military training or has military experience. Many of these men were trained in the United States.3 | A great proportion of the men involved in the Mexican drug cartels are experienced in violence and crime. An estimated one in three drug traffickers in Mexico has received military training or has military experience. Many of these men were trained in the United States.<ref name=Williams>Williams, P. (2009). "Illicit markets, weak states and violence: Iraq and Mexico." Crime, Law and Social Change 52(3): 323-336.</ref> | ||
=== Money Laundering === | === Money Laundering === | ||
| Line 63: | Line 59: | ||
=== Felipe Calderón === | === Felipe Calderón === | ||
Current Mexican President [[Felipe Calderón]] has taken many actions towards curbing the Mexican drug trade. Calderón has implemented prevention programs that emphasize providing treatment and care to drug addicts. He views drug users as victims rather than at fault for the drug trade. He aims to end the drug trade by reducing Mexican citizens’ dependence on illicit drugs, in turn decreasing the demand for illicit drugs.<ref>Boddiger, D. (2010). "Mexico eager to reduce demand for illicit drugs." Lancet 375(9708): 15-16.</ref> | Current Mexican President [[Felipe Calderón]] has taken many actions towards curbing the Mexican drug trade. Calderón has implemented prevention programs that emphasize providing treatment and care to drug addicts. He views drug users as victims rather than the people at fault for the drug trade. He aims to end the drug trade by reducing Mexican citizens’ dependence on illicit drugs, in turn decreasing the demand for illicit drugs.<ref name=Boddiger>Boddiger, D. (2010). "Mexico eager to reduce demand for illicit drugs." Lancet 375(9708): 15-16.</ref> | ||
President Calderón has also initiated many education programs aimed at | President Calderón has also initiated many education programs aimed at children to combat drug temptation. Studies have shown that youth between the ages of twelve and seventeen are the most likely to experiment with drugs. Calderón’s education programs aim to inform this vulnerable population and deter them from submitting to drugs.<ref name=Boddiger>Boddiger, D. (2010). "Mexico eager to reduce demand for illicit drugs." Lancet 375(9708): 15-16.</ref> | ||
=== Bilateral Action by Mexico and United States === | === Bilateral Action by Mexico and United States === | ||
==== War on Drugs ==== | ==== War on Drugs ==== | ||
Former Mexican President Luis Echeverría and American President Richard Nixon | Former Mexican President Luis Echeverría and American President Richard Nixon declared the war on drugs in 1972, a campaign to end drug use and the trade that fuels it. | ||
==== Merida Initiative ==== | ==== Merida Initiative ==== | ||
| Line 87: | Line 83: | ||
===Significance of the Merida Initiative=== | ===Significance of the Merida Initiative=== | ||
This initiative represents shared responsibility and cooperation between Mexico and the United States | This initiative represents shared responsibility and cooperation between Mexico and the United States and will be a key factor in putting an end to the Mexican Drug War. | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
==See Also== | |||
[http://www.stratfor.com/weekly/20090415_when_mexican_drug_trade_hits_border?fn=9915878287 STRATFOR Global Intelligence] | |||
[http://www.state.gov/p/inl/rls/fs/122397.htm U.S. Department of State Mérida Inititiave] | |||
Latest revision as of 14:34, 2 February 2023
The Mexican Drug War is an ongoing conflict between criminal groups that operate within the Mexican drug trade. These groups are commonly referred to as drug cartels or drug trafficking organizations (DTOs).[1] Rival drug cartels fight over control of “areas of influence,”[2] strategic strongholds for the drug business. The majority of these areas are pockets along the 200-mile long Mexican border with the United States.
Origins
The drugs that circulate through Mexico originate primarily from the South American countries of Colombia, Venezuela, and Brazil.[2] Drugs, namely marijuana, cocaine, and opiates, travel to Mexico as part of the global illegal drug trade. Mexico serves as the south-to-north transit route from South America to the United States.
Cultural Influence
In Latin American culture, the extended family maintains a tight knit relationship and Mexican drug cartels act along familial and kinship lines. Feuds between Mexican drug cartels have been known to last for months, years, and even decades as a result of their inherent allegiance to family.
Machismo, masculine pride, plays a large role in Mexican culture. Many drug-related killings revolve around personal disputes rather than business conflicts.[3] Just as cartels are established along familial lines, they fight as familial units against other cartels that threaten their hold on drug routes and markets.
Effects on the Mexican Population
In recent years, the effects of the Mexican Drug War have increased in scale. Cartel violence formerly affected innocent civilians. As of late, it has escalated to affect whole towns. Some communities have experienced systematic occupation by drug cartels, whom have taken over such institutions as public offices and police departments.[2]
Drug War escalation has exposed widespread corruption in Mexico. Numerous police and military officials have been discovered to be working with drug traffickers. The lack of just authority destabilizes the affected areas of Mexico and perpetuates the Drug War by infiltrating everyday life.
Violence
The illegal drug trade in Mexico has resulted in violence and chaos. This violence is present in Mexico as well as in the United States.
Rationale for Violence
Drug trafficking is an anarchic system with no overarching authority controlling it. There are no laws or governing principles that determine how to handle disputes. Therefore, although violence is not an inherent part of the drug trafficking system, it has become a consequence of illicit drug trading as a means to settle conflicts.
The violence in Mexico that has ensued as part of the drug trade is a consequence of the culture, geographic location, and history of Mexico. Mexican drug cartels have proven to be indiscriminate in their acts of violence. The only rationale which experts have been able to discern is that these acts of violence aim to make a statement, to inflict collateral damage.[3]
Escalation of Violence
The violence in Mexico has escalated at alarming rates in recent years. Between December 2006 and July 2010 an estimated 28,000 people were killed in drug-trafficking related violence.[1]
In response to the Mexican government’s attempts at interdiction, drug cartels have enacted more violence. Reactionary violence asserts the DTOs’ power and expresses their refusal to accede to laws, regulations, and norms. The escalation of violence has caused major setbacks for the government and its efforts to combat the Mexican Drug War.
US Involvement in the Mexican Drug Trade
The violence in Mexico has many roots in the United States. These sources include the weapons utilized in the violence, the personnel who make up the criminal organizations, and the practice of money laundering.
Arms
A significant number of weapons used in the conflicts in Mexico originate in the United States.[3] These weapons travel to Mexico through the illegal arms trade. Illicit arms trafficking from the United States to Mexico has been made easier by the formation of trade blocs between Mexico, the United States, and Canada. One example of this is the 1994 North Atlantic Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA).
Military Personnel
A great proportion of the men involved in the Mexican drug cartels are experienced in violence and crime. An estimated one in three drug traffickers in Mexico has received military training or has military experience. Many of these men were trained in the United States.[3]
Money Laundering
Immigration
Human Rights
Governmental Response
Felipe Calderón
Current Mexican President Felipe Calderón has taken many actions towards curbing the Mexican drug trade. Calderón has implemented prevention programs that emphasize providing treatment and care to drug addicts. He views drug users as victims rather than the people at fault for the drug trade. He aims to end the drug trade by reducing Mexican citizens’ dependence on illicit drugs, in turn decreasing the demand for illicit drugs.[4]
President Calderón has also initiated many education programs aimed at children to combat drug temptation. Studies have shown that youth between the ages of twelve and seventeen are the most likely to experiment with drugs. Calderón’s education programs aim to inform this vulnerable population and deter them from submitting to drugs.[4]
Bilateral Action by Mexico and United States
War on Drugs
Former Mexican President Luis Echeverría and American President Richard Nixon declared the war on drugs in 1972, a campaign to end drug use and the trade that fuels it.
Merida Initiative
The Mérida Initiative is a bilateral agreement established by American President Barack Obama and Mexican President Felipe Calderón. The Mérida Initiative encompasses allocation of American funds to Mexico and nearby susceptible areas such as Central America, Haiti, and the Dominican Republic.
Components of the Mérida Initiative include:[5]
- Equipment for inspection and surveillance
- Canines to “interdict trafficked drugs, arms, cash, and persons”
- Funds to bolster technology aimed to “improve and secure communications systems that collect criminal information”
- US “technical advice and training” in order to strengthen a new police force
- Witness protection programs for Mexico
- Corresponding software and supplemental technologies
- Aircrafts for the purpose of detection and quick response time of law enforcement agencies
- “Equipment, training, and community action programs” to educate and deter gang membership while thwarting current gang actions
Significance of the Merida Initiative
This initiative represents shared responsibility and cooperation between Mexico and the United States and will be a key factor in putting an end to the Mexican Drug War.
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Seelke, C. R. (2010). Mexico-U.S. Relations: Issues for Congress, Congressional Research Service: 38
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Ray Walser, P. D. (2008) Mexico, Drug Cartels, and the Merida Initiative: A Fight We Cannot Afford to Lose. Executive Summary, Backgrounder No. 2163, 12
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 Williams, P. (2009). "Illicit markets, weak states and violence: Iraq and Mexico." Crime, Law and Social Change 52(3): 323-336.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Boddiger, D. (2010). "Mexico eager to reduce demand for illicit drugs." Lancet 375(9708): 15-16.
- ↑ "The Mérida Initiative." U.S. Department of State. Web. 08 Oct. 2010. <http://www.state.gov/p/inl/rls/fs/122397.htm>.