TRC-190: Difference between revisions
imported>Howard C. Berkowitz (New page: A High Capacity Line of Sight (HCLOS) radio family, the AN/TRC-190 is used with the Joint Network Node of the U.S. Army to provide high-speed connectivity between nodes. In...) |
imported>Howard C. Berkowitz No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
A High Capacity Line of Sight (HCLOS) radio family, the [[AN-|AN/]]TRC-190 is used with the [[Joint Network Node]] of the [[U.S. Army]] to provide high-speed connectivity between nodes. Individual tactical radios connect separately to the switching and routing nodes. The AN/TRC-190 complements other non-line-of-sight commuincations, such as the [[AN-|AN/]][[TRC-170]] tropospheric scatter ([[troposcatter]]) radio and a variety of satellite earth stations. | {{subpages}} | ||
A High Capacity Line of Sight (HCLOS) radio family, the [[AN-|AN/]]TRC-190 is used with the [[Joint Network Node]] of the [[U.S. Army]] to provide high-speed connectivity between nodes.<ref name=FMI>{{citation | |||
| title = FMI 6-02.60 Tactics, Techniques, and Procedures (TTPs) for the Joint Network Node-Network (JNN-N) | |||
| date = September 2006 | |||
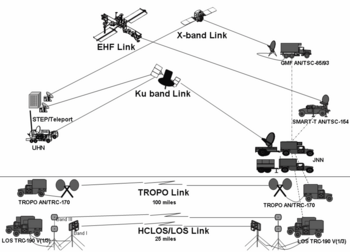
| author = U.S. Army}},pp 2-7</ref> Individual tactical radios connect separately to the switching and routing nodes. [[Image:JNN wireless air and satellite links.png|thumb|350px|Family of Joint Network Node over-the-air communications systems]] The AN/TRC-190 complements other non-line-of-sight commuincations, such as the [[AN-|AN/]][[TRC-170]] tropospheric scatter ([[troposcatter]]) radio and a variety of satellite earth stations. | |||
It uses [[electromagnetic spectrum|microwave]] of different wavelengths; each AN/TRC-190 V(3) contains three radio sets. Range and throughput of each channel depends on wavelengths selected and atmospheric connections. | It uses [[electromagnetic spectrum|microwave]] of different wavelengths; each AN/TRC-190 V(3) contains three radio sets. Range and throughput of each channel depends on wavelengths selected and atmospheric connections. | ||
The AN/TRC-190 is external to the JNN switching center itself, but connects to it at the JNN SEP MP2 panel. Initially connectivity is based on the Quad Multiplexer, to be replaced by the Flex Multiplexer, Fiber Optic Modem, or Tactical Fiber Optic Cable Assembly (TFOCA). | The AN/TRC-190 is external to the JNN switching center itself, but connects to it at the JNN SEP MP2 panel. Initially connectivity is based on the Quad Multiplexer, to be replaced by the Flex Multiplexer, Fiber Optic Modem, or Tactical Fiber Optic Cable Assembly (TFOCA). | ||
==References== | |||
{{reflist}} | |||
Revision as of 12:12, 28 January 2009
A High Capacity Line of Sight (HCLOS) radio family, the AN/TRC-190 is used with the Joint Network Node of the U.S. Army to provide high-speed connectivity between nodes.[1] Individual tactical radios connect separately to the switching and routing nodes.
The AN/TRC-190 complements other non-line-of-sight commuincations, such as the AN/TRC-170 tropospheric scatter (troposcatter) radio and a variety of satellite earth stations.
It uses microwave of different wavelengths; each AN/TRC-190 V(3) contains three radio sets. Range and throughput of each channel depends on wavelengths selected and atmospheric connections.
The AN/TRC-190 is external to the JNN switching center itself, but connects to it at the JNN SEP MP2 panel. Initially connectivity is based on the Quad Multiplexer, to be replaced by the Flex Multiplexer, Fiber Optic Modem, or Tactical Fiber Optic Cable Assembly (TFOCA).
References
- ↑ U.S. Army (September 2006), FMI 6-02.60 Tactics, Techniques, and Procedures (TTPs) for the Joint Network Node-Network (JNN-N),pp 2-7