Sildenafil: Difference between revisions
imported>David E. Volk m (medical links) |
imported>David E. Volk (chemistry and drug interactions) |
||
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
|synonyms= Viagra® | |synonyms= Viagra® | ||
|molformula= | |molformula= | ||
|molmass= | |molmass= 666.7 (citrate) | ||
|uses=Erectile Dysfunction | |uses=Erectile Dysfunction | ||
|properties=PDE-5 inhibitor | |properties=PDE-5 inhibitor | ||
|hazards=cardiovascular risks | |hazards=cardiovascular risks | ||
|iupac= | |iupac= see Chemistry | ||
|casnumber= | |casnumber= | ||
}} | }} | ||
'''Sildenafil''', widely known as [[Viagra]]®, is a medication used to treat [[erectile dysfunction]]. It was the first commercialized ''selective'' [[phosphodiesterase]] type 5 ([[PDE-5]]) inhibitor and was immediately popular both for treating erectile dysfunction and for recreational use. Sildenafil works by binding to phosphodiesterase type-5 enzymes, competing with the natural ligand [[cyclic guanine monophosphate]] (cGMP), which is structurally similar to sildenafil. [[Vardenafil]], a newer and more potent PDE-5 inhibitor, is nearly identical to sildenafil, while [[tadalafil]] is considerably different in structure. | '''Sildenafil''', widely known as [[Viagra]]®, is a medication used to treat [[erectile dysfunction]]. It is also marketed as Ravatio® as an oral treatment for pulmonary arterial hypertension. Both drugs are sold as the citrate salt of sildenafil. It was the first commercialized ''selective'' [[phosphodiesterase]] type 5 ([[PDE-5]]) inhibitor and was immediately popular both for treating erectile dysfunction and for recreational use. Sildenafil works by binding to phosphodiesterase type-5 enzymes, competing with the natural ligand [[cyclic guanine monophosphate]] (cGMP), which is structurally similar to sildenafil. [[Vardenafil]], a newer and more potent PDE-5 inhibitor, is nearly identical to sildenafil, while [[tadalafil]] is considerably different in structure. | ||
{{DailyMed}} | == Chemistry == | ||
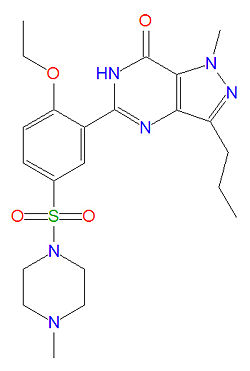
{{MedMaster}} | The IUPAC name of sildenafil is 1-[[3-(6,7-dihydro-1-methyl-7-oxo-3-propyl-1H-pyrazolo [4,3-d] pyrimidin-5-yl)-4-ethoxyphenyl] sulfonyl]-4-methylpiperazine and it has a molecular mass of 666.7 g/mol (as the citrate salt). | ||
{{DrugBank}} | |||
== Drug interactions == | |||
Because sildenafil has vasodilator properties that result in decreased blood pressure, the combined use of sildenafil with other vasodilators, such as [[alpha-blocker]]s, must be done cautiously. Patients with a history of [[myocardial infarction|heart attack]]s, [[stroke]]s, [[arrythmia]], [[hypertension]], [[retinitis pigmentosa]] or currently on [[bosentan therapy]]. | |||
== Up-to-Date Information== | |||
The most up-to-date information about this and other drugs can be found at the following sites. | |||
*{{DailyMed}} | |||
*{{MedMaster}} | |||
*{{DrugBank}} | |||
== References == | == References == | ||
{{cite journal|title=Molecular Biology and Pharmacology of PDE-5-Inhibitor Therapy for Erectile Dysfunction|author=J. D. Corbin and S. H. Sharron|journal=J. Androl.|volume=24|pages=S38-S41}} | {{cite journal|title=Molecular Biology and Pharmacology of PDE-5-Inhibitor Therapy for Erectile Dysfunction|author=J. D. Corbin and S. H. Sharron|journal=J. Androl.|volume=24|pages=S38-S41}} | ||
Revision as of 16:37, 21 June 2008
|
| |||||||
| sildenafil | |||||||
| |||||||
| Uses: | Erectile Dysfunction | ||||||
| Properties: | PDE-5 inhibitor | ||||||
| Hazards: | cardiovascular risks | ||||||
| |||||||
Sildenafil, widely known as Viagra®, is a medication used to treat erectile dysfunction. It is also marketed as Ravatio® as an oral treatment for pulmonary arterial hypertension. Both drugs are sold as the citrate salt of sildenafil. It was the first commercialized selective phosphodiesterase type 5 (PDE-5) inhibitor and was immediately popular both for treating erectile dysfunction and for recreational use. Sildenafil works by binding to phosphodiesterase type-5 enzymes, competing with the natural ligand cyclic guanine monophosphate (cGMP), which is structurally similar to sildenafil. Vardenafil, a newer and more potent PDE-5 inhibitor, is nearly identical to sildenafil, while tadalafil is considerably different in structure.
Chemistry
The IUPAC name of sildenafil is 1-[[3-(6,7-dihydro-1-methyl-7-oxo-3-propyl-1H-pyrazolo [4,3-d] pyrimidin-5-yl)-4-ethoxyphenyl] sulfonyl]-4-methylpiperazine and it has a molecular mass of 666.7 g/mol (as the citrate salt).
Drug interactions
Because sildenafil has vasodilator properties that result in decreased blood pressure, the combined use of sildenafil with other vasodilators, such as alpha-blockers, must be done cautiously. Patients with a history of heart attacks, strokes, arrythmia, hypertension, retinitis pigmentosa or currently on bosentan therapy.
Up-to-Date Information
The most up-to-date information about this and other drugs can be found at the following sites.
- Sildenafil - FDA approved drug information (drug label) from DailyMed (U.S. National Library of Medicine).
References
J. D. Corbin and S. H. Sharron. "Molecular Biology and Pharmacology of PDE-5-Inhibitor Therapy for Erectile Dysfunction". J. Androl. 24: S38-S41.