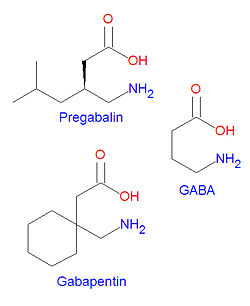
Pregabalin
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Pregabalin is structurally similar to gabapentin. It is also similar to the inhibitory neurotransmitter gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), and although it does not act on GABA receptors, it may increase the "density of GABA transporter protein and increases the rate of functional GABA transport".[1] It is approved by the FDA for neuropathic pain associated with diabetic peripheral neuropathy, postherpetic neuralgia adjunctive therapy for adult patients with partial onset seizures, and fibromyalgia.[1]
chemistry
The IUPAC chemical name for pregabalin is (S)-(+)-3-(aminomethyl)-5-methylhexanoic acid. Its chemical formula is C8H17NO2 giving it a molecular mass of 159.23 g/mol. It is both an amine and a carboxylic acid.
External links
- Pregabalin - FDA approved drug information (drug label) from DailyMed (U.S. National Library of Medicine).
- Template:MedMaster
- Template:DrugBank
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Pregabalin - FDA approved drug information (drug label) from DailyMed (U.S. National Library of Medicine).