Pregabalin: Difference between revisions
imported>Caesar Schinas m (Bot: Update image code) |
imported>Robert Badgett (Started Adverse effects) |
||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
</ref> | </ref> | ||
== | == Chemistry == | ||
The IUPAC chemical name for pregabalin is (S)-(+)-3-(aminomethyl)-5-methylhexanoic acid. Its chemical formula is C<sub>8</sub>H<sub>17</sub>NO<sub>2</sub> giving it a molecular mass of 159.23 g/mol. It is both an [[amine]] and a [[carboxylic acid]]. | The IUPAC chemical name for pregabalin is (S)-(+)-3-(aminomethyl)-5-methylhexanoic acid. Its chemical formula is C<sub>8</sub>H<sub>17</sub>NO<sub>2</sub> giving it a molecular mass of 159.23 g/mol. It is both an [[amine]] and a [[carboxylic acid]]. | ||
==Drug toxicity== | |||
At maximum doses of 600 mg per day, [[drug toxicity]] from pregabalin may include reduced cognitive function.<ref name="pmid20194915">{{cite journal| author=Salinsky M, Storzbach D, Munoz S| title=Cognitive effects of pregabalin in healthy volunteers: a double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. | journal=Neurology | year= 2010 | volume= 74 | issue= 9 | pages= 755-61 | pmid=20194915 | |||
| url=http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=clinical.uthscsa.edu/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=20194915 | doi=10.1212/WNL.0b013e3181d25b34 }} </ref> | |||
== External links == | == External links == | ||
Revision as of 10:19, 19 March 2010
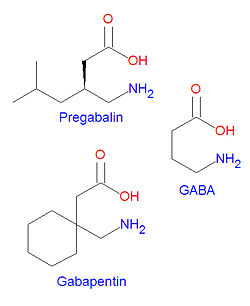
Pregabalin is structurally similar to gabapentin. It is also similar to the inhibitory neurotransmitter gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), and although it does not act on GABA receptors, it may increase the "density of GABA transporter protein and increases the rate of functional GABA transport".[1] It is approved by the FDA for neuropathic pain associated with diabetic peripheral neuropathy, postherpetic neuralgia adjunctive therapy for adult patients with partial onset seizures, and fibromyalgia.[1]
Chemistry
The IUPAC chemical name for pregabalin is (S)-(+)-3-(aminomethyl)-5-methylhexanoic acid. Its chemical formula is C8H17NO2 giving it a molecular mass of 159.23 g/mol. It is both an amine and a carboxylic acid.
Drug toxicity
At maximum doses of 600 mg per day, drug toxicity from pregabalin may include reduced cognitive function.[2]
External links
The most up-to-date information about Pregabalin and other drugs can be found at the following sites.
- Pregabalin - FDA approved drug information (drug label) from DailyMed (U.S. National Library of Medicine).
- Pregabalin - Drug information for consumers from MedlinePlus (U.S. National Library of Medicine).
- Pregabalin - Detailed information from DrugBank.
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 The most up-to-date information about Pregabalin and other drugs can be found at the following sites.
- Pregabalin - FDA approved drug information (drug label) from DailyMed (U.S. National Library of Medicine).
- Pregabalin - Drug information for consumers from MedlinePlus (U.S. National Library of Medicine).
- Pregabalin - Detailed information from DrugBank.
- ↑ Salinsky M, Storzbach D, Munoz S (2010). "Cognitive effects of pregabalin in healthy volunteers: a double-blind, placebo-controlled trial.". Neurology 74 (9): 755-61. DOI:10.1212/WNL.0b013e3181d25b34. PMID 20194915. Research Blogging.