Mission San Luis Rey de Francia
 Mission San Luis Rey de Francia (seen here in 1986) is architecturally distinctive due to the combination of Spanish, Moorish, and Mexican lines exhibited.[1] Part of California's most pristine mission complex, the baroque façade of the church was meant to be flanked by twin towers. Mission San Luis Rey de Francia (seen here in 1986) is architecturally distinctive due to the combination of Spanish, Moorish, and Mexican lines exhibited.[1] Part of California's most pristine mission complex, the baroque façade of the church was meant to be flanked by twin towers.
| |
| HISTORY | |
|---|---|
| Location: | Oceanside, California |
| Name as Founded: | La Misión de San Luis, Rey de Francia [2] |
| English Translation: | The Mission of Saint Louis, King of France |
| Namesake: | King Louis IX [3] |
| Nickname(s): | "King of the Alta California Missions" [4] |
| Founding Date: | June 13, 1798 [5] |
| Founded By: | Father Fermín Lasuén [6] |
| Founding Order: | Eighteenth [3] |
| Military District: | First [7][8] |
| Native Tribe(s): Spanish Name(s): |
Kumeyaay, Quechnajuichom [9] Diegueño, Luiseño Cite error: Closing </ref> missing for <ref> tag
|
| SPIRITUAL RESULTS | |
| Baptisms: | 5,399 [10] |
| Confirmations: | |
| Marriages: | 1,335 [10] |
| Burials: | 2,718 [10] |
| Neophyte Population: | 2,788 [10][11] |
| DISPOSITION | |
| Secularized: | 1834 [12] |
| Returned to the Church: | 1865 [12] |
| Governing Body: | Roman Catholic Diocese of San Diego |
| Current Use: | Franciscan College / Museum |
| Coordinates: | 33°15'63"N, 117°00'66"W |
| National Historic Landmark: | #NPS–70000142 |
| Date added to the NRHP: | 1970 |
| California Historical Landmark: | #239 |
| Web Site: | http://www.sanluisrey.org/ |
Mission San Luis Rey de Francia was founded on June 13, 1798 by Spanish Catholics of the Franciscan Order. Named after a thirteenth-century French monarch, the outpost boasts the largest intact mission chapel in southern California, earning it the nickname, "King of the Missions." [13] Mission San Luis Rey reached the height of its prosperity in 1818, becoming "The largest and most populous Indian mission of both Americas." [3] The mission maintained a vast network of outlying ranchos and asistencias, spread out over a 1,000-square-mile area.
In 1893, the Catholic Church rededicated the Mission as a Franciscan college, a function the facility continues to serve today.
Precontact
The current prevailing theory postulates that Paleo-Indians entered the Americas from Asia via a land bridge called "Beringia" that connected eastern Siberia with present-day Alaska (when sea levels were significantly lower, due to widespread glaciation) between about 15,000 to 35,000 years ago. The remains of Arlington Springs Man on Santa Rosa Island are among the traces of a very early habitation in California, dated to the last ice age (Wisconsin glaciation) about 13,000 years ago. The first humans are therefore thought to have made their homes among the southern valleys of California's coastal mountain ranges some 10,000 to 12,000 years ago; the earliest of these people are known only from archaeological evidence.[14] The cultural impacts resulting from climactic changes and other natural events during this broad expanse of time were negligible; conversely, European contact was a momentous event, which profoundly affected California's native peoples.[15]
History
The local Quechnajuichom tribe became known as the Luiseño, after the Mission. In its prime, the San Luis Rey compound covered almost 6 acres, making it one of the most extensive of all the missions.[16] An early account of life at the Mission was written by one of its neophytes, Pablo Tac, in his work Indian Life and Customs at Mission San Luis Rey: A Record of California Mission Life by Pablo Tac, An Indian Neophyte (written in Rome circa 1835, edited and translated by Minna Hewes and Gordon Hewes in 1958). In the book, Tac lamented the rapid decline of his people:
In Quechla not long ago there were 5,000 souls, with all their neighboring lands. Through a sickness that came to California 2,000 souls died, and 3,000 were left.[17]

In 1841, French explorer Eugene Duflot de Mofras produced a sketch of the Mission that depicted a second campanario, thereby supporting the theory that two bell towers were planned, but never completed; the lone tower was also used as a lookout post.[18]
Tac went on to describe the preferential treatment the padres received:
In the mission of San Luis Rey de Francia the Fernandino [sic] father is like a king. He has his pages, alcaldes, majordomos, musicians, soldiers, gardens, ranchos, livestock....[19]
The Mission-born, Franciscan-educated Tac noted that his people initially attempted to bar the Spaniards from their southern California lands. When the foreigners approached, "...the chief stood up...and met them," demanding, "...what are you looking for? Leave our country!"
In 1816, Mission San Antonio de Pala was established twenty miles inland as an asistencia ("sub-mission"). During the Mexican-American War, the Mission was utilized as a military outpost by the United States Army.[16] Following secularization, no religious services were held at the Mission until 1893, when two Mexican priests were given permission to restore the Mission as a Franciscan college.[16]
Father Joseph O'Keefe was assigned as an interpreter for the monks. It was he who began to restore the old Mission in 1895. Repairs to the cuadrángulo (quadrangle) and church were completed in 1905. Today, Mission San Luis Rey de Francia serves as a Franciscan college.
The fourth episode of the Walt Disney television series Zorro was filmed on the Mission grounds. The story line purported that the Mission was haunted, and the episode (entitled "The Ghost of the Mission") was aired on Halloween (October 31, 1957).
Mission industries
The goal of the missions was, above all, to become self-sufficient in relatively short order. Farming, therefore, was the most important industry of any mission. Prior to the establishment of the missions, the native peoples knew only how to utilize bone, seashells, stone, and wood for building, tool making, weapons, and so forth. The missionaries discovered that the Indians, who regarded labor as degrading to the masculine sex, had to be taught industry in order to learn how to be self-supportive. The result was the establishment of a great manual training school that comprised agriculture, the mechanical arts, and the raising and care of livestock. Everything consumed and otherwise utilized by the natives was produced at the missions under the supervision of the padres; thus, the neophytes not only supported themselves, but after 1811 sustained the entire military and civil government of California.[20]
Mission bells
Bells were vitally important to daily life at any mission. The bells were rung at mealtimes, to call the Mission residents to work and to religious services, during births and funerals, to signal the approach of a ship or returning missionary, and at other times; novices were instructed in the intricate rituals associated with the ringing the mission bells.
California pepper tree
The oldest pepper tree (Schinus molle) in California resides in Mission San Luis Rey de Francia's courtyard, propagated from a seed planted by Father Peyri.[16]
Notes

Inside the "cavernous" capilla (chapel) at Mission San Luís Rey de Francia, circa 1900. Dedicated in 1815, the cruciform design is shared only with the ruined "Great Stone Church" at Mission San Juan Capistrano, making the two structures unique among the Alta California missions in that regard.[21]
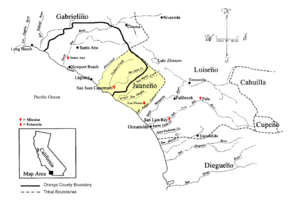
The territorial boundaries of the Southern California Indian tribes based on dialect, including the Cahuilla, Cupeño, Diegueño, Gabrieliño, Juaneño (highlighted), and Luiseño language groups.[22]

USNS Mission San Luis Rey (T-AO-128) was the eighteenth of twenty-seven Mission Buenaventura-class fleet oilers built during World War II for service in the United States Navy. Scrapped in 1972, she was the only U.S. Naval vessel to bear the name.[23]
- ↑ © Photo: Robert A. Estremo
- ↑ Leffingwell, p. 27
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 Krell, p. 273
- ↑ Yenne, p. 158
- ↑ Yenne, p. 156
- ↑ Ruscin, p. 196
- ↑ Forbes, p. 202
- ↑ Engelhardt 1920, pp. v, 228: "The military district of San Diego embraced the Missions of San Diego, San Luis Rey, San Juan Capistrano, and San Gabriel..."
- ↑ Yenne, p. 161
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 10.2 10.3 Krell, p. 316: as of December 31, 1832; information adapted from Engelhardt's Missions and Missionaries of California. Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; name "krell316" defined multiple times with different content - ↑ Johnson, et al: "In contrast to baptismal patterns documented at missions in much of the rest of California, Mission San Luis Rey appears to have coexisted with nearby native communities for a much longer period of time without fully absorbing their populations...This may be the result of a conscious decision by the head missionary at Mission San Luis Rey, Fr. Antonio Peyri, to permit a certain number of baptized Luiseños to remain living apart from the mission with their unconverted relatives at their rancherías [villages]. The native communities in this way gradually became converted into mission ranchos at Santa Margarita, Las Flores, Las Pulgas, San Jacinto, Temecula, Pala, etc."
- ↑ 12.0 12.1 Krell, p. 315
- ↑ Yenne, p. 158: The chapel, completed in 1815, measures out at 138 feet long, compared to the 180-foot-long "Great Stone Church" at Mission San Juan Capistrano, which was destroyed by earthquake in 1812.
- ↑ Paddison, p. 333: The first undisputable archaeological evidence of human presence in California dates back to circa 8,000 BCE.
- ↑ Jones and Klar 2005, p. 53: "Understanding how and when humans first settled California is intimately linked to the initial colonization of the Americas."
- ↑ 16.0 16.1 16.2 16.3 Young, p. 18
- ↑ Lightfoot, p. 108
- ↑ Krell, pp. 275-276
- ↑ Lightfoot, p. 105
- ↑ Engelhardt 1922, p. 211
- ↑ Krell, pp. 154, 275
- ↑ After Kroeber, 1925
- ↑ Mission San Luis Rey

