Joint Tactical Radio System: Difference between revisions
imported>Howard C. Berkowitz (New page: {{subpages}} {{TOC-right}} Replacing a wide range of military radios and communications security devices is the '''Joint Tactical Radio System (JTRS),'''pronounced "jitters" by mil...) |
imported>Howard C. Berkowitz (Continuing to clean up military standard citation) |
||
| Line 54: | Line 54: | ||
*[[Soldier Radio Waveform]] (SRW): 1.755-1.850 GHZ frequency range. The Soldier Radio and [[wireless local area network]] (WLAN) with digital 16 KBPS voice and data at 1 MBPS.<ref>The WLAN will be compliant with IEEE 802.11b, 802.11e and 802.11g</ref> | *[[Soldier Radio Waveform]] (SRW): 1.755-1.850 GHZ frequency range. The Soldier Radio and [[wireless local area network]] (WLAN) with digital 16 KBPS voice and data at 1 MBPS.<ref>The WLAN will be compliant with IEEE 802.11b, 802.11e and 802.11g</ref> | ||
*[[Joint Airborne Networking–Tactical Edge]] (JAN-TE): The precise technology for this part of the network, which will connect manned and unmanned aircraft, as well as [[precision-guided munition]]s, has not been selected, although the [[Tactical Targeting Network Technology]] waveform is under active consideration.<ref name=Walker2006-07-10 /> | *[[Joint Airborne Networking–Tactical Edge]] (JAN-TE): The precise technology for this part of the network, which will connect manned and unmanned aircraft, as well as [[precision-guided munition]]s, has not been selected, although the [[Tactical Targeting Network Technology]] waveform is under active consideration.<ref name=Walker2006-07-10 /> | ||
*[[Mobile User Objective System]] (MUOS): a narrowband (i.e., 2.4 to 64 Kbps) satellite communications system | *[[Mobile User Objective System]] (MUOS): a narrowband (i.e., 2.4 to 64 Kbps) satellite communications system <ref name=240-320>Operating in the 240-320 MHz range, at the high end of VHF and the low end of UHF</ref> | ||
*[[SINCGARS]] Enhanced SINCGARS Improvement Program (ESIP) operates in the 30-88 MHz VHF frequency band, for data, analog voice, and 16Kbps digital voice. <ref> | *[[SINCGARS]] Enhanced SINCGARS Improvement Program (ESIP) operates in the 30-88 MHz VHF frequency band, for data, analog voice, and 16Kbps digital voice. <ref name=MIL-STD-188-220> MIL-STD 188-220 for Digital Message Transfer Device and MIL-STD MIL-STD-2045-47001 for Connectionless Data Transfer Application Layer Standard Subsystems for Combat Net Radio (CNR) systems</ref> <ref name=MIL-STD-188-241>MIL-STD 188-241-1/2</ref> | ||
*[[Link-16]] for the [[Joint Tactical Information Distribution System]]: 960 to 1215 MHZ frequency range. | *[[Link-16]] for the [[Joint Tactical Information Distribution System]]: 960 to 1215 MHZ frequency range. LINK 16 will support voice mode of operation at 2.4 and 16 KBPS and data with [[error control#forward error correction|forward error correction (FEC)]] at rates of 28.8 KBPS to 1.137 MBPS. Link 16 will be compliant with <ref name=MIL-STD-6016>MIL-STD 6016 for Tactical Command, Control, Communications, and Intelligence (C4I) systems that implement the Link 16 Tactical Data Link (TDL)</ref> and [[NATO]] Standardization Agreement (STANAG) 5516</ref> | ||
*[[Enhanced Position Location Reporting System]] (EPLRS: 420-450 MHZ frequency range. EPLRS will start at a 57 Kbps data rate, and then, through a [[value engineering change process]], upgrade to 228 Kbps. | *[[Enhanced Position Location Reporting System]] (EPLRS): 420-450 MHZ frequency range. EPLRS will start at a 57 Kbps data rate, and then, through a [[value engineering change process]], upgrade to 228 Kbps. | ||
*[[ITU frequency bands|High Frequency (HF)]]: | *[[ITU frequency bands|High Frequency (HF)]]: | ||
**Independent Side Band (ISB) with Automatic Link Establishment (ALE) | **Independent Side Band (ISB) with Automatic Link Establishment (ALE) | ||
| Line 63: | Line 63: | ||
**STANAG 5066 HF Data Protoco) | **STANAG 5066 HF Data Protoco) | ||
**STANAG 4529 HF narrowband [[modem]]) | **STANAG 4529 HF narrowband [[modem]]) | ||
*[[ITU frequency bands|Ultra High Frequency (UHF)]] | *[[ITU frequency bands|Ultra High Frequency (UHF)]]<ref name=240-320 /> | ||
**satellite communications (SATCOM) <ref>MIL-STD-188-181 through 184<ref> | **satellite communications (SATCOM) <ref>MIL-STD-188-181 through 184</ref> | ||
**HAVE QUICK II [[frequency agility]] radio system: carries, but in UHF rather than HF, the basic types of user information that SINCGARS provides. <ref> | **HAVE QUICK II [[frequency agility]] radio system: carries, but in UHF rather than HF, the basic types of user information that SINCGARS provides.<ref name=MIL-STD-188-220 /> <ref>MIL-STD-188-243 and JIEO-9120A</ref> | ||
**UHF [[amplitude modulated]]/[[frequency modulated]] (AM/FM) phase shift keying (PSK) <ref>UHF AM/FM PSK will be compliant with MIL-STD-188-181B and MIL-STD-188-243</ref> | **UHF [[amplitude modulated]]/[[frequency modulated]] (AM/FM) phase shift keying (PSK) <ref>UHF AM/FM PSK will be compliant with MIL-STD-188-181B and MIL-STD-188-243</ref> | ||
*VHF FM: VHF FM operates in the 30-88 MHZ frequency range. VHF FM supports analog voice and digital voice at 16 KBPS. <ref> | *VHF FM: VHF FM operates in the 30-88 MHZ frequency range. VHF FM supports analog voice and digital voice at 16 KBPS. <ref name=MIL-STD-188-242>{{citation| id = MIL-STD-188-242| title = Interoperability and Performance Standards for Tactical Single Channel Very High Frequency (VHF) Radio Equipment | ||
|url = http://assist.daps.dla.mil/quicksearch/basic_profile.cfm?ident_number=35584 | |||
|date = June 20, 1985}}</ref> | |||
==References== | ==References== | ||
{{reflist|2}} | {{reflist|2}} | ||
Revision as of 19:07, 27 August 2008
Template:TOC-right Replacing a wide range of military radios and communications security devices is the Joint Tactical Radio System (JTRS),pronounced "jitters" by military personnel). JTRS is a large-scale project to deploy software-defined radio technology in the U.S. and allied militaries.
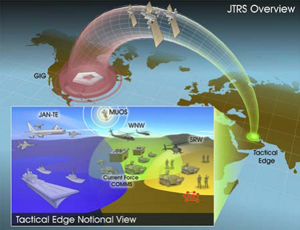
Under the U.S. Department of Defense, the applications that need wireless radio communications connectivity form the Global Information Grid (GIG), with the GIG being transmitted principally over fixed optical networks with massive bandwidth and extremely low error rates. In contrast, the JTRS edge networks will have limited bandwidth and not only electrically noisy environments, but may be under active electronic attack. The edge networks will not only not be fixed, but may be moving at high speed, and the overall networks must be to cope with the occasional exceptionally high speed separation of the pieces of a host or router into a rapidly expanding fireball.
JTRS is the "last mile" that connects the warfighters in the field to one another, and to their fixed facilities. JTRS equipment will form mobile ad hoc networks (MANET) with digital payloads encapsulated in Internet Protocol over a wide range of radio frequencies and waveforms. [1]
Software-defined radio (SDR) is a radical departure from traditional radio, in which many of the discrete electronic components, and even fundamental techniques such as superheterodyne operation, are replaced by computer-controlled digital signal processors.[2]
Program management
The proof-of-concept of SDR technology was a Army Special Operations Command radio, and the U.S. Army became the executive agent for what was becoming a massive and high-risk program. On March 31, 2006, Ken Krieg, undersecretary of defense for acquisition, technology and logistics, changed the program "big bang" procurement to an incremental one, lowering the risk and the capabilities of the radios that will initially be obtained. [3] Still, while interoperability testing has been scheduled, not all the specifications have been set.
Originally, each military service had a separate development program for a group of physical implementatins, called a "cluster", with the joint program office in charge of the software communications architecture and software waveforms used by all the radios. Problems with the Army-led Cluster 1 program to develop radios for ground vehicles and rotorcraft forced the restructuring.
At a May 3, 2006 briefing, the JTRS Joint Program executive officer, said that trying to bring out all the systems at one would take about USD $4 billion more than was in the research and development budget. The new method broke systems into phases based on difficulty, assuming that each new phase would learn from the success of the less complex phases that preceded it. The earlier system put the radios for Army helicopters and Army trucks under the same leadership because they were Army. Unfortunately, that meant five different programs that dealt with helicopters, rather than concentrating the knowledge of radios for flight. Under the new JTRS plan, the groupings are:
- ground: land vehicles and Handheld, Manpack and Small form-fit (HMS); HMS leading to the Future Combat System.
- airborne and maritime: helicopters airborne (including helicopters), maritime and fixed-site Airborne and Maritime Fixed station (AMF), and the multifunctional information distribution system (MIDS).
- network enterprise: routers, application gateways, and waveform speciication
- special radio systems: Special operations, concentrating on upgrading the hand-held multiband inter/intra-team radio
These groupings matrix against a set of physical packaging requirements.
Radio set physical implementations
Most of the basic electronics of JTRS implementations will be common, but they will vary in form factor, or physical packaging for different applications. 26 different form factors were identified as being in military use, and, with the smaller size and programmability of the JTRS electronics, reduced to 13 form factors:
- Manpack
- Handheld
- Airborne, Maritime and Fixed Site Small Airborne (AMF-SA)
- AMF-MF (Maritime/fixed site)
- Small form factor (SFF) A&H (for Intelligent Munitions Systems and Unattended Ground Sensors (UGS) in the Future Combat System(FCS))
- SFF B, C and I (for Ground Soldier Systems)
- SFF D (for aerial systems)
- SFF J (for Networked Missile Launcher System in FCS)
Waveform
In electronics, a waveform generically describes the nature of an electronic signal, typically as viewed in the time domain on an oscilloscope. JTRS uses "waveform" in a broader context: "the entire set of radio and/or communications functions that occur from the user input to the radio frequency output and vice versa. JTRS waveform implementation consists of a Waveform Application Code, Radio Set Devices and Radio System Applications. Every waveform involves the tuning of a mobile ad hoc networking "to its peculiar environment. These protocols interact with the IP layers in the radios to hide the network mobility and dynamics from the external commercial-based networking equipment to facilitate interoperability."[1]
Originally, there were 32 JTRS waveforms which have since been reduced to the following list:[4]
- Wideband Networking Waveform (WNW): still not fully defined, the waveform will operate in the 2 MHZ to 2 GHZ frequency range at up to 5 MBPS networked throughput.
- Soldier Radio Waveform (SRW): 1.755-1.850 GHZ frequency range. The Soldier Radio and wireless local area network (WLAN) with digital 16 KBPS voice and data at 1 MBPS.[5]
- Joint Airborne Networking–Tactical Edge (JAN-TE): The precise technology for this part of the network, which will connect manned and unmanned aircraft, as well as precision-guided munitions, has not been selected, although the Tactical Targeting Network Technology waveform is under active consideration.[3]
- Mobile User Objective System (MUOS): a narrowband (i.e., 2.4 to 64 Kbps) satellite communications system [6]
- SINCGARS Enhanced SINCGARS Improvement Program (ESIP) operates in the 30-88 MHz VHF frequency band, for data, analog voice, and 16Kbps digital voice. [7] [8]
- Link-16 for the Joint Tactical Information Distribution System: 960 to 1215 MHZ frequency range. LINK 16 will support voice mode of operation at 2.4 and 16 KBPS and data with forward error correction (FEC) at rates of 28.8 KBPS to 1.137 MBPS. Link 16 will be compliant with [9] and NATO Standardization Agreement (STANAG) 5516</ref>
- Enhanced Position Location Reporting System (EPLRS): 420-450 MHZ frequency range. EPLRS will start at a 57 Kbps data rate, and then, through a value engineering change process, upgrade to 228 Kbps.
- High Frequency (HF):
- Independent Side Band (ISB) with Automatic Link Establishment (ALE)
- HF Single Side Band (SSB) with ALE
- STANAG 5066 HF Data Protoco)
- STANAG 4529 HF narrowband modem)
- Ultra High Frequency (UHF)[6]
- satellite communications (SATCOM) [10]
- HAVE QUICK II frequency agility radio system: carries, but in UHF rather than HF, the basic types of user information that SINCGARS provides.[7] [11]
- UHF amplitude modulated/frequency modulated (AM/FM) phase shift keying (PSK) [12]
- VHF FM: VHF FM operates in the 30-88 MHZ frequency range. VHF FM supports analog voice and digital voice at 16 KBPS. [13]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 North, Rich; Norm Browne & Len Schiavone (October 23-35, 2006), "Joint Tactical Radio System -- Connecting the GIG to the Tactical Edge", Military Communications Conference
- ↑ Joint Program Executive Office, Joint Tactical Radio System
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Walker, Karen (July 10, 2006), "Restructuring Cuts Cost, Puts Radio Program Back on Track", C4ISR Journal
- ↑ U.S. Navy Space and Naval Systems Warfare Command (SPAWAR), JPEO JTRS - What is a waveform?
- ↑ The WLAN will be compliant with IEEE 802.11b, 802.11e and 802.11g
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Operating in the 240-320 MHz range, at the high end of VHF and the low end of UHF
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 MIL-STD 188-220 for Digital Message Transfer Device and MIL-STD MIL-STD-2045-47001 for Connectionless Data Transfer Application Layer Standard Subsystems for Combat Net Radio (CNR) systems
- ↑ MIL-STD 188-241-1/2
- ↑ MIL-STD 6016 for Tactical Command, Control, Communications, and Intelligence (C4I) systems that implement the Link 16 Tactical Data Link (TDL)
- ↑ MIL-STD-188-181 through 184
- ↑ MIL-STD-188-243 and JIEO-9120A
- ↑ UHF AM/FM PSK will be compliant with MIL-STD-188-181B and MIL-STD-188-243
- ↑ Interoperability and Performance Standards for Tactical Single Channel Very High Frequency (VHF) Radio Equipment, June 20, 1985, MIL-STD-188-242