Itraconazole: Difference between revisions
imported>David E. Volk (New page: {{subpages}} [[Image:Itraconazole structure.jpg|right|thumb|350px|{{#ifexist:Template:Itraconazole structure.jpg/credit|{{Itraconazole structure.jpg/credit}}<br/>|}}Itraconazole, a triazol...) |
imported>David E. Volk No edit summary |
||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
== Mechanism of action == | == Mechanism of action == | ||
Like other azole-based antifungal agents, itraconazole interacts with 14-<math>\alpha</math>-demethylase, a cytochrome P-450 enzyme necessary to convert [[lanosterol]] to [[ergosterol]], an essential component of fungal cell membranes, by stopping [[sterol]] C-14 <math>\alpha</math>-demethylation. Itraconazole may also inhibit endogenous respiration, interact with membrane phospholipids, inhibit the transformation of yeasts to mycelial forms, inhibit purine uptake, and impair triglyceride and/or phospholipid biosynthesis<ref> Drug Bank [http://www.drugbank.ca/cgi-bin/getCard.cgi?CARD=DB01167.txt]. | Like other azole-based antifungal agents, itraconazole interacts with 14-<math>\alpha</math>-demethylase, a cytochrome P-450 enzyme necessary to convert [[lanosterol]] to [[ergosterol]], an essential component of fungal cell membranes, by stopping [[sterol]] C-14 <math>\alpha</math>-demethylation. Itraconazole may also inhibit endogenous respiration, interact with membrane phospholipids, inhibit the transformation of yeasts to mycelial forms, inhibit purine uptake, and impair triglyceride and/or phospholipid biosynthesis<ref> Drug Bank [http://www.drugbank.ca/cgi-bin/getCard.cgi?CARD=DB01167.txt]</ref>. | ||
== chemical information == | == chemical information == | ||
| Line 28: | Line 28: | ||
== References and external links == | == References and external links == | ||
<references/> | |||
* {{DailyMed}} | * {{DailyMed}} | ||
Revision as of 11:08, 4 March 2008
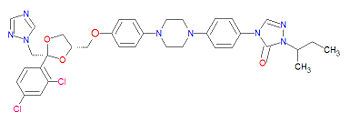
Itraconazole is an azole-based antifungal drug containing three azoles, like fluconazole. It inhibits cytochrom P450-dependent enzymes and impairs the biosynthesis of ergosterol. It can be used to treate apergillosis, blasoplasmosis, cryptococcal meningitis, histoplasmosis and onychomycosis.
Mechanism of action
Like other azole-based antifungal agents, itraconazole interacts with 14--demethylase, a cytochrome P-450 enzyme necessary to convert lanosterol to ergosterol, an essential component of fungal cell membranes, by stopping sterol C-14 -demethylation. Itraconazole may also inhibit endogenous respiration, interact with membrane phospholipids, inhibit the transformation of yeasts to mycelial forms, inhibit purine uptake, and impair triglyceride and/or phospholipid biosynthesis[1].
chemical information
The IUPAC name for itraconazole is 2-butan-2-yl-4-[4-[4-[4-[[(2R,4S)-2-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)-2-(1,2,4-triazol-1-ylmethyl)-1,3-dioxolan-4-yl]methoxy]phenyl]piperazin-1-yl]phenyl]-1,2,4-triazol-3-one, and its chemical formula, C35H38Cl2N8O4, gives a molecular mass of 705.6334 g/mol.
Synonyms
- ITC
- ITCZ
- ITR
- Itraconazol
- Itraconazolum
- ITZ
Brand names
- Itrizole®
- Oriconazole®
- Sporal®
- Sporanos®
- Sporanox®
- Sporonox®
- Triasporn®
References and external links
- Itraconazole - FDA approved drug information (drug label) from DailyMed (U.S. National Library of Medicine).