Hypertension
Hypertension is a multisystem disease whose hallmark is the elevation of blood pressure.
Classification
| Blood pressure classification | Initial blood pressure mm Hg | Followup recommended | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SBP | DBP | |||
| Normal | <120 | and | <80 | Recheck in 2 years |
| Prehypertension | 120-139 | or | 80-99 | Recheck in 1 year |
| Stage 1 Hypertension | 140-159 | or | 90-99 | Confirm within 2 months |
| Stage 2 Hypertension | >160 | or | >100 | "Evaluate or refer to source of care within 1 month. For those with higher pressures (e.g., >180/110 mmHg), evaluate and treat immediately or within 1 week depending on clinical situation and complications." |
Diagnosis
A systematic review by the Rational Clinical Examination has reviewed the research on measuring the blood pressure.[1]
If the diastolic pressure is below 110 mm Hg, it should be confirmed on two addition visits as some patients will have a lower blood pressure on repeat measurements.[2] A larger cuff should be used for obese patients.[3]
21% of patients with untreated borderline hypertension (diastolic pressure between 90 and 104 mm Hg) may have normal blood pressures outside of the doctor's office.[4]
Some patients may have their blood pressure rise by as much as 25 mm Hg due to an alarm reaction upon seeing a doctor.[5]
Elderly patients may have pseudohypertension due to inability of the blood pressure cuff to compress stiff arteries.[6] Pseudohypertension may be detected by Osler's maneuver.[6]
Excluding secondary hypertension
Listening for an abdominal bruit, especially if it is both systolic and diastolic, may help detect underlying renal artery stenosis.[7]
Treatment
Current clinical practice guidelines are based on The Seventh Report of the Joint National Committee on Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Pressure (JNC 7)[8] and the 2007 guidelines by the European Society of Hypertension (ESH) and of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC).[9] Drugs for hypertension have been reviewed by the Medical Letter.[10]
Treatment goals
Per the JNC7 Guidelines:[8]
- "Treating "most patients" SBP and DBP to targets that are <140/90 mmHg is associated with a decrease in cardiovascular complications.
- In patients with hypertension and diabetes or renal disease, the BP goal is <130/80 mmHg.
Initial medication
- "Thiazide-type diuretics for most" patients are recommended by the JNC7 clinical practice guidelines.[8]
- "ß-blockers, especially in combination with a thiazide diuretic, should not be used in patients with the metabolic syndrome or at high risk of incident diabetes" is noted by the European ESH/ESC clinical practice guidelines.[9] The ESH/ESC guidelines cite the LIFE[11] and ASCOT[12] trials. Unlike the ALHAT study, both of these trials were in largely anglo populations, supported by industry, and at the same institution. All patients in the LIFE trial had left ventricular hypertension (LVH). Based on these two trials, a meta-analysis has concluded that beta-blockers should not be the first choice treatment.[13]
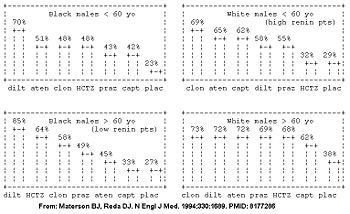
However, the initial drug may be better selected based on the patient's age, race, and gender.[14][15] The patient's demographic roughly corresponds with their renin profile, but is more predictive than the renin profile.[15] The molecular basis is being determined.[16]
In the high renin demographic (young whites), diuretics had similar efficacy to placebo; whereas in the low renin demographic (older blacks), the ace-inhibitors had similar efficacy to placebo in the Masterson Veterans Affairs Cooperative Study Group on Antihypertensive Agents (see figure).[14]
| Category name | demographics | Comments | Best anti-hypertensive categories |
|---|---|---|---|
| High renin demographic | less than 50 years old, anglo | salt-sensitive; diuretic responsive | diuretics, calcium channel blockers |
| Low renin demographic | more than 50 years old, non-anglo* | ace-inhibitors, beta-blockers | |
| * Obesity and female[17] are also associated with low renin. | |||
Several randomized controlled trials have compared initial medications for hypertension.[18][19][20][14]
- In the Second Australian National Blood Pressure study (ANBP2),[19] ace-inhibitors were better in a population that was 95% white with a body-mass index of 27. This demographic has features of both high (age) and low (race) renin status.
- In the ALLHAT study,[18] diuretics were better in a population that was 47% white with a body-mass index of 30.
For patients with Stage 2 Hypertension (SBP >160 or DBP>100 mmHg), start with two drugs.[8]
The race and age demographic may partly predict frequency of drug toxicity to different anti-hypertensive medications.[21]
Resistant hypertension
Clinical practice guidelines from the American Heart Association (AHA) address resistant hypertension.[22] The AHA defines resistant hypertension as "blood pressure that remains above goal in spite of the concurrent use of 3 antihypertensive agents of different classes."
First, 'pseudoresitance' should be considered:[22]
- Medication noncompliance
- White coat hypertension
Next, secondary hypertension should be considered:[22]
- obstructive sleep apnea
- renal artery stenosis
- primary aldosteronism
Lastly, the AHA recommends that one of the three medicines use for hypertension should be a diuretic.[22]
Systolic hypertension
Elderly patients
Treating patients aged 80 years or older for two years who have a systolic pressure over 160 mm hg (the average entry pressure was 173/91 mm Hg) and treating to 150/80 mm Hg may reduce morbidity.[23] In this trial, the average seated blood pressure at the end of the study in the treatment group was 143/78.
See also
Prognosis
References
- ↑ Reeves RA (1995). "The rational clinical examination. Does this patient have hypertension? How to measure blood pressure". JAMA 273 (15): 1211–8. PMID 7707630. [e]
- ↑ Hartley RM, Velez R, Morris RW, D'Souza MF, Heller RF (1983). "Confirming the diagnosis of mild hypertension". Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 286 (6361): 287–9. PMID 6402075. [e] PubMed Central
- ↑ Nielsen PE, Larsen B, Holstein P, Poulsen HL (1983). "Accuracy of auscultatory blood pressure measurements in hypertensive and obese subjects". Hypertension 5 (1): 122–7. PMID 6848459. [e]
- ↑ Pickering TG, James GD, Boddie C, Harshfield GA, Blank S, Laragh JH (1988). "How common is white coat hypertension?". JAMA 259 (2): 225–8. PMID 3336140. [e]
- ↑ Mancia G, Parati G, Pomidossi G, Grassi G, Casadei R, Zanchetti A (1987). "Alerting reaction and rise in blood pressure during measurement by physician and nurse". Hypertension 9 (2): 209–15. PMID 3818018. [e]
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Messerli FH, Ventura HO, Amodeo C (1985). "Osler's maneuver and pseudohypertension". N. Engl. J. Med. 312 (24): 1548–51. PMID 4000185. [e]
- ↑ Turnbull JM (1995). "The rational clinical examination. Is listening for abdominal bruits useful in the evaluation of hypertension?". JAMA 274 (16): 1299–301. PMID 7563536. [e]
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 8.2 8.3 Chobanian AV, Bakris GL, Black HR, et al (2003). "The Seventh Report of the Joint National Committee on Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Pressure: the JNC 7 report". JAMA 289 (19): 2560-72. DOI:10.1001/jama.289.19.2560. PMID 12748199. Research Blogging. http://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/guidelines/hypertension/jnc7full.pdf
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 Mancia G, De Backer G, Dominiczak A, et al (June 2007). "2007 Guidelines for the management of arterial hypertension: The Task Force for the Management of Arterial Hypertension of the European Society of Hypertension (ESH) and of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC)". Eur. Heart J. 28 (12): 1462–536. DOI:10.1093/eurheartj/ehm236. PMID 17562668. Research Blogging.
- ↑ (June 2005) "Drugs for hypertension". Treat Guidel Med Lett 3 (34): 39–48. PMID 15912125. [e]
- ↑ Dahlöf B, Devereux RB, Kjeldsen SE, et al (March 2002). "Cardiovascular morbidity and mortality in the Losartan Intervention For Endpoint reduction in hypertension study (LIFE): a randomised trial against atenolol". Lancet 359 (9311): 995–1003. DOI:10.1016/S0140-6736(02)08089-3. PMID 11937178. Research Blogging.
- ↑ Dahlöf B, Sever PS, Poulter NR, et al (2005). "Prevention of cardiovascular events with an antihypertensive regimen of amlodipine adding perindopril as required versus atenolol adding bendroflumethiazide as required, in the Anglo-Scandinavian Cardiac Outcomes Trial-Blood Pressure Lowering Arm (ASCOT-BPLA): a multicentre randomised controlled trial". Lancet 366 (9489): 895–906. DOI:10.1016/S0140-6736(05)67185-1. PMID 16154016. Research Blogging.
- ↑ Lindholm LH, Carlberg B, Samuelsson O (2005). "Should beta blockers remain first choice in the treatment of primary hypertension? A meta-analysis". Lancet 366 (9496): 1545–53. DOI:10.1016/S0140-6736(05)67573-3. PMID 16257341. Research Blogging. ACP Journal Club review
- ↑ 14.0 14.1 14.2 14.3 Materson BJ, Reda DJ (1994). "Correction: single-drug therapy for hypertension in men". N. Engl. J. Med. 330 (23): 1689. PMID 8177286. [e]
Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; name "pmid8177286" defined multiple times with different content - ↑ 15.0 15.1 Preston RA, Materson BJ, Reda DJ, et al (1998). "Age-race subgroup compared with renin profile as predictors of blood pressure response to antihypertensive therapy. Department of Veterans Affairs Cooperative Study Group on Antihypertensive Agents". JAMA 280 (13): 1168–72. PMID 9777817. [e]
- ↑ Materson BJ (2007). "Variability in response to antihypertensive drugs". Am. J. Med. 120 (4 Suppl 1): S10–20. DOI:10.1016/j.amjmed.2007.02.003. PMID 17403377. Research Blogging.
- ↑ Cowley AW, Skelton MM, Velasquez MT (1985). "Sex differences in the endocrine predictors of essential hypertension. Vasopressin versus renin". Hypertension 7 (3 Pt 2): I151–60. PMID 3888837. [e]
- ↑ 18.0 18.1 ALLHAT Officers and Coordinators for the ALLHAT Collaborative Research Group. The Antihypertensive and Lipid-Lowering Treatment to Prevent Heart Attack Trial (2002). "Major outcomes in high-risk hypertensive patients randomized to angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor or calcium channel blocker vs diuretic: The Antihypertensive and Lipid-Lowering Treatment to Prevent Heart Attack Trial (ALLHAT)". JAMA 288 (23): 2981-97. PMID 12479763. [e]
- ↑ 19.0 19.1 Wing LM, Reid CM, Ryan P, et al (2003). "A comparison of outcomes with angiotensin-converting--enzyme inhibitors and diuretics for hypertension in the elderly". N. Engl. J. Med. 348 (7): 583-92. DOI:10.1056/NEJMoa021716. PMID 12584366. Research Blogging.
- ↑ Materson BJ, Reda DJ, Cushman WC, et al (1993). "Single-drug therapy for hypertension in men. A comparison of six antihypertensive agents with placebo. The Department of Veterans Affairs Cooperative Study Group on Antihypertensive Agents". N. Engl. J. Med. 328 (13): 914-21. PMID 8446138. [e]
- ↑ McDowell SE, Coleman JJ, Ferner RE (2006). "Systematic review and meta-analysis of ethnic differences in risks of adverse reactions to drugs used in cardiovascular medicine". BMJ 332 (7551): 1177–81. DOI:10.1136/bmj.38803.528113.55. PMID 16679330. Research Blogging.
- ↑ 22.0 22.1 22.2 22.3 Calhoun, D. A., Jones, D., Textor, S., Goff, D. C., Murphy, T. P., Toto, R. D., et al. (2008). Resistant Hypertension: Diagnosis, Evaluation, and Treatment. A Scientific Statement From the American Heart Association Professional Education Committee of the Council for High Blood Pressure Research. Hypertension, HYPERTENSIONAHA.108.189141. DOI:10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.108.189141.
- ↑ Beckett, N. S., Peters, R., Fletcher, A. E., Staessen, J. A., Liu, L., Dumitrascu, D., et al. (2008). Treatment of Hypertension in Patients 80 Years of Age or Older. N Engl J Med, NEJMoa0801369. DOI:10.1056/NEJMoa0801369