Harmonic oscillator (classical): Difference between revisions
imported>Paul Wormer No edit summary |
imported>Mark Widmer (Intro: Changed reason for decay to air drag (was "friction of the atoms in the spring")) |
||
| (14 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{subpages}} | |||
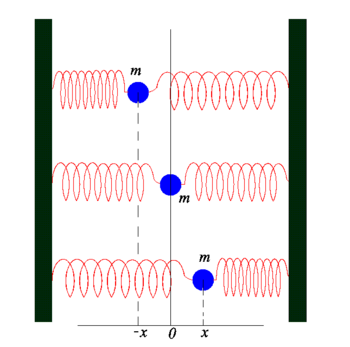
In [[ | {{Image|Springs.png|right|350px|Harmonic oscillator: mass ''m'' oscillates between −''x'' and ''x''. Equilibrium at ''x'' <nowiki>= 0 </nowiki>.}} | ||
The uppermost mass ''m'' feels a force acting to the right equal to '' | In [[physics]], a '''harmonic oscillator''' appears frequently as a simple model for many different types of phenomena. The simplest physical realization of a harmonic oscillator consists of a mass ''m'' on which a force acts that is linear in a displacement from equilibrium. By [[Hooke's law]] a spring gives a force that is linear for small displacements and hence figure 1 shows a simple realization of a harmonic oscillator. | ||
The uppermost mass ''m'' feels a force acting to the right equal to ''k x'', where ''k'' is Hooke's spring constant (a positive number). The mass in the middle is in equilibrium, and the mass at the bottom feels a force to the left equal to −''k x''. The force executed by the springs always acts so as to restore the mass back toward its equilibrium position. If the mass is pulled out of equilibrium to ''x'' = ''A'' and then let go, the mass will (in an ideal setup) oscillate forever between ±''A''. In practice, energy will be lost due to air drag, so that the oscillation will die out after some time. | |||
==Mathematical description== | ==Mathematical description== | ||
The motion of the mass as a function of time ''t'' may be obtained from [[Newton]]'s second law | The motion of the mass (the blue ball in figure 1) as a function of time ''t'' may be obtained from [[Newton]]'s second law | ||
( | (''F'' = ''ma''). Bringing the force ''F'' and the acceleration ''a'' (times mass ''m'') to the same side of Newton's equation, the ''harmonic oscillator equation'' becomes the following equation on the left: | ||
:<math> | :<math> | ||
m\ddot{x} + | m\ddot{x} + k x = 0\;\Longrightarrow\; | ||
\ddot{x} = -\frac{ | \ddot{x} = -\frac{k}{m} x\quad\hbox{with}\quad \ddot{x} \equiv \frac{d^2 x}{dt^2}. | ||
</math> | </math> | ||
We see that the second derivative of ''x'' is proportional to −''x''. There are several functions known to have this property (sine, cosine, exponent with imaginary argument), we choose fairly arbitrarily the cosine as a trial function. The equation is a second order ordinary [[differential equation]] and its general solution contains two integration constants. Further the unit of time is undetermined and hence we scale time by a real number ω. In total the trial function is | We see that the second derivative of ''x'' is proportional to −''x''. There are several functions known to have this property (sine, cosine, exponent with imaginary argument), we choose fairly arbitrarily the cosine as a trial function. The oscillator equation is a second order ordinary [[differential equation]] and its general solution contains two integration constants. Further the unit of time is undetermined and hence we scale time by a real number ω. In total the trial function is | ||
:<math> | :<math> | ||
x(t) = A \cos(\omega t +\phi)\;, | x(t) = A \cos(\omega t +\phi)\;, | ||
</math> | </math> | ||
where the integration constants are to be determined from the initial conditions. Substitution into the | where the integration constants ''A'' and φ are to be determined from the initial conditions. Substitution into the harmonic oscillator equation gives | ||
:<math> | :<math> | ||
-Am\omega^2 \cos(\omega t +\phi) + | -Am\omega^2 \cos(\omega t +\phi) + k A \cos(\omega t +\phi) = 0\;, | ||
</math> | </math> | ||
which fixes <math>\omega = \sqrt{ | which fixes <math>\omega = \sqrt{k/m}</math>. The quantity ω, called ''angular frequency'', has dimension of frequency (1/time) and is often written as ω = 2''π'' ''ν'', where ''&nu''; is the ''frequency'' (number of oscillation cycles per second). The time ''T'' ≡ 1/''ν'' is called the ''period'' of the cycle (duration of one cycle), | ||
<table border="2" align="center" rules="all" cellpadding="10%"> | |||
where ν is the frequency | <tr><td><math>T = \frac{1}{\nu} = \frac{2\pi}{\omega} = 2\pi \sqrt{\frac{m}{k}}</math> | ||
</tr> | |||
</table> | |||
As stated, the [[amplitude]] ''A'' and the [[phase angle]] φ are integration constants. Often it is possible to choose the zero of time such that ω''t'' + φ = 0, implying that φ is zero: | |||
:<math> | :<math> | ||
x(t) = A \cos(\sqrt{\frac{ | x(t) = A \cos(\sqrt{\frac{k}{m}} t )= A \cos\omega t. | ||
</math> | </math> | ||
The amplitude ''A'' is determined by how far we move initially (at ''t'' = 0) the mass (in figure 1) away from equilibrium | The amplitude ''A'' is determined by how far we move initially (at ''t'' = 0) the mass (in figure 1) away from equilibrium | ||
:<math> x(0) = A\; </math> . | :<math> x(0) = A\; </math> . | ||
The value of ''x'' is maximum (mass in point ''x'' = ''A'' in figure 1) for multiples of full periods, | |||
:<math> | :<math> | ||
t_\mathrm{max} = 0,\;T,\; \ldots,\; n\,T,\;\ldots \qquad\hbox{with}\quad n = 0,1,2, \ldots | |||
</math> | </math> | ||
It takes time ''T'' for a full cycle, i.e., for a round trip of the mass from ''A'' back to ''A''. | |||
From the form of the [[cosine]] function we know that ''x'' goes through zero (mass in equilibrium ''x'' = 0 in figure 1) at the following points in time: | |||
:<math> | :<math> | ||
t_0 = \frac{1}{4}\,T,\; \frac{3}{4}\,T,\;\ldots,\; \frac{(2n+1)}{4}\,T,\; \ldots \qquad\hbox{with}\quad n = 0,1,2, \ldots | |||
</math> | </math> | ||
The | The displacement is minimum (mass in point ''x'' = −''A'' in figure 1, i.e., furthest to the left) for multiples of half period ''T''/2, | ||
:<math> | :<math> | ||
t_\mathrm{ | t_\mathrm{min} = \frac{1}{2}\,T,\;\frac{3}{2}\,T,\; \dots,\; \frac{(2n+1)}{2}\,T,\; \ldots \qquad\hbox{with}\quad n = 0,1,2, \ldots | ||
</math> | </math> | ||
The speed of the mass is the first derivative of position with respect to time, | |||
:<math> | :<math> | ||
\dot{x}(t) = - A\omega\sin\omega t | \dot{x}(t) = - A\omega\sin\omega t | ||
</math>, | </math>, | ||
which for the specific values of time | which for the specific values of time becomes | ||
:<math> | :<math> | ||
\begin{align} | \begin{align} | ||
\dot{x}(t_0) &= \pm A\omega && (\hbox{maximum speed})\\ | \dot{x}(t_0) &= \pm A\omega && (\hbox{maximum speed})\\ | ||
\dot{x}(t_\mathrm{min}) &= \dot{x}(t_\mathrm{max}) = 0 | \dot{x}(t_\mathrm{min}) &= \dot{x}(t_\mathrm{max}) = 0 &&\hbox{(turning points)}\\ | ||
\end{align} | \end{align} | ||
</math> | </math> | ||
Physically, after the mass is displaced from equilibrium a distance ''A'' to the right, the restoring force '' | Physically, after the mass is displaced from equilibrium over a distance ''A'' to the right, the restoring force −''kx'' pushes the mass back toward its equilibrium position, causing it to accelerate to the left. When it reaches equilibrium (''x'' = 0), there is no force acting on it at that instant, but it is moving at maximum speed −''A''ω (to the left), and by Newton's first (inertia) law it persists in its motion moving beyond equilibrium position. Before it is stopped it reaches position −''A'', and by this time there is a force acting on it again, pulling it back toward equilibrium (to the right in figure 1). The direction of the motion is turned around in the points ''x'' = ±''A'', which is why these are called ''turning points''. | ||
The whole process, known as simple harmonic motion, repeats itself endlessly with | The whole process, known as simple ''harmonic motion'', repeats itself endlessly with a period given by ''T'' = 2π √''m''/''k''. This relation means that the stiffer the springs (i.e., the larger ''k''), the shorter the period (the faster the oscillations). Making the mass ''m'' greater has exactly the opposite effect, slowing the motion down. | ||
One of the most important features of harmonic motion is the fact that the frequency | One of the most important features of harmonic motion is the fact that the frequency (ω, ν) and duration (''T'') of a cycle depend only on the mass ''m'' and the stiffness ''k'' of the spring. That is, ''m'' and ''k'' only affect the argument of the cosine, but not the amplitude ''A''. If the amplitude is increased, the mass moves faster, but the argument of the cosine remains the same. This invariance of frequency is used in timekeeping and in musical string instruments (the pitch does not depend on the amplitude of the string). | ||
==Harmonic potential== | ==Harmonic potential== | ||
From [[classical mechanics]] it is known that the potential energy is minus the force integrated over distance: | |||
:<math> | |||
V(x)-V(x_0) = \int_{x_0}^{x} \; ky\;\mathrm{d}y = \frac{1}{2}k x^2 - \frac{1}{2}k x_0^2, | |||
</math> | |||
where the zero of the potential is at the arbitrary point ''x''<sub>0</sub> (the lower limit of the integral). Upon choosing ''x''<sub>0</sub> = 0, we find ''V''(''x''<sub>0</sub>) = 0, so that ''V''(''x'') = (''k''/2)''x''<sup>2</sup>. | |||
Introducing a minor generalization, we shift the origin on the ''x''-axis from 0 to the arbitrary point ''x''<sub>0</sub>, i.e. we make the substitution ''x'' → ''x''−''x''<sub>0</sub>. Then the ''harmonic potential'' becomes the following quadratic function in the displacement ''x'' − ''x''<sub>0</sub>, | |||
:<math> | |||
V(x-x_0) = \frac{1}{2} k (x-x_0)^2. | |||
</math> | |||
It is of interest to show the connection with the [[Taylor series|Taylor expansion]] of an arbitrary potential around ''x''<sub>0</sub> | |||
:<math> | |||
V(x-x_0) = V(x_0)\; +\; (x-x_0)\;\left[\frac{d V(x)}{dx}\right]_{x_0}\; +\; \frac{1}{2}\;(x-x_0)^2\; \left[\frac{d^2 V(x)}{dx^2}\right]_{x_0}\; + \cdots | |||
</math> | |||
The expansion is truncated after these three terms. Take ''V''(''x''<sub>0</sub>) as zero of potential and assume that ''x''<sub>0</sub> is a [[stationary point]] of the potential, i.e., that the potential at ''x''<sub>0</sub> has a minimum, a maximum, or a point of inflection (saddle point). This means that we assume that | |||
:<math> | |||
\left[\frac{d V(x)}{dx}\right]_{x_0} = 0. | |||
</math> | |||
Then the truncated Taylor series shrinks to | |||
:<math> | |||
V(x-x_0) = \frac{1}{2}\; (x-x_0)^2\; \left[\frac{d^2 V(x)}{dx^2}\right]_{x_0}. | |||
</math> | |||
If Hooke's (spring) constant is identified thus: | |||
:<math> | |||
k = \left[\frac{d^2 V(x)}{dx^2}\right]_{x_0}, | |||
</math> | |||
we have found the harmonic potential from the truncated Taylor series. Note that since ''k'' > 0, the potential has a minimum at ''x''<sub>0</sub> (the stationary point is a minimum). It is exactly by his truncated Taylor expansion of the potential near a minimum that the harmonic oscillator enters many physical problems. | |||
The derivation went from the force to the potential by integrating over distance. Conversely, given a potential ''V'', it is known from [[classical mechanics]] that the corresponding force ''F'' is minus the derivative <i>V</i>', | |||
:<math> | |||
F = -V' = - (x-x_0)\;\left[\frac{dV(x)}{dx}\right]_{x_0} = - (x-x_0)\; k. | |||
</math> | |||
So, one could say that [[Hooke's law]] (force linear in displacement) is proved by use of a truncated Taylor expansion. | |||
==Energy== | |||
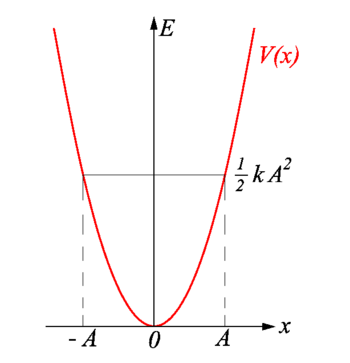
{{Image|Harmonic field.png|right|350px|''E''-''x'' diagram. Vertical axis energy; horizontal axis displacement ''x''. The potential energy ''V''(''x'')<nowiki> =</nowiki> ½ ''kx''<sup>2</sup> is shown in red.}} | |||
The oscillating mass has kinetic plus potential [[energy]]: | |||
:<math> | |||
E = \frac{1}{2} m \dot{x}^2 + \frac{1}{2} k x^2, \quad\hbox{with}\quad x=x(t). | |||
</math> | |||
Above it was shown that | |||
:<math> | |||
x(t) = A\cos\omega t\quad \hbox{and}\quad \dot{x}(t) = -A\omega \sin\omega t | |||
</math> | |||
so that | |||
:<math> | |||
\begin{align} | |||
E &= \frac{A^2}{2} \left( m\omega^2 (\sin\omega t)^2 + k (\cos \omega t)^2 \right) \\ | |||
&= \frac{A^2}{2} \left( m \Big(\frac{k}{m}\Big) (\sin\omega t)^2 + k (\cos \omega t)^2 \right) \\ | |||
&= \frac{k A^2}{2} | |||
\end{align} | |||
</math> | |||
where it was used that ω<sup>2</sup> = ''k''/''m'' and cos<sup>2</sup> + sin<sup>2</sup> = 1. Hence, the total energy of the harmonic oscillator is constant (independent of time). It is quadratic in the amplitude ''A'' and proportional to the spring constant ''k''. The stiffer the string the more energy. | |||
'''( | During the oscillation the energy is converted from potential energy to kinetic energy and back. | ||
Consider the turning point ''x'' = ''A''. Above it was shown that the velocity at the turning points is zero. Hence all energy ½''k A''<sup>2</sup> is potential energy at these points. The mass travels to the left and picks up speed and therewith kinetic energy. At the equilibrium point ''x'' = 0 the potential energy ''V''(''x'') = 0, all energy ½''k A''<sup>2</sup> is turned into kinetic energy. Moving beyond ''x'' = 0 the mass loses speed and comes to a momentary standstill at the left turning point ''x'' = −''A'', where again all energy is converted into potential energy. | |||
Latest revision as of 11:17, 11 September 2021
In physics, a harmonic oscillator appears frequently as a simple model for many different types of phenomena. The simplest physical realization of a harmonic oscillator consists of a mass m on which a force acts that is linear in a displacement from equilibrium. By Hooke's law a spring gives a force that is linear for small displacements and hence figure 1 shows a simple realization of a harmonic oscillator. The uppermost mass m feels a force acting to the right equal to k x, where k is Hooke's spring constant (a positive number). The mass in the middle is in equilibrium, and the mass at the bottom feels a force to the left equal to −k x. The force executed by the springs always acts so as to restore the mass back toward its equilibrium position. If the mass is pulled out of equilibrium to x = A and then let go, the mass will (in an ideal setup) oscillate forever between ±A. In practice, energy will be lost due to air drag, so that the oscillation will die out after some time.
Mathematical description
The motion of the mass (the blue ball in figure 1) as a function of time t may be obtained from Newton's second law (F = ma). Bringing the force F and the acceleration a (times mass m) to the same side of Newton's equation, the harmonic oscillator equation becomes the following equation on the left:
We see that the second derivative of x is proportional to −x. There are several functions known to have this property (sine, cosine, exponent with imaginary argument), we choose fairly arbitrarily the cosine as a trial function. The oscillator equation is a second order ordinary differential equation and its general solution contains two integration constants. Further the unit of time is undetermined and hence we scale time by a real number ω. In total the trial function is
where the integration constants A and φ are to be determined from the initial conditions. Substitution into the harmonic oscillator equation gives
which fixes . The quantity ω, called angular frequency, has dimension of frequency (1/time) and is often written as ω = 2π ν, where ν is the frequency (number of oscillation cycles per second). The time T ≡ 1/ν is called the period of the cycle (duration of one cycle),
As stated, the amplitude A and the phase angle φ are integration constants. Often it is possible to choose the zero of time such that ωt + φ = 0, implying that φ is zero:
The amplitude A is determined by how far we move initially (at t = 0) the mass (in figure 1) away from equilibrium
- .
The value of x is maximum (mass in point x = A in figure 1) for multiples of full periods,
It takes time T for a full cycle, i.e., for a round trip of the mass from A back to A.
From the form of the cosine function we know that x goes through zero (mass in equilibrium x = 0 in figure 1) at the following points in time:
The displacement is minimum (mass in point x = −A in figure 1, i.e., furthest to the left) for multiples of half period T/2,
The speed of the mass is the first derivative of position with respect to time,
- ,
which for the specific values of time becomes
Physically, after the mass is displaced from equilibrium over a distance A to the right, the restoring force −kx pushes the mass back toward its equilibrium position, causing it to accelerate to the left. When it reaches equilibrium (x = 0), there is no force acting on it at that instant, but it is moving at maximum speed −Aω (to the left), and by Newton's first (inertia) law it persists in its motion moving beyond equilibrium position. Before it is stopped it reaches position −A, and by this time there is a force acting on it again, pulling it back toward equilibrium (to the right in figure 1). The direction of the motion is turned around in the points x = ±A, which is why these are called turning points.
The whole process, known as simple harmonic motion, repeats itself endlessly with a period given by T = 2π √m/k. This relation means that the stiffer the springs (i.e., the larger k), the shorter the period (the faster the oscillations). Making the mass m greater has exactly the opposite effect, slowing the motion down.
One of the most important features of harmonic motion is the fact that the frequency (ω, ν) and duration (T) of a cycle depend only on the mass m and the stiffness k of the spring. That is, m and k only affect the argument of the cosine, but not the amplitude A. If the amplitude is increased, the mass moves faster, but the argument of the cosine remains the same. This invariance of frequency is used in timekeeping and in musical string instruments (the pitch does not depend on the amplitude of the string).
Harmonic potential
From classical mechanics it is known that the potential energy is minus the force integrated over distance:
where the zero of the potential is at the arbitrary point x0 (the lower limit of the integral). Upon choosing x0 = 0, we find V(x0) = 0, so that V(x) = (k/2)x2.
Introducing a minor generalization, we shift the origin on the x-axis from 0 to the arbitrary point x0, i.e. we make the substitution x → x−x0. Then the harmonic potential becomes the following quadratic function in the displacement x − x0,
It is of interest to show the connection with the Taylor expansion of an arbitrary potential around x0
The expansion is truncated after these three terms. Take V(x0) as zero of potential and assume that x0 is a stationary point of the potential, i.e., that the potential at x0 has a minimum, a maximum, or a point of inflection (saddle point). This means that we assume that
Then the truncated Taylor series shrinks to
If Hooke's (spring) constant is identified thus:
we have found the harmonic potential from the truncated Taylor series. Note that since k > 0, the potential has a minimum at x0 (the stationary point is a minimum). It is exactly by his truncated Taylor expansion of the potential near a minimum that the harmonic oscillator enters many physical problems.
The derivation went from the force to the potential by integrating over distance. Conversely, given a potential V, it is known from classical mechanics that the corresponding force F is minus the derivative V',
So, one could say that Hooke's law (force linear in displacement) is proved by use of a truncated Taylor expansion.
Energy
The oscillating mass has kinetic plus potential energy:
Above it was shown that
so that
where it was used that ω2 = k/m and cos2 + sin2 = 1. Hence, the total energy of the harmonic oscillator is constant (independent of time). It is quadratic in the amplitude A and proportional to the spring constant k. The stiffer the string the more energy.
During the oscillation the energy is converted from potential energy to kinetic energy and back. Consider the turning point x = A. Above it was shown that the velocity at the turning points is zero. Hence all energy ½k A2 is potential energy at these points. The mass travels to the left and picks up speed and therewith kinetic energy. At the equilibrium point x = 0 the potential energy V(x) = 0, all energy ½k A2 is turned into kinetic energy. Moving beyond x = 0 the mass loses speed and comes to a momentary standstill at the left turning point x = −A, where again all energy is converted into potential energy.














![{\displaystyle V(x-x_{0})=V(x_{0})\;+\;(x-x_{0})\;\left[{\frac {dV(x)}{dx}}\right]_{x_{0}}\;+\;{\frac {1}{2}}\;(x-x_{0})^{2}\;\left[{\frac {d^{2}V(x)}{dx^{2}}}\right]_{x_{0}}\;+\cdots }](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/900856fec63c441c2de6b00bc6aad5a8565006e7)
![{\displaystyle \left[{\frac {dV(x)}{dx}}\right]_{x_{0}}=0.}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/fc8c1708d52e5198accd21762bcf2d7c38a2f952)
![{\displaystyle V(x-x_{0})={\frac {1}{2}}\;(x-x_{0})^{2}\;\left[{\frac {d^{2}V(x)}{dx^{2}}}\right]_{x_{0}}.}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/010fb4283193f95163e412103d877a004dee77b2)
![{\displaystyle k=\left[{\frac {d^{2}V(x)}{dx^{2}}}\right]_{x_{0}},}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/9482a4fdf23f109babe09a93845d3653eb16d931)
![{\displaystyle F=-V'=-(x-x_{0})\;\left[{\frac {dV(x)}{dx}}\right]_{x_{0}}=-(x-x_{0})\;k.}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/3ae2231c05260a94235862fd2391920ae6783595)