Equation (mathematics): Difference between revisions
imported>Chris Day No edit summary |
imported>Boris Tsirelson (→Differential equations and integral equations: some functional space) |
||
| (8 intermediate revisions by 4 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{subpages}} | {{subpages}} | ||
''' | In [[mathematics]], an '''equation''' is a statement that two quantities are equal. It is usually regarded as a kind of mathematical problem in which you have to find a value which makes the equation true. A simple example is the question: What do you have to fill in on the dots in … + 2 = 3? The answer is 1, because 1 + 2 = 3. The unknown quantity in such problems is frequently denoted by a letter, often ''x'', so that the equation becomes ''x'' + 2 = 3. The solution of this equation is ''x'' = 1. In general, an equation may have no solution, one solution or many solutions. | ||
or | |||
By contrast, an '''identity''' is an equality which is stated to be universally true for all permissible values of the variables, rather than representing a condition on those values. For example, <math>x+y = y+x</math> is an identity for [[real number]]s, since it is true for all real values of ''x'' and ''y''. | |||
[[Science|Scientific]] laws are often formulated as equations, especially in [[physics]] and other [[natural sciences]]. Examples are [[Newton's laws]], the equation of a [[harmonic oscillator]] and the [[Schrödinger equation]]. | |||
The term ''equation'' is used also in [[chemistry]], indicating conservation of atomic or [[isotopic content|isotopic]] content (and rarely other forms of energy, e.g. light) during [[chemical reaction]]s. | |||
==Domain of the unknown== | |||
Technically, an equation has to indicate what values the unknown variable can take. This is called the ''domain'' of the variable. For instance, the equation ''x'' + 1 = 0 has no solutions if ''x'' is supposed to be a [[natural number]], but it does have a solution | |||
(namely, ''x'' = −1) if ''x'' is supposed to be an [[integer|integer number]]. | |||
== | Similarly, the equation <math>x^2=2</math> has no solutions if the domain is formed by the [[rational number]]s, it has two solutions (namely, <math>x=\sqrt{2}</math> and <math>x=-\sqrt{2}</math>) among the [[real number]]s, and it has only one solution | ||
(namely, <math>x=\sqrt{2}</math>) among the [[positive]] real numbers. | |||
Often, the domain is not specified explicitly, but it is assumed that the reader knows what it is supposed to be. | |||
==Inverse function== | |||
(<math>x= | The equation may have the form | ||
:(1) <math>F(x)=0</math> | |||
or | |||
:(2) <math>F(x)=G(x)</math> | |||
where <math> F </math> and <math>G</math> are [[known function]]s and <math>x</math> is the [[unknown variable]]. | |||
Function <math> F </math> in equation (1) ; or functions <math> F </math> and <math> G </math> in equation (2) | Function <math> F </math> in equation (1) ; or functions <math> F </math> and <math> G </math> in equation (2) | ||
may also depend on some [[parameter]](s). In this case, the solution(s) <math> x </math> also may depend on parameter(s). | may also depend on some [[parameter]](s). In this case, the solution(s) <math> x </math> also may depend on parameter(s). | ||
| Line 35: | Line 30: | ||
<math>F_b(x)</math>, <math>G_b(x)</math>. | <math>F_b(x)</math>, <math>G_b(x)</math>. | ||
In relatively simple | In relatively simple cases, function <math> F </math> depends only on the unknown variable, and <math>G</math> | ||
depends on the parameter; for example, | depends on the parameter; for example, | ||
(3) <math>F(x)=b</math> . | (3) <math>F(x)=b</math> . | ||
In this case, the solution <math>x</math> is considered as [[inverse function]] of <math>b</math>, which can be written as | In this case, the solution <math>x</math> is considered as an [[inverse function]] of <math>b</math>, which can be written as | ||
(4) <math> x=F^{-1}(b)</math>. | (4) <math> x=F^{-1}(b)</math>. | ||
Dependending on the function <math>F</math>, range of values of <math>b</math> and set <math>\mathbf A</math>, there may exist no inverse function, | |||
one inverse function or several inverse functions. | one inverse function or several inverse functions. | ||
==Graphical solution of equations== | ==Graphical solution of equations== | ||
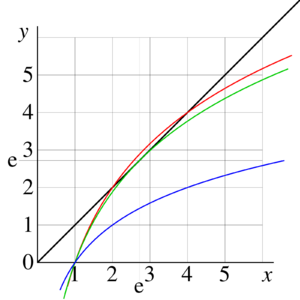
{{Image|ExampleEquationLog01.png|right|300px|Fig.1. Example of graphic solution of equation <math>x=\log_b(x)</math> for | |||
<math>b=\sqrt{2}</math> (two solutions, <math>x=2</math> and <math>x=4</math>), | <math>b=\sqrt{2}</math> (two solutions, <math>x=2</math> and <math>x=4</math>), | ||
<math>b=\exp(1/\rm e)</math> (one solution <math>x=\rm e</math>), and | <math>b=\exp(1/\rm e)</math> (one solution <math>x=\rm e</math>), and | ||
<math>b=2</math> (no real solutions). | <math>b=2</math> (no real solutions).}} | ||
Solving equations, it may worth to begin with [[graphic solution]] of the equation, which allows the [[quick and dirty]] estimates. One plots both functions, | Solving equations, it may worth to begin with [[graphic solution]] of the equation, which allows the [[quick and dirty]] estimates. One plots both functions, | ||
<math>F</math> and <math>G</math> at the same graphic, and watch the point (s) of the intersection of the curves. In | <math>F</math> and <math>G</math> at the same graphic, and watch the point (s) of the intersection of the curves. In figure 1, functions | ||
<math>y=F(x)=x</math> is plotted with black line, | <math>y=F(x)=x</math> is plotted with black line, | ||
and function <math>y=G(x)=\log_{\sqrt{2}}(x)</math> is plotted with red curve. The intersections with black curve indicate values of <math>x</math> which are solutions. | and function <math>y=G(x)=\log_{\sqrt{2}}(x)</math> is plotted with red curve. The intersections with black curve indicate values of <math>x</math> which are solutions. | ||
| Line 64: | Line 59: | ||
==System of equations== | ==System of equations== | ||
In the equations (1) or (2), <math> x </math> may denote several numbers at once, <math>x=\{x_0,x_2,.. x_{n-1}\}</math>; and | In the equations (1) or (2), <math> x </math> may denote several numbers at once, <math>x=\{x_0,x_2,.. x_{n-1}\}</math>; and | ||
functions <math>F</math> and <math>G</math> may return values from | functions <math>F</math> and <math>G</math> may return values from multidimensional space <math>\{F_0,F_1,F_2,..F_{m-1} \}</math>. | ||
In this case, one says that there is [[system of equations]]. For example, there is well developed theory of systems of [[linear equations]], while unknown variables <math>x</math> are [[real number|real]] or [[complex number|complex]] numbers. | In this case, one says that there is [[system of equations]]. For example, there is well developed theory of systems of [[linear equations]], while unknown variables <math>x</math> are [[real number|real]] or [[complex number|complex]] numbers. | ||
==[[Differential equation]]s and [[integral equation]]s== | ==[[Differential equation]]s and [[integral equation]]s== | ||
In particular, | In particular, the variable may denote a function of one or several variables, so that the set of possible values is some functional space, usually a [[Banach space|Banach]] or even [[Hilbert space|Hilbert]] space; the function <math> F </math> is then an [[operator]] on this space which may be expressed in terms of derivatives or integrals of the function elements. | ||
function <math> F </math> may be expressed in terms of derivatives or integrals of | In these cases, the equation is called a [[differential equation]] or an [[integral equation]]. | ||
In these cases, the equation is called [[differential equation]] | |||
==[[Operator equation]]s== | ==[[Operator equation]]s== | ||
Equations can be used for objects of any | Equations can be used for objects of any origin, as soon, as the operation of [[equality]] is defined. In particular, in [[Quantum mechanics]], the [[Heisenberg equation]] deals with non-[[commutativity|commuting]] objects ([[operator (quantum mechanics)|operator]]s). | ||
[[Heisenberg equation]] deals with non-commuting objects ([[operator(quantum mechanics)|operator]]s). | |||
Latest revision as of 05:01, 8 December 2009
In mathematics, an equation is a statement that two quantities are equal. It is usually regarded as a kind of mathematical problem in which you have to find a value which makes the equation true. A simple example is the question: What do you have to fill in on the dots in … + 2 = 3? The answer is 1, because 1 + 2 = 3. The unknown quantity in such problems is frequently denoted by a letter, often x, so that the equation becomes x + 2 = 3. The solution of this equation is x = 1. In general, an equation may have no solution, one solution or many solutions.
By contrast, an identity is an equality which is stated to be universally true for all permissible values of the variables, rather than representing a condition on those values. For example, is an identity for real numbers, since it is true for all real values of x and y.
Scientific laws are often formulated as equations, especially in physics and other natural sciences. Examples are Newton's laws, the equation of a harmonic oscillator and the Schrödinger equation. The term equation is used also in chemistry, indicating conservation of atomic or isotopic content (and rarely other forms of energy, e.g. light) during chemical reactions.
Domain of the unknown
Technically, an equation has to indicate what values the unknown variable can take. This is called the domain of the variable. For instance, the equation x + 1 = 0 has no solutions if x is supposed to be a natural number, but it does have a solution (namely, x = −1) if x is supposed to be an integer number.
Similarly, the equation has no solutions if the domain is formed by the rational numbers, it has two solutions (namely, and ) among the real numbers, and it has only one solution (namely, ) among the positive real numbers.
Often, the domain is not specified explicitly, but it is assumed that the reader knows what it is supposed to be.
Inverse function
The equation may have the form
- (1)
or
- (2)
where and are known functions and is the unknown variable.
Function in equation (1) ; or functions and in equation (2) may also depend on some parameter(s). In this case, the solution(s) also may depend on parameter(s). Indicating the function, the parameter, say, , can be specified as a second argument, writing , or as subscript, writing , .
In relatively simple cases, function depends only on the unknown variable, and depends on the parameter; for example,
(3) .
In this case, the solution is considered as an inverse function of , which can be written as
(4) .
Dependending on the function , range of values of and set , there may exist no inverse function, one inverse function or several inverse functions.
Graphical solution of equations
Solving equations, it may worth to begin with graphic solution of the equation, which allows the quick and dirty estimates. One plots both functions, and at the same graphic, and watch the point (s) of the intersection of the curves. In figure 1, functions is plotted with black line, and function is plotted with red curve. The intersections with black curve indicate values of which are solutions.
At the same figure, the cases (only one solution, ) and (no solutions among real numbers) are shown with green and blue curves.
System of equations
In the equations (1) or (2), may denote several numbers at once, ; and functions and may return values from multidimensional space . In this case, one says that there is system of equations. For example, there is well developed theory of systems of linear equations, while unknown variables are real or complex numbers.
Differential equations and integral equations
In particular, the variable may denote a function of one or several variables, so that the set of possible values is some functional space, usually a Banach or even Hilbert space; the function is then an operator on this space which may be expressed in terms of derivatives or integrals of the function elements. In these cases, the equation is called a differential equation or an integral equation.
Operator equations
Equations can be used for objects of any origin, as soon, as the operation of equality is defined. In particular, in Quantum mechanics, the Heisenberg equation deals with non-commuting objects (operators).