Clindamycin: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search

imported>Felipe Gerhard m (added reference section which was missing) |
imported>David E. Volk mNo edit summary |
||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
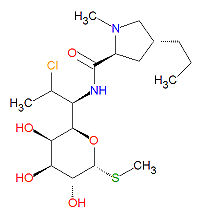
'''Clindamycin''' is an [[antibiotic]] drug, in the [[lincomycin]] class, used to treat infections. It is a semisynthetic version of lincomycin. It is used to treat [[streptococci]], [[pneumococci]] and [[staphylococci]]. | '''Clindamycin''' is an [[antibiotic]] drug, in the [[lincomycin]] class, used to treat infections. It is a semisynthetic version of lincomycin. It is used to treat [[streptococci]], [[pneumococci]] and [[staphylococci]]. | ||
Revision as of 16:37, 5 April 2009
Clindamycin is an antibiotic drug, in the lincomycin class, used to treat infections. It is a semisynthetic version of lincomycin. It is used to treat streptococci, pneumococci and staphylococci.