Cephalosporin: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search

imported>David E. Volk mNo edit summary |
imported>David E. Volk mNo edit summary |
||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
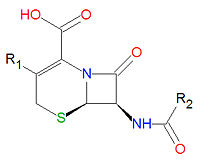
'''Cephalosporins''' are a class of [[antibiotic]] compounds sharing a common base structure, 7-aminocephalosporanic acid (7-ACA), that was derived from the first cephalosporin discovered, [[cephalosporin C]]. [[Penicillin]]s are very similar, although they contain a five-membered ring in place of the six-membered ring present in the cephalosporin. The activity of cephalosporins, penicillins, and some other antibiotics are due to the presence of a [[lactam|beta-lactam]], which binds irreversibly, via acylation, to penicillin-binding proteins, thereby inhibiting the peptidogycan layer of bacterial cell wall synthesis. Cephalosporins are often made semisynthetically. Cephalosporins and the very closely related[[cephamycin]]s are collectively referred to as [[cephems]]. | '''Cephalosporins''' are a class of [[antibiotic]] compounds sharing a common base structure, 7-aminocephalosporanic acid (7-ACA), that was derived from the first cephalosporin discovered, [[cephalosporin C]]. [[Penicillin]]s are very similar, although they contain a five-membered ring in place of the six-membered ring present in the cephalosporin. The activity of cephalosporins, penicillins, and some other antibiotics are due to the presence of a [[lactam|beta-lactam]], which binds irreversibly, via acylation, to penicillin-binding proteins, thereby inhibiting the peptidogycan layer of bacterial cell wall synthesis. Cephalosporins are often made semisynthetically. Cephalosporins and the very closely related[[cephamycin]]s are collectively referred to as [[cephems]]. | ||
Revision as of 16:32, 5 April 2009
Cephalosporins are a class of antibiotic compounds sharing a common base structure, 7-aminocephalosporanic acid (7-ACA), that was derived from the first cephalosporin discovered, cephalosporin C. Penicillins are very similar, although they contain a five-membered ring in place of the six-membered ring present in the cephalosporin. The activity of cephalosporins, penicillins, and some other antibiotics are due to the presence of a beta-lactam, which binds irreversibly, via acylation, to penicillin-binding proteins, thereby inhibiting the peptidogycan layer of bacterial cell wall synthesis. Cephalosporins are often made semisynthetically. Cephalosporins and the very closely relatedcephamycins are collectively referred to as cephems.