Cefaclor: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search

imported>David E. Volk m (→External links) |
imported>David E. Volk mNo edit summary |
||
| Line 20: | Line 20: | ||
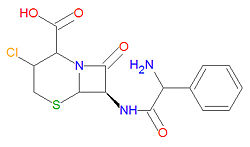
'''Cefaclor''', also spelled as '''cephaclor''', is a semisynthetic broad-spectrum [[antibiotic]] drug used to treat a variety of bacterial infections. It is a second generation [[cephalosporin]] antibiotic with similar activities. It is similar in structure to [[cephalexin]] and is also similar to penicillin-like drugs because it contains a [[beta-lactam]] moiety which binds to and interferes with bacterial cell wall synthesis. It can be used to treat a wide variety of both [[Gram-positive]] and [[Gram-negative]] aerobic bacteria. | '''Cefaclor''', also spelled as '''cephaclor''', is a semisynthetic broad-spectrum [[antibiotic]] drug used to treat a variety of bacterial infections. It is a second generation [[cephalosporin]] antibiotic with similar activities. It is similar in structure to [[cephalexin]] and is also similar to penicillin-like drugs because it contains a [[beta-lactam]] moiety which binds to and interferes with bacterial cell wall synthesis. It can be used to treat a wide variety of both [[Gram-positive]] and [[Gram-negative]] aerobic bacteria. | ||
Revision as of 16:28, 5 April 2009
|
| |||||||
| cefaclor (cephaclor) | |||||||
| |||||||
| Uses: | antibiotic drug | ||||||
| Properties: | beta-lactam | ||||||
| Hazards: | see drug interactions | ||||||
| |||||||
Cefaclor, also spelled as cephaclor, is a semisynthetic broad-spectrum antibiotic drug used to treat a variety of bacterial infections. It is a second generation cephalosporin antibiotic with similar activities. It is similar in structure to cephalexin and is also similar to penicillin-like drugs because it contains a beta-lactam moiety which binds to and interferes with bacterial cell wall synthesis. It can be used to treat a wide variety of both Gram-positive and Gram-negative aerobic bacteria.