Carotene: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search

imported>David E. Volk m (→Beta-caroteine) |
imported>David E. Volk mNo edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{subpages}} | {{subpages}} | ||
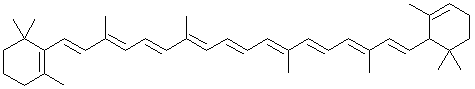
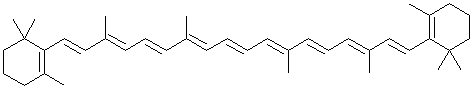
'''Carotenes''', a subgroup of the larger [[carotenoid]] group of chemicals, are hydrophobic, highly unsaturated compounds with a variety of beneficial health effects due to their [[antioxidant]] properties. Both <math>\alpha</math>-carotene and <math>\beta</math>-carotene are chemical precursors of [[vitamin A]]. They are structurally very similar to a number of other carotenoids including [[lutein]], [[zeaxanthin]], [[cryptoxanthin]] and [[lycopene]]. | |||
Latest revision as of 12:01, 28 October 2009
Carotenes, a subgroup of the larger carotenoid group of chemicals, are hydrophobic, highly unsaturated compounds with a variety of beneficial health effects due to their antioxidant properties. Both -carotene and -carotene are chemical precursors of vitamin A. They are structurally very similar to a number of other carotenoids including lutein, zeaxanthin, cryptoxanthin and lycopene.