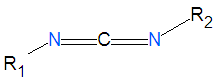
Carbodiimide
|
| |||||||
| carbodiimide | |||||||
| |||||||
| Uses: | dehydration reagent | ||||||
| Properties: | activates carboxylates | ||||||
| Hazards: | |||||||
| |||||||
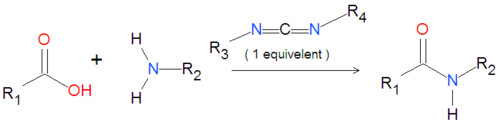
Carbodiimides are a type of dehydrating chemical most often used to activate carboxylic acids for subsequent coupling with primary amines, producing an amide compound. the carboxyl group is often converted to an activated compound by forming an N-hydroxysuccinamide ester or other esters.
A variety of carbodiimides are commonly used, including EDAC, DIC and DCC, illustrated below. EDAC is particularly useful in aqueous reactions and is sold in a variety of biochemical reagent kits designed for coupling proteins to amines, including amines on the surface of quantum dots or nanocrystal.
EDAC
The reagent 1-ethyl-3-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)-carbodiimide, abbreviated as EDAC, EDC or EDCI, is a widely used reagent for coupling water soluble carboxylic acids with water soluble primary amides.