Asparagine: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search

imported>David E. Volk (stub + structure) |
imported>David E. Volk mNo edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{subpages}} | {{subpages}} | ||
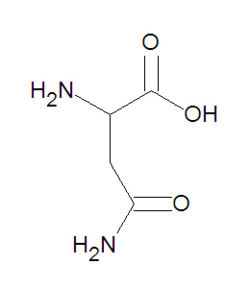
[[Image:Asparagine DEVolk.jpg|right|thumb| | [[Image:Asparagine DEVolk.jpg|right|thumb|250px|{{#ifexist:Template:Asparagine DEVolk.jpg/credit|{{Asparagine DEVolk.jpg/credit}}<br/>|}}Asparagine (ASP, D), a common amino acid.]] | ||
'''Asparagine''', abbreviated either as '''ASP''' or '''D''', is one of the twenty common [[amino acid]]s used by living organisms to build [[protein]]s. It is one of the neutral, polar amino acids. The ''side chain'' of asparagine is the amide group -CH<sub>2</sub>-C(O)-NH<sub>2</sub>. This side chain is capable of forming [[hydrogen bond]]s with other chemical entities that are electron donors. | '''Asparagine''', abbreviated either as '''ASP''' or '''D''', is one of the twenty common [[amino acid]]s used by living organisms to build [[protein]]s. It is one of the neutral, polar amino acids. The ''side chain'' of asparagine is the amide group -CH<sub>2</sub>-C(O)-NH<sub>2</sub>. This side chain is capable of forming [[hydrogen bond]]s with other chemical entities that are electron donors. | ||
Revision as of 13:42, 17 January 2008
Asparagine, abbreviated either as ASP or D, is one of the twenty common amino acids used by living organisms to build proteins. It is one of the neutral, polar amino acids. The side chain of asparagine is the amide group -CH2-C(O)-NH2. This side chain is capable of forming hydrogen bonds with other chemical entities that are electron donors.