Anceps: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search

imported>Thomas Wright Sulcer (created this page) |
imported>David Finn (external link moved to subpage) |
||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
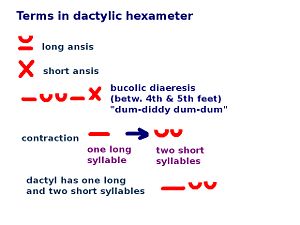
'''Anceps''' is a term in [[epic]] [[poetry]] relating to the [[dactylic hexameter]]. In [[Latin (language)|Latin]], anceps means ''two-headed'', and an anceps is the final syllable in a hexameter verse which can be either long or short. Dactylic hexameter was the most common [[meter (poetry)|meter]] in the poetry of [[Ancient Greece|ancient Greece]] and [[Ancient Rome|Rome]] and was used in the ''[[Iliad]]'' and the ''[[Odyssey]]'' by [[Homer]] and in the ''[[Aeneid]]'' by the Roman poet [[Virgil]]. See diagram. | '''Anceps''' is a term in [[epic]] [[poetry]] relating to the [[dactylic hexameter]]. In [[Latin (language)|Latin]], anceps means ''two-headed'', and an anceps is the final syllable in a hexameter verse which can be either long or short. Dactylic hexameter was the most common [[meter (poetry)|meter]] in the poetry of [[Ancient Greece|ancient Greece]] and [[Ancient Rome|Rome]] and was used in the ''[[Iliad]]'' and the ''[[Odyssey]]'' by [[Homer]] and in the ''[[Aeneid]]'' by the Roman poet [[Virgil]]. See diagram. | ||
[[Image:Terms In Dactylic Hexameter.jpg|thumb|right|300px|alt=Diagram.|Selected terms relating to the dactylic hexameter.]] | [[Image:Terms In Dactylic Hexameter.jpg|thumb|right|300px|alt=Diagram.|Selected terms relating to the dactylic hexameter.]] | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
{{reflist}} | {{reflist}} | ||
Latest revision as of 08:38, 10 December 2011
Anceps is a term in epic poetry relating to the dactylic hexameter. In Latin, anceps means two-headed, and an anceps is the final syllable in a hexameter verse which can be either long or short. Dactylic hexameter was the most common meter in the poetry of ancient Greece and Rome and was used in the Iliad and the Odyssey by Homer and in the Aeneid by the Roman poet Virgil. See diagram.