Lactobacillus acidophilus
For the course duration, the article is closed to outside editing. Of course you can always leave comments on the discussion page. The anticipated date of course completion is May 21, 2009. One month after that date at the latest, this notice shall be removed. Besides, many other Citizendium articles welcome your collaboration! |
| Lactobacillus acidophilus | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | ||||||||||||||
| Scientific classification | ||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||
| Binomial name | ||||||||||||||
| Lactobacillus acidophilus |
Description and significance
Lactobacillus acidophilus is a species of gram-positive bacteria commonly used in dairy production. L. acidophilus is also one of the most common forms of probiotics, which are "friendly bacteria".[1] L. acidophilus is found in the human and animal gut, mouth, and vagina. It functions as a lactic acid producer, by metabolizing lactose to lactic acid. The acid produced by L. acidophilus can control the growth of the fungus Candida albicans, which is the cause of Oral thrush and vaginal yeast infections.[2][3] The acid produced can also prevent unwanted organisms living in the gut. L. acidophilus has been shown to drastically reduce E. coli in cattle.[4] L. acidophilus is commonly used in the production of yogurt, where it is labeled as an active or live culture. People that are lactose intolerant are able to digest dairy products containing L. acidophilus better than dairy products without it.[5] Selected strains of L. acidophilus have shown significant reductions of cholesterol in humans, lowering the risk of coronary heart disease.[6]
Genome structure
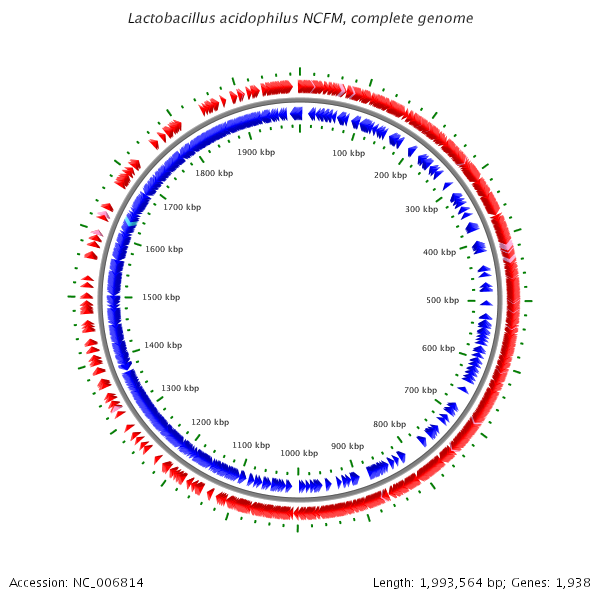
The complete genome of Lactobacillus acidophilus NCFM contains 1,993,564 nucleotides and has no plasmids. Its average GC content is 34.71% and 1,864 ORFs are predicted. 72.5% of the open reading frames (ORFs) are classified as functional. Several proteins which allow L. acidophilus to survive in the gut were identified. These proteins included gene clusters that allow the transport of a diverse group of carbohydrates, including fructooligosaccharides and raffinose. Nine two-component regulatory systems are predicted, which are involved in bacteriocin production and acid tolerance.[7]
Ecology, Cell Structure, and Metabolism
L. acidophilus is rod-shaped and gram-positive. It grows in anaerobic, low pH (<5.0) conditions with an optimal growth temperature of 30°C. It can only perform fermentation. L. acidophilus is homofermentative, meaning that it can only produce lactic acid from fermentation. Because it needs sugar for fermentation, it inhabits environments rich in sugar, such as the human and animal gut. L. acidophilus is non-pathogenic. L. acidophilus keeps the environment in the gut free from harmful organisms by lowering the pH of the environment, and by producing bacteriocins, which attack the harmful bacteria. It is also suggested that L. acidophilus decreases lactose intolerance since it aids in the metabolism of lactose.[8]
Application to Biotechnology
L. acidophilus is frequently used in the production of dairy products, such as yogurt. The added health benefits associated with L. acidophilus allow more yogurt to be bought and consumed, thus affecting the economy in a positive manner. L. acidophilus allows more people to live healthier lives, and allow people with lactose intolerance to enjoy dairy products. L. acidophilus supplements are currently available on the market, in pill and powder form.
Current Research
Functional Analysis of Putative Adhesion Factors in Lactobacillus acidophilus NCFM Lactobacilli are major inhabitants of the normal microflora of the gastrointestinal tract, and some select species have been used extensively as probiotic cultures. One potentially important property of these organisms is their ability to interact with epithelial cells in the intestinal tract, which may promote retention and host-bacterial communication. However, the mechanisms by which they attach to intestinal epithelial cells are unknown. The objective of this study was to investigate cell surface proteins in Lactobacillus acidophilus that may promote attachment to intestinal tissues. Using genome sequence data, predicted open reading frames were searched against known protein and protein motif databases to identify four proteins potentially involved in adhesion to epithelial cells.[9]
Antisecretory Activity of Lactobacillus acidophilus Strain LB Against Nonrotavirus Diarrhea Previous studies have shown that selected strains of Lactobacillus have the capacity to antagonize rotavirus-induced diarrhea. However, only a few reports have documented their efficacy against nonrotavirus diarrhea. This study involved an experimental investigation and a clinical trial of the antisecretory activity of Lactobacillus acidophilus strain LB in the context of nonrotavirus diarrhea.[10]
References
- ↑ http://www.umm.edu/altmed/articles/lactobacillus-acidophilus-000310.htm
- ↑ http://jds.fass.org/cgi/reprint/63/5/830.pdf
- ↑ http://www.ebi.ac.uk/2can/genomes/bacteria/Lactobacillus_acidophilus.html
- ↑ http://ard.unl.edu/rn/0902/ecoli.html
- ↑ http://jds.fass.org/cgi/content/abstract/66/5/959
- ↑ http://www.jacn.org/cgi/reprint/18/1/43.pdf
- ↑ http://www.pnas.org/content/102/11/3906.full.pdf+html
- ↑ http://dwb.unl.edu/Teacher/NSF/C11/C11Links/www.bact.wisc.edu/scienceed/lactobacillusacidophilus.html
- ↑ http://aem.asm.org/cgi/reprint/71/12/8344.pdf
- ↑ http://pediatrics.aappublications.org/cgi/reprint/120/4/e795.pdf
1. Ernest B. Hawkins, MS, BSPharm, RPh and Steven D. Ehrlich, N.M.D. "Lactobacillus acidophilus", University of Maryland Medical Center. [1]
2. Collins, E.B. and Hardt, Pamela. (1980) "Inhibition of Candida albicans by Lactobacillus acidophilus". Journal of Dairy Science Vol. 63, No. 5. [2]
3. European Bioinformatics Institute. "Lactobacillus acidophilus". [3]
4. Miller, Vicki. (2002) "Good bacteria look promising for reducing E. coli". University of Nebraska-Lincoln Agricultural Research Division. [4]
5. Gilliland, Stanley E. and Kim, Hyung Soo. (1983) "Lactobacillus acidophilus as a Dietary Adjunct for Milk to Aid Lactose Digestion in Humans". Journal of Dairy Science Vol. 66 No. 5 [5]
6. Anderson, James W and Gilliland, Stanley E.. (1999) "Effect of Fermented Milk (Yogurt) Containing Lactobacillus Acidophilus L1 on Serum Cholesterol in Hypercholesterolemic Humans". Journal of the American College of Nutrition, Vol. 18, No. 1, 43–50. [6]
7. Altermann, Eric, et al. (2005) "Complete genome sequence of the probiotic lactic acid bacterium Lactobacillus acidophilus NCFM". PNAS Vol. 102, No. 11. [7]
8. Jones, Faro. (1999) "Lactobacillus acidophilus". University of Wisconsin-Madison Department of Bacteriology. [8]
9. Buck, B. Logan, et al. (2005) "Functional Analysis of Putative Adhesion Factors in Lactobacillus acidophilus NCFM". Applied and Environmental Microbiology Vol. 71, No. 12. [9]
10. Lie´vin-Le Moal, Vanessa, et al. (2007) "An Experimental Study and a Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trial to Evaluate the Antisecretory Activity of Lactobacillus acidophilus Strain LB Against Nonrotavirus Diarrhea". PEDIATRICS Volume 120, Number 4. [10]