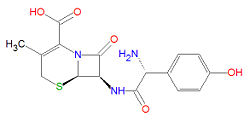
Cefadroxil
|
| |||||||
| cefadroxil | |||||||
| |||||||
| Uses: | antibiotic drug | ||||||
| Properties: | beta-lactam | ||||||
| Hazards: | see drug interactions | ||||||
| |||||||
Cefadroxil is a first-generation cephalosporin antibiotic, is used to treat urinary tract infections, skin infections, pharyngitis, and tonsillitis. The compound is active against bacteria due to the beta-lactam moiety and thus is similar to penicillin.
Mechanism of action
Like all beta-lactam antibiotics, cefadroxil binds to specific penicillin-binding proteins located inside the bacterial cell wall, disrupting the last stage of bacterial cell wall synthesis. Due to the defective bacterial cell walls, cell lysis is induced by the autolytic enzymes autolysins. Cefadroxil may interfere with an autolysin inhibitor.
Chemistry
The IUPAC chemical name for cefacroxil is 7-[[2-amino-2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)acetyl]amino]-3-methyl-8-oxo-5-thia-1-azabicyclo[4.2.0]oct-2-ene-2-carboxylic acid and it has chemical formula C16H17N3O5S, giving it a molecular mass of 363.3883 g/mol. The compound is active against bacteria due to the presence of the beta-lactam moiety. Like other cephalosporins, it is similar to penicillin but contains a six-membered ring rather than the five-membered ring present in penicillins.