Infant growth and development
Growth and development are the main themes of every baby's life. There are very short periods during any stage when a youngster is mainly just getting bigger; but infancy, childhood and adolescence are never focused on a mere increase in size. Instead, growing up transforms the shape, composition, and abilities of the individual. No one word in English that encompasses that concept, and in life sciences, "growth and development" is the conventional term for all the serial changes of the body (and mind) that occur from birth to maturity.
Through them, a newborn becomes a toddler -and then a child, and it is continued growth and development in childhood and through puberty, that usher that child into adulthood. There are two stages in human life when growth and development are most rapid and profound; one is in infancy and early childhood, and the other is during puberty and adolescence. This article examines the early portion of growth and development in the human lifespan, covering the normal progress of a newborn up to the time of walking; about the first year to 18 months of life. The next stage of life is discussed in Toddler growth and development, which will cover the normal child from the time of walking to the socialization of the preschool era; from about age 1 year to age 4 years.
Oddly enough, there is an inherent connection between the very immature state of the newborn brain, a fundamental feature at the starting point of infancy; and the very human act of walking upright, the end point of our discussion here, and the one that marks the beginning of a child's "toddler stage". Human beings, as a species, have a large brain that is capable of a high intelligence, and an upright body position that is propelled by walking on two legs. Walking upright allows for less leeway in size and structure in the human pelvis than exists for those animals that walk on all fours. That means that big-headed babies are born to mothers with relatively constrained birth canals. If both mother and baby are to survive the birth process unscathed, that means the baby's brain cannot be fully developed in size; or complexity; at birth. No matter how precocious we may fancy that our children are, no human baby is precocious as a horse's newborn foal or a duckling just out of the egg- unlike those new babies, that can run and swim within hours of age, humans are unable to do much more than feed and interact with their caregivers until several months of life have passed.
Our newborns have a skull that contains a brain case only one quarter the size that it will become in the adult. "The brain comprises 100 billion neurons at birth, with each neuron developing on average 15,000 synapses by 3 yr of age." reference for quote: Robert D. Needlman: Part 2 – Growth and Development. Chapter 7 – Overview and Assessment of Variability in Behrman: Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics, 17th ed., Copyright © 2004 Much of the growth of the brain; and the concommittent expansion of the head; has occurred by the age of 2 years; at that age the neurocranium (which means the bony skull that surrounds the brain) is 75% of the adult size by volume, and the brain is about 80% of its adult weight. By about 10 years of age, the brain (and skull) are aproximately 95% their ultimate size. Overall, the human brain more than triples in size (3.5 X) from birth to adulthood.
Even with the relatively small head diameter of the newborn, that skull has some adaptations that allow it to be molded in the birth canal, so that the diameter can become even smaller, allowing the baby to emerge without harm to itself or to its mother. These same adaptations give the baby's skull the ability to expand to accomodate the growing brain - they are the suture lines and fontanelles of the infant skull. The suture lines allow the bony plates of the skull to slide a bit, and provide an extra dimension of flexibility for the emergence of the baby's head without damage to the brain. The fontanelles are areas that XXXX.
When babies are brought to the pediatrician or other health care provider for well-child care, the infant's length, weight, and head circumference are routinely measured. The "soft spots" of the skull, the fontanelles, are gently touched and assured to be either properly open or closing, and not unduly tense. The baby is also checked for reflexes and activities that are the signs of normal physical and mental progress. Although the rate of change is a bit different for each individual child, the changes follow a set of curves that are so similar for all children that deviations from the expected values are signs that trouble may be afoot. Since youngsters are so adaptable, and so many problems are now amenable to treatment with early intervention and proper medical care, many things that would have once proved devastating to the baby's future can be averted or minimized with careful monitoring of our infants progress and judicious evaluation of possible abnormalities.
This article reviews the important milestones, and their timing, that unfold during an infant's life. Strictly, the term "infant" only applies to baby during the first year, but since such activities as walking can normally occur either during the first year or after, a broader range of ages is considered here.
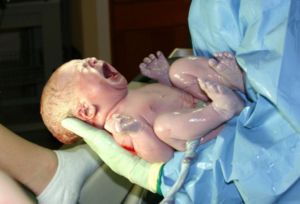
Newborns
A newborn baby has
THE NEWBORN INFANT - Richard D. Bland RUDOLPH'S PEDIATRICS - 21st Ed. (2003)
Normal full term newborn infants
Premature newborns
When babies are born prematurely, they leave the intrauterine environment "too soon". In a sense, there are different dimensions of "too soon", ranging from what appear to be insignificant lengths of time, in which the baby has achieved all the characteristics that are associated, objectively, with a full term infant, all the way to so early that the baby, even with maximal life-support technology, cannot survive.
The concept of "gestational age adjustments"
Gestational age is the amount of time that the baby has developed in the womb, and when full-term, this is a total of about 37 weeks from conception to birth."Infants who are born after completing less than 37 completed weeks of gestation are considered to be preterm (or premature). Term infants have completed 37 to 42 weeks, and infants past 42 weeks of gestation are postterm (or postmature)." 2.8 EXAMINATION OF THE NEWBORN INFANT - Andrew R. Wilkinson, Valerie E. Charlton, Roderic H. Phibbs, Claudine Amiel-Tison Rudolf's Pediatrics
If a baby is born prematurely, say at 33 weeks instead of 37, then the baby's age after birth is adjusted, in the minds of physicians, nurses, and other allied health science caregivers, to reflect that prematurity. The baby born at 33 weeks has an adjusted age of 11 months on his first birthday, at least in terms of of his expected development.
Just how precisely can we judge the gestational age of any newborn? Unless the birth mother had used some accurate means to calculate ovulation at the time of conception, or has had such extremely regular menstrual periods that conception can reliably be assumed to have occured about 14 days before the first missed period, or, for some reason, has had a series of ultrasounds during prenatal care, before about 20 weeks, the gestational age of infants is always an estimated one.
"Small for gestational age" newborns
Not every small baby is a premature baby.
"Large for gestational age" newborns
When the fetus gets enriched nutrition in the womb, the baby may be born "extra-large". Mothers who have high blood glucose (diabetes) during the last trimesters of pregnancy are more likely to have such babies. The size of a newborn is more closely related to the efficiency of the placenta and the nutrients available in the mother's bloodstream, than to the size of the mother and father.
Physical size and growth
Height (length), weight (body mass), and head circumference
Babies are measured after birth because this information not only provides some immediate means for evaluating the infant, but because the measuremenrts serve as a baseline to follow future growth. Length is measured from the tip of the newborns skull (vertex) to her heels, with legs fully stretched out in an extended position. Weight is measured when the baby is wiped off and the umbilical cord has been cut. The head circumference is measured around the head from back to front, above the ears.
The face
Baby faces are different than adult faces, and for good reason. The newborn's forehead is relatively enormous, with the eyes more or less centered mid-height of the face. In an adult, the eyes are about a third of the way down from the top of the face, with the forehead, the midface, and the lower face each making up about a third of the total height.
Teeth, ears and sinuses
Neurologic development
Milestones
smiling
rolling over
sitting up
grasp (thumb and fingers)
crawling
standing up
walking
Changes in the body that come from activities
Body parts are not static structures, they change depending on how they are used. Weight bearing and mechanical forces thicken bone, and so muscles and bone change together as they grow. For example, the mastoid process, which is the thick bump that can be felt behind any adult's ear (down around the region of the upper earlobe), does not exist in the newborn baby, instead the baby's skull is flat behind the ear. A muscle in the neck, the sternocleidomastoid muscle, runs, in part, from this spot on the skull, down to the collar bone and the top of the sternum. As the muscle contracts with the greater force as the baby grows and develops the ability to raise his head and hold it up, the bone actually thickens and the mastoid process developes. Other changes in the body occur with standing and walking. The spine developes what is called "lordosis", the straight backed baby has a different back contour than the walking toddler. The bottom of the feet in the baby who does not stand are "rocker-bottom" shape, and change as the child puts weight on those feet and change still more with walking. In those disabled children who never walk , the feet retain their infant contour.