Lipostatic hypothesis
For the course duration, the article is closed to outside editing. Of course you can always leave comments on the discussion page. The anticipated date of course completion is 01 April 2012. One month after that date at the latest, this notice shall be removed. Besides, many other Citizendium articles welcome your collaboration! |
In 1953, Kennedy [1] proposed what became known as the lipostatic hyothesis. Specifically, he postulated the existence, in the hypothalamus, of a centre that was sensitive to the concentration of metabolites in the circulation, which prevented "an overall surplus of energy intake over expenditure."
Introduction
What is leptin?
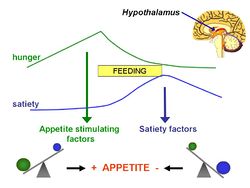
Hypothalamic leptin signaling
Leptin receptor mediated hypothalamic signaling involves multiple pathways. Of these, the Janus tyrosine kinase 2 (JAK2)/cytosolic signal transducer and activator of transcription protein 3 (STAT3) pathway is the best characterized thus far, although the JAK2-Phosphotidylinosital 3 kinase (PI3K) pathway has received some recent attention. With respect to the JAK2/STAT3 pathway, leptin binding to the long form of the leptin receptor (Ob-Rb) initiates tyrosine phosphorylation of Ob-Rb by JAK2. Phosphorylated leptin receptor then recruits STAT3 that is activated through phosphorylation by JAK2. The activated STAT3 proteins dimerize and translocate to the nucleus where they bind DNA and initiate gene transcription. Suppresser of cytokine signaling 3 (SOCS-3) and phosphotyrosine phosphotase 1B (PTP1B) are two known negative regulators of leptin signaling following Ob-Rb activation. The JAK2/STAT3 pathway is believed to be essential for mediating leptin's effects on homeostatic energy regulation.
Parabolis evidence
Conclusion
References
Zhang Y & Scarpace PJ (2006) The role of leptin in leptin resistance and obesity. Physiol Behav. 88, 249-256.