Tetrazole
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
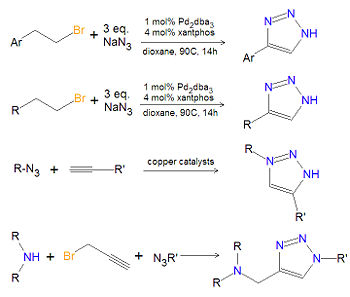
Tetrazoles are cyclic chemical compounds having a base structure (C1N4H2) in which four nitrogen atoms and one carbon atom form a 5-atom heterocycle. They can be synthesized by reacting a cyanide with an azide, as depicted below. The base tetrazole compound (R1 = R2 = H) is commonly used as a base in chemical reactions. Some tetrazoles are angiotensin receptor antagonists used to treat high blood pressure (hypertension).