Fluid flow past a cylinder
Fluid flow past a cylinder is classical mathematical solution for the flow of an inviscid, incompressible fluid around a cylinder that is transverse to the flow. Far from the cylinder, the flow is unidirectional and uniform.
"The flow of an incompressible fluid past a cylinder is one of the first mathematical models that a student of fluid dynamics encounters. This flow is an excellent vehicle for the study of concepts that will be encountered numerous times in mathematical physics, such as vector fields, coordinate transformations, and most important, the physical interpretation of mathematical results." [1]
Mathematical solution
A cylinder (or disk) of radius is placed in two-dimensional, incompressible, inviscid flow. The goal is to find the steady velocity vector and pressure in a plane, subject to the condition that far from the cylinder the velocity vector is
where is a constant, and at the boundary of the cylinder
where is vector normal to the cylinder surface. The upstream flow is uniform and has no vorticity. The flow is inviscid, incompressible and has constant mass density . The flow therefore remains without vorticity, or is said to be irrotational, with everywhere. Being irrotational, there must exist a velocity potential :
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \vec{V}=\nabla\phi}
Being incompressible, Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \nabla\cdot\vec{V}=0} , so Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \phi} must satisify Laplace's equation:
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \nabla^2\phi=0}
The solution for Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \phi} is obtained most easily in polar coordinates Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle r} and Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \theta} , related to conventional Cartesian coordinates by Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle x=r\cos\theta} and Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle y=r\sin\theta} . In polar coordinates, Laplace's equation is:
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \frac{\partial^2\phi}{\partial r^2} + \frac{1}{r}\frac{\partial \phi}{\partial r} + \frac{1}{r^2} \frac{\partial^2\phi}{\partial \theta^2}=0}
The solution that satisfies the boundary conditions is [2]
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \phi(r,\theta)=U\left(r+\frac{R^2}{r}\right)\cos\theta}
The velocity components in polar coordinates are obtained from the components of Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \nabla\phi} in polar coordinates:
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle V_r=\frac{\partial \phi}{\partial r} = U\left(1-\frac{R^2}{r^2}\right)\cos\theta}
and
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle V_\theta=\frac{1}{r}\frac{\partial \phi}{\partial \theta} = - U\left(1+\frac{R^2}{r^2}\right)\sin\theta}
Being invisicid and irrotational, Bernoulli's equation allows the solution for pressure field to be obtained directly form the velocity field:
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle p=\frac{1}{2}\rho\left(U^2-V^2\right) + p_\infty}
where the constants Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle U} and Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle p_\infty} appear so that Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle p\rightarrow p_\infty } far from the cylinder, where Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle V=U} . Using
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle V^2=V_r^2+V_\theta^2} ,
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle p=\frac{1}{2}\rho U^2\left(2\frac{R^2}{r^2}\cos(2\theta)-\frac{R^4}{r^4}\right) + p_\infty }
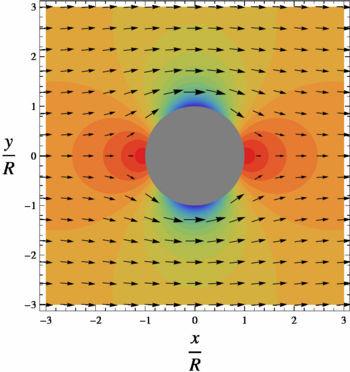
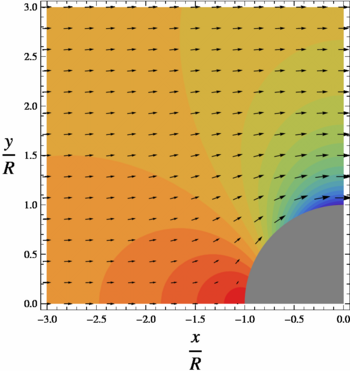
In the figures, the colorized field referred to as "pressure" is a plot of
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle 2 \frac{p - p_\infty}{\rho U^2} =2\frac{R^2}{r^2}\cos(2\theta)-\frac{R^4}{r^4}}
On the surface of the cylinder, or Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle r=R} , pressure varies from a maximum of 1 (red color) at the stagnation points at Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \theta=0} and Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \theta=\pi} to a minimum of -3 (purple) on the sides of the cylinder, at Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \theta=\tfrac{1}{2}\pi} and Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \theta=\tfrac{3}{2}\pi} . Likewise, Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle V} varies from V=0 at the stagnation points to Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle V=2U} on the sides, in the low pressure.
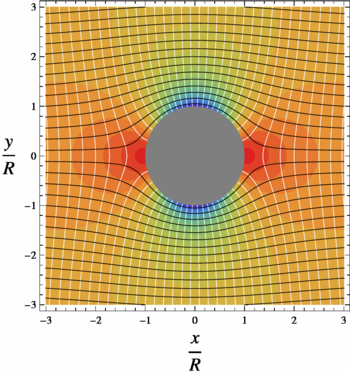
Stream function
The flow being incompressible, a stream function can be found such that
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \vec{V}=\nabla\psi \times \widehat{k}}
It follows from this definition, using vector identities,
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \vec{V}\cdot\nabla{\psi}=0}
Therefore a contour of a constant value of Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \psi} will also be a stream line, a line tangent to Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \vec{V}} . For the flow past a cylinder, we find:
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \psi= U \left( r - \frac{R^2}{r} \right) \cos\theta }
Physical interpretation
Laplace's equation is linear, and is one of the most elementary partial differential equations. This simple equation yields the entire solution for both Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \vec{V}} and Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle p} because of the constraint of irrotation and incompressibility. Having obtained the solution for Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \vec{V}} and Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle p} , the consistency of the pressure gradient with the accelerations can be noted.
The dynamic pressure at the upstream stagnation point has value of , a value needed to decelerate the free stream flow of speed U. This same value appears at the downstream stagnation point, this high pressure is again need to decelerate the flow to zero speed. This symmetry arises only because the flow is completely frictionless.
The low pressure on sides on the cylinder is need to provide the centripetal acceleration of the flow.
where is the radius of curvature of the flow. But , and . The integral of the equation for centripetal acceleration, which will over a distance will thus yield
The exact solution has, for the lowest pressure,
The low pressure, which must be present to provide the centripetal acceleration, will also increase the flow speed as the fluid travels from higher to lower values of pressure. Thus we find the maximum speed in the flow, , in the low pressure on the sides of the cylinder.
A value of is consistent with conservation of the volume of fluid. With the cylinder blocking some of the flow, V must be greater than U somewhere in the plane through the center of the cylinder and transverse to the flow.
Comparison with flow of a real fluid past a cylinder
This symmetry of this ideal solution has the peculiar property of having zero net drag on the cylinder, a property known as D'Alembert's paradox. Unlike an ideal inviscid fluid, a viscous flow past a cylinder, no matter how small the viscosity, will acquire vorticity in a thin boundary layer adjacent to the cylinder. Boundary layer separation can occur, and a trailing wake will occur behind the cylinder. The pressure will be lower on the wake side of the cylinder, than on the upstream side, resulting in a drag force in the downstream direction.
References
- ↑ http://library.wolfram.com/infocenter/Articles/2731/
- ↑ William S. Janna, Introduction to Fluid Mechanics, PWS Publishing Company, Boston (1993)