User:Milton Beychok/Sandbox
Petrochemicals are chemical products made from the hydrocarbons present in raw natural gas and petroleum crude oil. The largest petrochemical manufacturing industries are to be found in the United States, Western Europe, Asia and the Middle East.
A relatively small number of hydyrocarbon feedstocks form the basis of the petrochemical industries, namely methane, ethylene, propylene, butenes, butadiene, benzene, toluene and xylenes.[1][2]
As of 2007, there were 2,980 operating petrochemical plants in 4,320 locations worldwide.[3] The petrochemical end products from those plants include plastics, soaps, detergents, solvents, paints, drugs, fertilizer, pesticides, explosives, synthetic textile fibers and rubbers, flooring and insulating materials and much more. Petrochemicals are found in such common consumer products as aspirin, cars, clothing, compact discs, video tapes, electronic equipment, furniture, and a great many others.[4]
Feedstocks sources
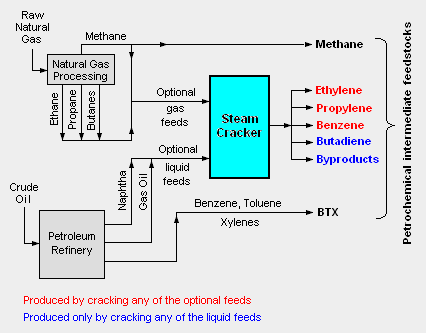
The major hydrocarbon sources used in producing petrochemicals are:[2][5][6]
- Methane, ethane, propane and butanes: Obtained primarily from natural gas processing plants.
- Naphtha obtained from petroleum refineries.
- Benzene, toluene and xylenes, as a whole referred to as BTX and primarily obtained from petroleum refineries.
- Gas oil obtained from petroleum refineries.
Methane and BTX are used directly as feedstocks for producing petrochemicals.
However, the ethane, propane, butanes, naphtha and gas oil serve as optional feedstocks for processing in steam-assisted thermal cracking plants known as steam crackers to produce these intermediate petrochemical feedstocks:
- Ethylene
- Propylene
- Butenes and butadiene
- Benzene
In 2008, the amounts of ethylene and propylene produced in steam crackers were about 125 Mt (megatonnes) and 75 Mt, respectively.
The adjacent diagram depicts the all of the major petrochemical feedstocks.
Feedstocks and example petrochemical products
The table below includes some representative examples of the petrochemical end products produced from the eight hydrocarbon feedstocks – methane, ethylene, propylene, butenes, butadiene, benzene, toluene and xylenes:
| methane | ethylene | propylene | butenes and butadienes | benzene | toluene | xylenes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| hydrogen | polyethylene | polypropylene | styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) | styrene | benzoic acid | phthalic anhydride |
| ammonia | ethanol | isopropanol | methyl tert-butyl ether (MTBE) | polystyrene | toluene diisocyanate | polyesters |
| methanol | ethylene glycol | propylene glycol | polybutadiene | phenol | polyurethanes | dimethyl terephthalate |
| methyl chloride | vinyl acetate | allyl chloride | acrylonitrile-butadiene-styrene (ABS) | cumene | caprolactam | terephthalate acid |
| carbon black | perchloroethylene | acrylonitrile | polybutenes | aniline | nylons | polyethylene terephthalate |
| acetylene | polyvinyl acetate | acrylic acid | methyl ethyl ketone (MEK) | adipic acid | polyureas | dioctyl phthalate |
| formaldehyde | glycol ethers | epoxy resins | tert-butanol | nylons |
References
- ↑ Richard Meyers (2003). The Basics of Chemistry. Greenwood Press. ISBN 0-313-31664-3.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Staff (March 2001). "Petrochemical Processes 2001". Hydrocarbon Processing: pp. 71-246. ISSN 0887-0284.
- ↑ Petrochemical Industry – Worldwide
- ↑ Petrochemicals Chart From the website of the National Petrochemical & Refiners Association
- ↑ SBS Polymer Supply Ooutlook
- ↑ Jean-Pierre Favennec (Editor) (2001). Petroleum Refining: Refinery Operation and Management. Editions Technip. ISBN 2-7108-0801-3.
Miscellaneous notes