Tuberculosis
Overview
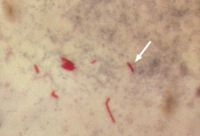
Tuberculosis, also known as "TB" or "consumption", is a multi-system disease caused by the organism Mycobacterium tuberculosis. There are several other species of the genus Mycobacterium that are also human pathogens, but all of these organisms are of much lower virulence than Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Such "minor" species of Mycobacteria, like , cause disease in humans that is called Atypical tuberculosis.
As with individual organisms in any species, including bacteria, there are variations from one to the next. The tubercle bacillus is well known for individual strains that vary, independently, in both virulence and antibiotic resistance.
Epidemiology
Approximately one-third of the world population is infected with TB at any given time, with approximately 2 million TB-related deaths per year worldwide.
People with HIV disease, cancer, malnutrition, chemotherapy, drug or alcohol abuse are especially susceptible to developing active TB. TB rates and deaths are greatest in the developing world, and TB is one of the leading causes of death in people with HIV. In the United States, TB rates increased during the early years of the HIV epidemic, but have since declined, and are in fact the lowest they have been since surveillance began in 1953. However, TB still affects tens of thousands of Americans, and kills several hundred per year.
Microbiology
Natural History
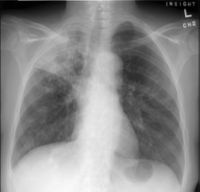
Tuberculosis can affect any organ in the body, but the primary disease is in the lungs. TB is spread by prolonged contact with someone with active pulmonary TB. This most often occurs in household contacts, or in people who work with an infected person in a workplace with poor ventilation.
Latent Tuberculosis
In most people, especially those who have a normal immune system, after becoming infected, the body controls the illness. They have no symptoms, and are not contagious. Signs of illness can be a positive TB test or typical changes on X-rays of the chest. In a small, but significant, percentage of people, latent TB can "reactivate" and make the person ill. Therefore, most people with latent TB are treated to eliminate the infection.
Active Pulmonary Tuberculosis
In some people, the initial infection can make them ill, in others, latent TB reactivates and makes them ill. In pulmonary tuberculosis the usual symptoms are cough for longer than three weeks, bloody sputum, fevers, night sweats, and weight loss. At this stage, the disease is very contagious, and is likely to be fatal if not treated.
Extrapulmonary Tuberculosis
- Laryngeal Tuberculosis
- Pott's Disease
- Tuberculosis Adenitis ("Scrofula")
Treatment
Latent TB is usually treated fairly easily with one to two medications, depending on local resistance patterns. The treatment often lasts up to a year.
Active TB usually requires hospitalization and treatment with multiple medications. Given that the treatment regimen is lengthy and complicated, Directly Observed Therapy (DOT) is often recommended. There have been many legal and ethical issues involving involuntary isolation of non-compliant patients with active TB.
Multi Drug Resistant TB (MDR-TB): Certain geographical areas have seen rises in "MDR-TB". This is especially a problem when patients are intermittently-compliant with their therapy, as the organism develops drug-resistance.
References
- http://www.cdc.gov
- Mandell, Douglas and Bennett's Principles and Practice of Infectious Diseases, Chirchill Livingstone.