Melanocortins and appetite
For the course duration, the article is closed to outside editing. Of course you can always leave comments on the discussion page. The anticipated date of course completion is 01 February 2011. One month after that date at the latest, this notice shall be removed. Besides, many other Citizendium articles welcome your collaboration! |
Melanocortins and appetite
Overview of Pro-opiomelanocortin (POMC)
Pro-opiomelanocortin (POMC) is an important pro-hormone that gives rise to an array of bioactive peptide hormones that are implicated in energy balance, stress responses, pain, immune modulation, satiety, pigmentation and even exocrine gland secretions. It is expressed in the pituitary gland, skin, immune system and brain. In the brain it is expressed in the arcuate nucleus of the hypothalamus (ARH). POMC is post-translationally cleaved by a complex set of enzymes into a variety of hormones (see fig 1).
POMC was first noted for its importance in appetite and obesity in rodent studies. POMC-null mice were seen to exhibit hyperphagia and obesity without insulin resistance. Their adrenal gland was also atrophic and glucocorticoid levels were undetectable as a result of a lack of ACTH stimulating adrenal cell secretion and proliferation. This suggestion that POMC has a role in energy balance was supported by studies on rare individuals with POMC mutations. In humans a lack of POMC is fatal unless glucocorticoids are administered from birth as cortisol is essential for humans. A few rare individuals with the mutation have shown very similar phenotype to the POMC knockout mouse.
While these studies show that POMC-derived hormones may have a role in energy balance they don’t tell us which peptides are responsible for the effects and furthermore the lack of adrenal hormones as a secondary result of POMC lack may overshadow the primary POMC effects. Therefore we are required to look at the peptides in more detail. The main system implicated in energy balance is the MELANOCORTIN SYSTEM.
COULD GO ON ABOUT THE TRIGGERS FOR POMC PRODUCTION:
ENZYMES IN CLEAVAGE
LEPTIN, INSULIN, CCK ETC- I think pretty interesting.
Melanocyte-stimulating hormones and their Receptors
This is made up of several endogenous agonists such as alpha, beta, gamma MSH and interestingly has two endogenous antagonists as well namely the AgRP and agouti. These act on 5 different subtypes of the MCR (MCR1-5). See table…
The Melanocortin Pathway
The control and regulation of feeding involves a complex interplay between a number of circulating hormones, neurotransmitters and nutrients, and the Melanocortin system has been identified as being a central component. The melanocortin system is the name collectively given for;
- Neurons arising in the arcuate nucleus of the hypothalamus, and express AgRP,NPY or POMC.
- POMC neurons that project to the brainstem
- Melanocortin receptors, predominately MC3R and MC4R that respond to POMC peptides and AgRP.
In addition to its involevement in regulating energy homeostasis, the Melancortin system plays a role in mediating a number of physiological processes within the body including (3)
Although the Melanocortin system is known to be central to the regulatory mechanisms controlling appetite and satiety, the precise mechanism is not fully understood. Complexity arises from both the direct and indirect effects of a number of compounds including leptin, insulin, glucose, ghrelin, NPY, serotonin, peptide YY and endorphin, all of which act in isolation and in sync to mediate their effects on these POMC neurons.
Below is a table showing the opposing effects that POMC agonists and antagonists have on feeding behaviour.
Agonists Antagonists Reduce food intake Enhance food intake (hyperphagia) Increase energy expenditure Decrease energy expenditure Reduce body weight Increase body weight
This highlights the role of the melanocortin system in regulating energy homeostasis, and why disruption in the genes controlling this system, i.e. genetic mutations of the system, can result in individuals which are hyperphagic and consequentially obese.
A number of mutations of this system have been identified in mice, all of which show a dysregulation in energy homeostasis. Many of the mutations discovered involve excess production of POMC antagonists, so that POMC agonists can’t bind to POMC receptors in order to suppress appetite.
- Excess production of the agouti protein induces its’ antagonistic effects through binding to both the MC1R and MC4R.
- An increase in the expression of AGRP which functions by antagonising receptors MC3R and MC4R. This prevents the potent appetite suppressor alpha MSH from binding.
- A mutation which results in a deficiency in the number of MC4R receptors.
- The insufficient production of POMC derived peptides to bind to these receptors.
Obese individuals have presented with POMC deleterious gene mutations, as well heterozygous mutations in the MC4R receptor.
POMC neurons and their peptides mediate satiety signals, while NPY neurons induce hunger signals with decreased energy expenditure. The median eminence of the arcuate nucleus receives projections from both POMC and NPY neurons, highlighting its role in controlling both energy expenditure as well as hunger/satiety signals. This integration involves both long term signals (leptin from adipose tissue and insulin), as well as acute hunger/satiety signals from the brainstem.
The melancortin Alpha MSH has been identified as one of the most important regulators of energy homeostasis in the hypothalamus, where it induces a state of satiety within an individual through its actions on the MC4R. Additionally, administration of ACTH into certain regions of the hypothalamus has similar effects. Agouti is an antagonist at MC1R and MC4R receptors, while AGRP incurs antagonistic effects through its action on MC3R and MC4R receptors. Due to suppression of the alpha MSH anorectic signal, mutant mice with ectopic expression of these peptides are hyperphagic with an increase in adipose mass, lean mass, hyperinsulinemia and consequentially are clinically obese.
Melanocortins are peptides derived form the common POMC precursor and are determined by tissue specific post translational cleavage. POMC gene expression has been identified in a number of tissues including the pituitary, skin, immune system and hypothalamus, which highlights the many physiological processes that POMC is involved in. Co- expression of POMC and CART occurs in the arcuate, both of which are stimulated by leptin. Peptides produced within neurons of the hypothalamus are involved in appetite regulation, via their action on MC4R. Melanocortin receptors MC3R and MC4R are unique in the sense that have both endogenous agonists and antagonists Obesity can arise as a result of a POMC deficiency as a consequence of these POMC derived peptides which bind to these receptors. Some melancortin receptors have been found on adipocytes (MC4R), suggesting that peripheral detection of these circulating melanocortins may also be involved in regulating energy homeostasis. Expression of these peptides in the anterior pitiutuary, results in the production of ACTH via the cleavage of POMC by the enzyme prohormone convertase1 (PC1). Stimulation of adrenal steroiogenesis then occurs via the action of ACTH on MC2R.
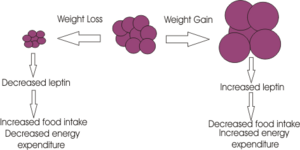
Leptin is produced primarily in white adipose tissue but also to some extent in brown and also to some extent in brown adipose tissue, stomach, placenta, while mopre recent studies have suggested that it may also be produced in the brain. Numerous leptin receptors have been identified, all of which transmit their signal via the JAK-STAT pathway. The leptin receptor involved in regulating appetite is the receptor type Ob-Rb, which is present in many brain regions including ARC, PVN, DMH and LHA of the hypothalamus. Following binding of leptin to the Ob-Rb receptor, the subsequent signalling cascade results in a decrease in appetite through inhibition of the peptides involved in inducing orexigenic effects (NPY, MCY, AGRP and orexins). Additionally the anorexigenic peptides peptides (alpha-MSH, MC4R, CART and CRH) are stimulated. Excess body weight results in excess leptin production from adipose tissue(released in a regular pulsatile manner) and hence leptin can act to restore normal energy homeostasis, by suppressing appetite and increasing energy expenditure through its effect on anorextic peptides. Leptin released form adipose tissue and insulin from the pancreas, also serve to regulate food intake. Excess adipose tissue (i.e. as occurs in obese individuals) results in an increase in leptin production (which normally induces a feeling of satiety), but excess production of NPY peptides (as occurs in some mutations of the melancortin system), can suppress its effects. Similarly insulin levels show a marked increase in obese individuals, with hyperinsuliemia being one of the first metabolic disturbances identified in those obese subjects with mutations of the melanocortin system.
Insulin Following meal ingestion, a dramatic increase in insulin levels is observed, some of which passes through the blood brain barrier in a concentration that is representative of circulating insulin levels. Central administration of insulin has been shown to act on both NPY and POMC systems, and increases POMC mRNA synthesis as well inhibiting food intake in fasting rats. Rats with untreated diabetes have shown to have a diminished amount of POMC mRNA which is indicative of its involvement in stimulating its synthesis.
Ghrelin
Ghrelin stimulates arcuate nucleus production of NPY and AGRP, both of which induce food intake, while simultaneously inhibiting the suppressive effects that leptin induces on appetite. Ghrelin administration in rats has been shown to produce a state of hyperphagia and increased body weight, proportional to the amount of ghrelin given.
The role of the potent appetite stimulant within the melanocortin system has been verified, whereby central administration of this peptide results in excessive eating, but if NPY antagonists are given in conjunction,a state of hyperphagia is not induced. During periods of meal deprivation, Ghrelin levels increase. They induce their potent appetite stimulating properties by activating arcuate NPY and AgRP expression. In contrast, following food consumption, ghrlein levels show a marked decrease.
An example of the complexity that arises in fully understanding the precise mechanism governing this system arises from mice AgRP KO models. Interestingly, while the involvement of AgRP in the melanocortin system is undisputed, one would expect such KO to present with altered phenotypes and eating patterns, yet these AgRP were just like their wild type counterparts. NPY has been identified as one of the most abundant and potent orexigenic peptides of the hypothalamus. While ghrelin ahs short term effects, administration of NPY produces a prolonged and substantial increase in food consumption and a decrease in thermogenesis, resulting in an overall increase in body weight and leading to obesity. NPY exerts its action via G- protein coupled receptors, 5 of which have been identified, of which Y5 has been identified as being involved in meidatign its effect on feeding. Circulating levels of leptin and insulin can regulate NPY synthesis, while glucocorticoids serve to stimulate it. During times of fasting, low levels of insulin and leptin result in the up-regulation of NPY synthesis. Interestingly, an obvious increase in ARC NPY neuronal activity is not recorded in diet induced obese individuals, which suggests that it may be involved in ensuring a certain amount of energy stores, but when this store is in excess, NPY neurons exhibit diminished activity, potentially in an effort to restore normal energy homeostasis.
AGRP- Acts to inhibit the effects of alpha MSH on inducing its anorexigeneic effect through MC1R. AGRP is potent in activating appetite through its anatagonistic activity on both MC3R and MC4R and is expressed only in the ARC region of the hypothalamus, yet all neurons expressing this peptide similarly produce NPY, projecting to various brain sites including PVN and DMH. Leptin inhibits the release of AGRP, while periods of starvation result in an increase in its secretion. Unlike NPY which induces strong, short lived effects on stimulating appetite, AGRP administration can induce a state of hyperphagia for up to one week.
Thus, when energy stores are low, there is reduced leptin released from adipose tissue, which in turn allows in an increase in the production of orexigenic peptides including NPY, AGRP and a decrease in alpha MSH and CART. The opposite is true in times if positive energy imbalance.
Although Peptide YY has been identified as an appetite suppressor, it appears to mediate its effects through a distinct pathway that does not involve the melanocortin system as both POMC and MC4R KO continued to show a decrease in food intake following its administration, indicating that another system may be involved. This further highlights the complexity of the mechanisms controlling energy homeostasis.
Animal models and human examples of defects in the melanocortin system
Experimental evidence and methods used to investigate melanocortin
Suggested future studies
Discussion
Figures and Diagrams
You can also insert diagrams or photographs (to Upload files Cz:Upload)). These must be your own original work - and you will therefore be the copyright holder; of course they may be based on or adapted from diagrams produced by others - in which case this must be declared clearly, and the source of the orinal idea must be cited. When you insert a figure or diagram into your article you will be asked to fill out a form in which you declare that you are the copyright holder and that you are willing to allow your work to be freely used by others - choose the "Release to the Public Domain" option when you come to that page of the form.
When you upload your file, give it a short descriptive name, like "Adipocyte.png". Then, if you type {{Image|Adipocyte.png|right|300px|}} in your article, the image will appear on the right hand side.
Begin your article with a brief overview of the scope of the article on interest group. Include the article name in bold in the first sentence.[1]
Remember you are writing an encyclopedia article; it is meant to be readable by a wide audience, and so you will need to explain some things clearly, without using unneccessary jargon. But you don't need to explain everything - you can link specialist terms to other articles about them - for example adipocyte or leptin simply by enclosing the word in double square brackets.
You can write your article directly onto the wiki- but at first you'll find it easier to write it in Word and copy and paste it onto the wiki.
Construct your article in sections and subsections, with headings and subheadings like this:
References
To insert references and/or footnotes in an article, put the material you want in the reference or footnote between <ref> and </ref>, like this:
<ref>Person A ''et al.''(2010) The perfect reference for subpart 1 ''J Neuroendocrinol'' 36:36-52</ref> <ref>Author A, Author B (2009) Another perfect reference ''J Neuroendocrinol'' 25:262-9</ref>.
Look at the reference list below to see how this will look.[2] [3]
If there are more than two authors just put the first author followed by et al. (Person A at al. (2010) etc.)
Select your references carefully - make sure they are cited accurately, and pay attention to the precise formatting style of the references. Your references should be available on PubMed and so will have a PubMed number. (for example PMID: 17011504) Writing this without the colon, (i.e. just writing PMID 17011504) will automatically insert a link to the abstract on PubMed (see the reference to Johnsone et al. in the list.)
[4]
Use references sparingly; there's no need to reference every single point, and often a good review will cover several points. However sometimes you will need to use the same reference more than once.
How to write the same reference twice:
Reference: Berridge KC (2007) The debate over dopamine’s role in reward: the case for incentive salience. Psychopharmacology 191:391–431 PMID 17072591
First time: <ref name=Berridge07>Berridge KC (2007) The debate over dopamine’s role in reward: the case for incentive salience. ''Psychopharmacology'' 191:391–431 PMID 17072591 </ref>
Second time:<ref name=Berridge07/>
This will appear like this the first time [5] and like this the second time [5]
- ↑ See the "Writing an Encyclopedia Article" handout for more details.
- ↑ Person A et al. (2010) The perfect reference for subpart 1 J Neuroendocrinol 36:36-52
- ↑ Author A, Author B (2009) Another perfect reference J Neuroendocrinol 25:262-9
- ↑ Johnstone LE et al. (2006)Neuronal activation in the hypothalamus and brainstem during feeding in rats Cell Metab 2006 4:313-21. PMID 17011504
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Berridge KC (2007) The debate over dopamine’s role in reward: the case for incentive salience. Psychopharmacology 191:391–431 PMID 17072591