User:Milton Beychok/Sandbox: Difference between revisions
imported>Milton Beychok No edit summary |
imported>Milton Beychok No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
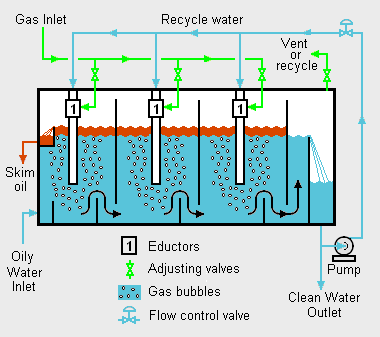
{{Image|Hydraulic IGF.png|right|380px|}} | {{Image|Hydraulic IGF.png|right|380px|}} | ||
'''Induced gas flotation''' (IGF) is a treatment process that clarifies [[wastewater]]s (or other [[water]]s) by the removal of suspended oil. The removal is achieved by introducing very small bubbles of [[air]] or other [[gas]]es into the water or wastewater. The bubbles adhere to the suspended oil | '''Induced gas flotation''' (IGF) is a treatment process that clarifies [[wastewater]]s (or other [[water]]s) by the removal of suspended oil. The removal is achieved by introducing very small bubbles of [[air]] or other [[gas]]es into the water or wastewater. The bubbles adhere to and enhance the [[buoyancy]] of the suspended oil which accelerates the rate at which the oil floats to the surface of the water where it can then be skimmed off for removal (see the adjacent drawing). | ||
A similar process, known as [[dissolved air flotation]] is commonly used in treating the wastewater effluents from [[Petroleum refining processes|oil refineries]], [[petrochemical]] and [[chemical plant]]s, [[Natural gas processing|natural gas processing plants]]. | A similar process, known as [[dissolved air flotation]] is commonly used in treating the wastewater effluents from [[Petroleum refining processes|oil refineries]], [[petrochemical]] and [[chemical plant]]s, [[Natural gas processing|natural gas processing plants]]. | ||
================================== | |||
Revision as of 12:13, 21 March 2011
Induced gas flotation (IGF) is a treatment process that clarifies wastewaters (or other waters) by the removal of suspended oil. The removal is achieved by introducing very small bubbles of air or other gases into the water or wastewater. The bubbles adhere to and enhance the buoyancy of the suspended oil which accelerates the rate at which the oil floats to the surface of the water where it can then be skimmed off for removal (see the adjacent drawing).
A similar process, known as dissolved air flotation is commonly used in treating the wastewater effluents from oil refineries, petrochemical and chemical plants, natural gas processing plants.
======================
"'Froth flotation is commonly used in the processing of mineral ores.
IGF Units in the oil industry do not use air as the flotation medium due to the explosion risk. These IGF Units use natural gas to create the bubbles.
The Educator creates a gas-rich fluid stream of small bubbles