Stem cell: Difference between revisions
imported>Matt Mahlmann m (added wikilinks) |
imported>Subpagination Bot m (Add {{subpages}} and remove any categories (details)) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{subpages}} | |||
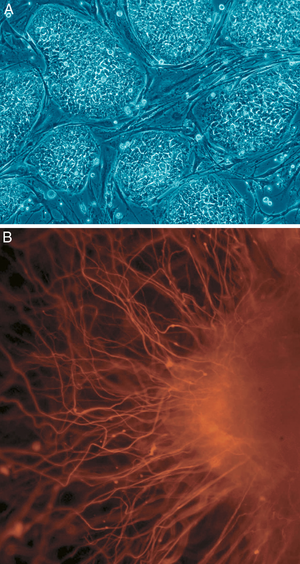
[[Image:Human embryonic stem cells.png|thumb|(A) shows human embryonic stem cells. (B) shows neurons derived from human embryonic stem cells]] | [[Image:Human embryonic stem cells.png|thumb|(A) shows human embryonic stem cells. (B) shows neurons derived from human embryonic stem cells]] | ||
The term "'''stem cell'''" is generally used to describe cells that are [[totipotent]], [[pluripotent]], or [[multipotent]].<ref name=Bioessays>Shostak, Stanley: "(Re)defining stem cells", Bioessays 28(3), March 2006: pages 301 - 308</ref> Totipotent cells have the capacity to differentiate to all cell types, including [[somatic]] cells, [[germ]] cells, and certain cells that exist outside the [[embryo]] and are important to [[fetal development]] that are termed extraembryonic cells. Pluripotent cells may differentiate to cells of most types, and multipotent cells are capable only of differentiating to certain types within a group of cells that perform similar functions. "Stem cell" is also used in reference to any adult cells that are capable of assisting in the restoration of adult tissue via self-renewal.<ref name=Bioessays/> Self renewal involves the production of a transit amplifying cell via a process known as [[asymmetric division]]. The transit amplifying cell divides repeatedly, after which the resulting cells differentiate and "[refresh] tissues and organs with replacement cells."<ref>Shostak, Stanley: "(Re)defining stem cells", Bioessays 28(3), March 2006: pages 301 - 308, page 305</ref> Moreover, self-renewal allows the production of new cells where the division of existing cells incorporated into an organ would be disruptive:<blockquote>the somatic stem cell play[s] its role when cell division conflict[s] with function (e.g. stem cells suppl[y] neuroblasts when [[neurons]] [can] not afford to sacrifice half their [[synapses]] for the sake of cell division).<ref>Shostak, Stanley: "(Re)defining stem cells", Bioessays 28(3), March 2006: pages 301 - 308, page 303</ref></blockquote> | The term "'''stem cell'''" is generally used to describe cells that are [[totipotent]], [[pluripotent]], or [[multipotent]].<ref name=Bioessays>Shostak, Stanley: "(Re)defining stem cells", Bioessays 28(3), March 2006: pages 301 - 308</ref> Totipotent cells have the capacity to differentiate to all cell types, including [[somatic]] cells, [[germ]] cells, and certain cells that exist outside the [[embryo]] and are important to [[fetal development]] that are termed extraembryonic cells. Pluripotent cells may differentiate to cells of most types, and multipotent cells are capable only of differentiating to certain types within a group of cells that perform similar functions. "Stem cell" is also used in reference to any adult cells that are capable of assisting in the restoration of adult tissue via self-renewal.<ref name=Bioessays/> Self renewal involves the production of a transit amplifying cell via a process known as [[asymmetric division]]. The transit amplifying cell divides repeatedly, after which the resulting cells differentiate and "[refresh] tissues and organs with replacement cells."<ref>Shostak, Stanley: "(Re)defining stem cells", Bioessays 28(3), March 2006: pages 301 - 308, page 305</ref> Moreover, self-renewal allows the production of new cells where the division of existing cells incorporated into an organ would be disruptive:<blockquote>the somatic stem cell play[s] its role when cell division conflict[s] with function (e.g. stem cells suppl[y] neuroblasts when [[neurons]] [can] not afford to sacrifice half their [[synapses]] for the sake of cell division).<ref>Shostak, Stanley: "(Re)defining stem cells", Bioessays 28(3), March 2006: pages 301 - 308, page 303</ref></blockquote> | ||
| Line 42: | Line 44: | ||
[[Category:CZ Live]] | [[Category:CZ Live]] | ||
[[Category:Genetics]]--> | [[Category:Genetics]]--> | ||
Revision as of 20:33, 14 November 2007
The term "stem cell" is generally used to describe cells that are totipotent, pluripotent, or multipotent.[1] Totipotent cells have the capacity to differentiate to all cell types, including somatic cells, germ cells, and certain cells that exist outside the embryo and are important to fetal development that are termed extraembryonic cells. Pluripotent cells may differentiate to cells of most types, and multipotent cells are capable only of differentiating to certain types within a group of cells that perform similar functions. "Stem cell" is also used in reference to any adult cells that are capable of assisting in the restoration of adult tissue via self-renewal.[1] Self renewal involves the production of a transit amplifying cell via a process known as asymmetric division. The transit amplifying cell divides repeatedly, after which the resulting cells differentiate and "[refresh] tissues and organs with replacement cells."[2] Moreover, self-renewal allows the production of new cells where the division of existing cells incorporated into an organ would be disruptive:
the somatic stem cell play[s] its role when cell division conflict[s] with function (e.g. stem cells suppl[y] neuroblasts when neurons [can] not afford to sacrifice half their synapses for the sake of cell division).[3]
The use of the pluripotent and/or self-renewing qualities of stem cells is believed to have therapeutic benefits for the regeneration of tissue in humans. Such tissue renewal may be accomplished via the use of adult stem cells, or embryonic stem cells, which may be derived from a human embryo in the blastocyst stage. The use of embryonic stem cells has been a source of considerable controversy due to its sacrifice of human embryos in the blastocyst stage, which some people view as the destruction of human life.
Use Of Adult Stem Cells For Tissue Regeneration
Much research suggests that adult stem cells may be pluripotent in humans and animals. However the research does not directly establish therapeutic benefits for adult stem cells, as it did not examine attempts to use stem cells to treat illnesses or injuries that would theoretically be corrected by tissue regeneration. Instead, these studies have merely shown that when adult stem cells are implanted in test subjects, these stem cells appear to migrate to organs other than those from which they were extracted and differentiate to cells of the appropriate type.
An early study in mice is typical of this line of research.[4] In that study, bone marrow was transplanted "from transgenic mice (8 to 10 weeks of age) that ubiquitously expressed enhanced green fluorescent protein (GFP)"[5] and implanted "into lethally irradiated, isogenic adult (8- to 10-week-old) recipients..."[6] The GFP was used to identify neurons in the transplant recipients that were descendants of stem cells in the bone marrow they received. Bone marrow stem cells were found to migrate to the brains of the recipients:
Brains harvested several months after the transplant... and examined by light microscopy revealed the presence of GFP1 cells throughout the CNS, including the olfactory bulb, hippocampus, cortical areas, and cerebellum.[4]
These cells produced proteins normally created by neurons, suggesting that the stem cells had been differentiated to neurons. Furthermore, the GFP labeled cells adopted the electrical properties of neurons:
A major signal transduction pathway present in neurons is also intact in bone marrow-derived cells that express neuron-specific genes in the brain.[7]
Thus, the study clearly demonstrated the in vivo pluripotency of bone marrow derived stem cells in mice.
A study representative of this line of research in humans examined the migration of bone marrow stem cells in human bone marrow transplant recipients to their brains.[8] The brains of female patients who had received "bone marrow transplants from male donors"[8] and had died from cancer were examined to discover neurons which contained Y chromosomes, which would indicate that they were derived from stem cells in the bone marrow. Y chromosomes were labeled with radioactive isotopes and fluorescent dyes. Many Y chromosomes were found in cells that also contained proteins indicating that they were neurons:
In each of the transplanted patients examined we readily detected Y-positive cells by means of autoradiography. In all patients using conventional fluorescent microscopy we observed double-labeled cells that were positive for both the Y chromosome and one of the neuronal markers as shown in an example in Fig. 1. Most of the cells that were double-labeled with the Y chromosome and the neuronal markers were detected in the hippocampus and the neocortex of patients...[9]
However, a far smaller percentage of bone marrow stem cell derived neurons were observed than in the analagous, previously described study on mice: the human study "found 2-5 Y-positive neurons per 10,000 human neurons vs. 50 per 10,000 rodent neurons."[10], which may indicate that bone marrow derived stem cells had a reduced efficacy in producing neurons in humans, possibly due to a reduced pluripotency.
While the research on adult stem cells suggests that they may have significant medical value, further study is necessary to demonstrate their safety and efficacy in practice for curing medical problems via tissue regeneration.
Use Of Embryonic Stem Cells
The most infamous study of embryonic stem cells asserted that cloned human embryos had been created via somatic cell nuclear transfer, and stem cells had been generated from these embryos.[11] The authors claimed that these stem cells were genetically indistinguishable from the donors from whom the somatic cells were taken, and were pluripotent: the stem cells allegedly
express hESC pluripotency markers... DNA fingerprinting with human short tandem-repeat probes... shows with high certainty that every NT-hESC line derived here originated from the respective patient donor and that these lines were not the result of enucleation failures and subsequent parthenogenetic activation.[12]
Ironically, the authors of this study deride "cruel hoaxes... regarding human... cloning"[13], a reference the claim of Clonaid that it had produced five cloned human infants.[14] This study was retracted when it was discovered that the authors had falsified their data.[15] Cloning via somatic cell nuclear transfer apparently has yet to be used to produce human stem cells.
However, human embryos fertilized in the ordinary manner and harvested in the blastocyst stage have been used as an extensive source of stem cells for research purposes, and have been shown to possess therapeutic value in laboratory animals. In a study characteristic of this line of research, human embryonic stem cells were injected into mice whose spinal cords had been wounded:
Nine days after spinal cord injury, mice received four injections bilaterally 0.75mm from midline at both the anterior aspect of T10 and the posterior aspect of T8. Each site received 250 nl of cells or vehicle.[16]
After sixteen weeks, the injured mice who received human stem cell injections experienced a significant improvement in the motor functions that had been impaired by their injuries. Furthermore, the use of diphtheria toxin -- which is far more toxic to human cells than mouse cells -- to destroy the human neurons in the mice reversed the observed improvements in motor function. This result suggests that the observed increase in motor function was indeed produced by neurons derived from the human embryonic stem cells. Cross-species transplantation was possible without the rejection of the human embryonic stem cells by the mice's immune systems because the mice were genetically modified to suppress certain immune responses that would have interfered with transplantation.
Properly controlled, adequately sized studies have yet to demonstrate that human embryonic stem cells have medical value in humans.[17]
Ethical Considerations Of Embryonic Stem Cells
Ethical objections to the use of human embryonic stem cells revolve around the destruction of human embryos in the blastocyst stage to obtain the stem cells. Those who oppose this practice often argue that human life begins from the moment of conception, and that, therefore, destruction of a blastocyst stage embryo is morally equivalent to abortion and infanticide. However, supporters of embryonic stem cell research frequently contend that even the comparison to abortion is inappropriate, since while a several month old fetus might have sufficient neurological development to be conscious in some meaningful sense, a human embryo in the blastocyst stage has so little development that one can safely conclude that it cannot exist as a conscious being.
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Shostak, Stanley: "(Re)defining stem cells", Bioessays 28(3), March 2006: pages 301 - 308
- ↑ Shostak, Stanley: "(Re)defining stem cells", Bioessays 28(3), March 2006: pages 301 - 308, page 305
- ↑ Shostak, Stanley: "(Re)defining stem cells", Bioessays 28(3), March 2006: pages 301 - 308, page 303
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Brazelton et al: "From Marrow to Brain: Expression of Neuronal Phenotypes in Adult Mice", Science Volume 290, December 1, 2000, pages 1775 - 1779
- ↑ Brazelton et al: "From Marrow to Brain: Expression of Neuronal Phenotypes in Adult Mice", Science Volume 290, December 1, 2000, pages 1775-1776
- ↑ Brazelton et al: "From Marrow to Brain: Expression of Neuronal Phenotypes in Adult Mice", Science Volume 290, December 1, 2000, page 1776
- ↑ Brazelton et al: "From Marrow to Brain: Expression of Neuronal Phenotypes in Adult Mice", Science Volume 290, December 1, 2000, page 1778
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 Mezey et al.:"Transplanted bone marrow generates new neurons in human brains." Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 100 (3), February 4, 2003, pages 1364 - 1369
- ↑ Mezey et al.:"Transplanted bone marrow generates new neurons in human brains." Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 100 (3), February 4, 2003, page 1365
- ↑ Mezey et al.:"Transplanted bone marrow generates new neurons in human brains." Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 100 (3), February 4, 2003, page 1368
- ↑ Hwang et al: "Patient-Specific Embryonic Stem Cells Derived from Human SCNT Blastocysts", Science Volume 308, June 17, 2005, pages 1777 - 1783 (RETRACTED)
- ↑ Hwang et al: "Patient-Specific Embryonic Stem Cells Derived from Human SCNT Blastocysts", Science Volume 308, June 17, 2005, pages 1778-1779 (RETRACTED)
- ↑ Hwang et al: "Patient-Specific Embryonic Stem Cells Derived from Human SCNT Blastocysts", Science Volume 308, June 17, 2005, page 1783 (RETRACTED)
- ↑ Schatten et al: "Cloning Claim is Science Fiction, Not Science", Science Volume 299, January 17, 2003, page 344
- ↑ "Editorial Retraction", Science Vol. 311, January 20, 2006, page 335
- ↑ Cummings et al: "Human neural stem cells differentiate and promote locomotor recovery in spinal cord-injured mice", Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 102 (39), September 27, 2005, pages 14069 - 14074, page 14069
- ↑ National Institutes of Health: "FAQs [Stem Cell Information]", http://stemcells.nih.gov/info/faqs.asp, Healthcare Questions: 2