Separative Work Units (SWUs): Difference between revisions
m (→References: update access-date for ref 3) |
(rework the lead) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
'''Separative | '''Separative Work Units (SWUs)''' are the measure of work done in separating the isotopes of uranium. SWUs are not units of ''energy'', but rather a measure of enrichment ''services'' provided by an enrichment plant. This unit, introduced by Paul Dirac in 1941, is ''proportional'' to the amount of energy or time spent, and to the total mass processed. Gaseous diffusion plants typically require 2,400 to 2,500 kW hours of electricity per SWU, while gas centrifuge plants require just 50 kWh per SWU. | ||
The | The average price of uranium enrichment was $106.97 per SWU in 2023, up 6% from $101.03 in 2022.<ref name=price/> | ||
<ref name=price/> | |||
== Calculation == | == Calculation == | ||
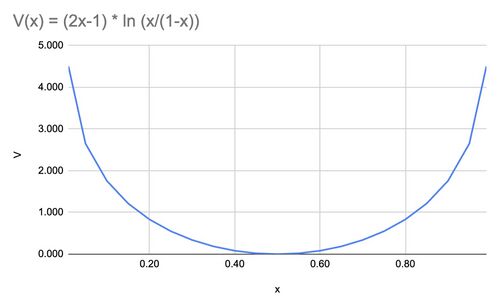
{{Image|SWUfunction.jpg|right|500px|Fig.1 Logarithmic function used in calculating Separative Work Units.}} | {{Image|SWUfunction.jpg|right|500px|Fig.1 Logarithmic function used in calculating Separative Work Units.}} | ||
SWUs are a function of the concentrations of the feedstock, the enriched output, and the depleted tailings; and is expressed in units which are so calculated as to be proportional to the total input (energy / machine operation time) and to the mass processed. | |||
The work <math>W_\mathrm{SWU}</math> necessary to separate a mass <math>F</math> of feed of assay <math>x_{f}</math> into a mass <math>P</math> of product assay <math>x_{p}</math>, and tails of mass <math>T</math> and assay <math>x_{t}</math> is given by the expression:<ref name=Fuchs/> | The work <math>W_\mathrm{SWU}</math> necessary to separate a mass <math>F</math> of feed of assay <math>x_{f}</math> into a mass <math>P</math> of product assay <math>x_{p}</math>, and tails of mass <math>T</math> and assay <math>x_{t}</math> is given by the expression:<ref name=Fuchs/> | ||
Revision as of 10:05, 28 July 2024
Separative Work Units (SWUs) are the measure of work done in separating the isotopes of uranium. SWUs are not units of energy, but rather a measure of enrichment services provided by an enrichment plant. This unit, introduced by Paul Dirac in 1941, is proportional to the amount of energy or time spent, and to the total mass processed. Gaseous diffusion plants typically require 2,400 to 2,500 kW hours of electricity per SWU, while gas centrifuge plants require just 50 kWh per SWU.
The average price of uranium enrichment was $106.97 per SWU in 2023, up 6% from $101.03 in 2022.[1]
Calculation
SWUs are a function of the concentrations of the feedstock, the enriched output, and the depleted tailings; and is expressed in units which are so calculated as to be proportional to the total input (energy / machine operation time) and to the mass processed.
The work necessary to separate a mass of feed of assay into a mass of product assay , and tails of mass and assay is given by the expression:[2]
where is the value function, defined as:[3]
and satisfies
The feed to product ratio is given by the expression
whereas the tails to product ratio is given by the expression
Examples
Starting with 102 kg of natural uranium (NU), it takes about 62 SWU to produce 10 kg of Low Enriched Uranium (LEU) with 235U content at 4.5%, and a tails assay of 0.3%.
A large nuclear power station with a net electrical capacity of 1300 MW requires about 25 tonnes per year of LEU with a 235U concentration of 3.75%. This quantity is produced from about 210 tonnes of NU using about 120 kSWU. An enrichment plant with a capacity of 1000 kSWU per year can enrich the uranium needed to fuel about eight large nuclear power stations.
For more examples see Uranium Enrichment / Separative Work Units These examples are relevant to the question - Will worldwide distribution of MEU (Moderately Enriched Uranium, 20% U-235, or HALEU to use official industry jargon) will this massive production and shipment of fissile material be an easy target for the Bad Guys?
Note for Wannabe Bomb Makers:
Enriching uranium is very difficult. To get above 90% (weapons grade) it takes a lot of "work" by the centrifuges. The work increases asymptotically as you approach 100% (see Figure 1). It is also difficult starting with natural uranium (0.7%). Centrifuges work best with a 50/50 mixture of isotopes. If you can steal some 20% from a nearby power plant with a "new generation" reactor, it will be a bit easier than starting with 5%, which is the best you can find in an "old generation" power plant.
References
- ↑ Uranium Marketing Annual Report. US Energy Information Administration. accessed 28 July 2024.
- ↑ Fuchs, K. (1997). Selected Scientific Papers Of Sir Rudolf Peierls, With Commentary By The Author. World Scientific Publishing Company. ISBN 9789814498883.
- ↑ Bernstein, J. (2009). SWU for You and Me. arXiv:0906.2505
Attribution
- Some content on this page may previously have appeared on Wikipedia. See Separative_work_units for more details.