Fourier operator: Difference between revisions
imported>Dmitrii Kouznetsov |
imported>Dmitrii Kouznetsov |
||
| Line 84: | Line 84: | ||
==Numerical implementation of the Fourier operator== | ==Numerical implementation of the Fourier operator== | ||
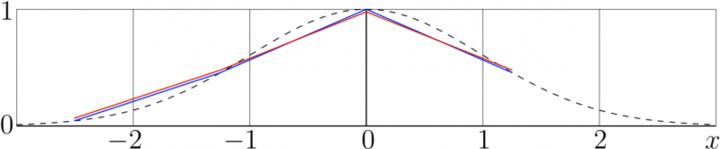
[[File:FourierExampleGauss04Ta.png|720px|right|thumb| $A(x)=\exp(-x^2/2)$, dashed; its representation at the grid of 4 nodes, blue, and the numerical Fourier (\mathrm{Fourier}_NA)(x)</math>, red]] | [[File:800px-FourierExampleGauss04Ta.png|720px|right|thumb| $A(x)=\exp(-x^2/2)$, dashed; its representation at the grid of 4 nodes, blue, and the numerical Fourier (\mathrm{Fourier}_NA)(x)</math>, red]] | ||
In order to approximate the Fourier operator, the [[Discrete Fourier]] operator is used. | In order to approximate the Fourier operator, the [[Discrete Fourier]] operator is used. | ||
Revision as of 08:25, 4 September 2012
Fourier operator is linear integral operator with the exponential kernel.
Let some complex–valued function be defined for real values of the argument, id est, . Then the Fourier operator, acting on , gives function , or, simply, , such that
If the integral converges, then, function is called Fourier transform of function .
Other notations
Slightly different notations are used in the article Fourier transform; operator is defined such that
In such a way,
Inverse operator
The inverse of the Fourier operator is its conjugate, id est,
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!(4) ~ ~ ~ \displaystyle {\mathrm {Fourier}}^{-1} = \mathrm{Fourier}^*}
where Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mathrm{Fourier}^*} acts on a function Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle A} in such a way, that
Then, for the operator Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mathcal F} , the inverse acts on a fiction Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle A} as follows:
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!(6) ~ ~ ~ \displaystyle {\mathcal F}^{-1} ~A~ (x) = \sqrt{2 \pi} \mathrm{Fourier}^* ~ A~ (2 \pi x) }
Application of the Fourier operator
The Fourier transform is used in various sciences and, especially, in physics. In Quantum mechanics, function Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle A} may have sense of the wave function in the coordinate representation, then Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle B=\mathrm{Fourier}~ A} corresponds to the momentum representation. Many equations can be solved using the Fourier Transform. Especially efficient is the Fourier transform in the consideration of the paraxial approximation of the wave equations.
General properties of the Fourier operator
The Fourier operator is linear: for complex constants Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \alpha} and ,
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!(7) ~ ~ ~ \displaystyle \mathrm{Fourier} (\alpha A+\beta B)= \alpha \mathrm{Fourier}(A) + \beta \mathrm{Fourier} (B)}
Norm of the Fourier operator
The norm Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle ||A||} of a function Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle A} can be defined as
The norm of any function is assumed to be non–negative; Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle ||A||\ge 0} .
The Fourier operator is unitary, so, it preserves the norm of a function; if Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle A=\mathrm{Fourier}(B)} then Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle ||A||=||B||}
Iteration of the Fourier operator
The iterations of the Fourier operator do not provide a wide variety, because
Any integrable continuous function Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle A} can be used as a an origin to construct a self–Fourier function as a polynomial
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\displaystyle (11) ~ ~ ~ S(A)= A+ \mathcal{F} A+ \mathcal{F}^2 A+ \mathcal{F}^3 A}
which is self-Fourier function; id set, $~S~$ is eigenfunction of the Fourier operator with eigenvalue unity.
Self–Fourier functions
In general, function Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle A} is called self-Fourier function, if
All the self-Fourier functions are eigenfunction of the Fourier operator with eigenvalue unity. Any self–Fourier function can be represented as series,
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\displaystyle (13) ~ ~ ~ A(x) ~=~ \sum_{n=0}^{\infty} ~c_n~ \mathrm{HermiteH}_{4n}\!(x)~ \exp(-x^2/2)}
where Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mathrm{HermiteH}} are the Hermit polynomials [1], and $c$ are arbitrary complex coefficients; the sequence Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle c} should decay quickly enough to provide the convergence of the series [2].
In particular, the first three self-Fourier functions can be defined with
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\displaystyle (13) ~ ~ ~ A_0(x)=\exp(-x^2/2)}
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\displaystyle (14) ~ ~ ~ A_4(x)=\exp(-x^2/2) (x^4-3x^2)}
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\displaystyle (15) ~ ~ ~ A_8(x)=\exp(-x^2/2) (x^8-14x^6+35x^4)}
The self-Fourier functions are good for testing of the numerical implementations of the Fourier operator $\mathcal{F}$.
Numerical implementation of the Fourier operator
In order to approximate the Fourier operator, the Discrete Fourier operator is used. In this section, the numerical implementation is discussed. The C++ implementation fafo.cin of operator $\mathrm{Fourier}$ is used to plot figures. This implementation is described below. The codes used to plot figures are supplied in the descriptions of the figures.
There is no need to describe functions , Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle f(x)\!=\!\sin(kx)} , Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle f(x)\!=\!\sin(2 \pi x/T)} and so on separately, it is sufficient to have function sin. In the similar way, it is sufficient to describe the discrete implementation of the Fourier operator at some grid. Then, other implementations can be built-up with minimal modifications of the algorithm, shifting and scaling the argument of the function and applying the corresponding modifications to the Fourier transform.
For the number Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle N=2^m} of grid points, the step of the grid is chosen as follows:
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\displaystyle (16) ~ ~ ~ d = \sqrt{2 \pi /N}}
The grid points Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle x_j} , Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle j=0..N} are chosen for natural number Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle ~j~} ; Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle ~0\!\le \! j \!<\! N} in the following way:
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\displaystyle (17) ~ ~ ~ x_j = (j-N/2) d ~}
At such a discretization, the node with number Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle N/2} always corresponds to the argument zero. The 0th node is assumed to be at the left hand side of the sampled range. However, it can be placed also at the right hand side as well, and interpreted as $x_{N}$. The algorithm makes no difference between these points.
The same grid is used both for the function and for its Fourier–transform. Functions Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle A} and Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle B=\mathrm{Fourier}(A)} are represented with the arrays;
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\displaystyle (18) ~ ~ ~ A(x_j)=A_j~ ~; ~ ~ ~ B(x_j)=B_j~}
The approximation of Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle B} corresponds to the replacement of the integral to the discrete sum:
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\displaystyle (19) ~ ~ ~ B_j=\frac{d}{\sqrt{2 \pi}} \sum_{n=0}^{N-1} A_n \exp( -\mathrm{i} ~ x_j ~ x_n) }
It is convenient to chose Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle N=2^m} for some natural number ; then the fast implementation of such a summation is especially simple.
For the testing of the algorithm, the transform of discrete analogy of the Gaussian exponential is suggested at the figure above.
Such a Gaussian is self-Fourier function, and it coincides with its Fourier-transform. However, at small number of the grid points, , the deviation of the blue segmented line (that represents the array Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle A} ) deviates from the red line, that represents the array Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle B} as the numeric transform of Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle A} . At larger number Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle N} of grid points, the strong zooming-in is necessary to see the deviation.

A little bit more complicated example with self-Fourier function
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\displaystyle (20) ~ ~ ~ A(x)\!=\!\exp(-x^2/2)(−3x^2+x^4)}
is shown in figure at right in the same notations, as in previous figure, but Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle N\!=\!16} . In this case, the segmented lines for arrays Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle A} and Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle B} overlap so perfectly, that the deviation is not seen. This deviation Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle A\!-\!B} scaled with factor 100 is shown with the saw-like line along the abscissa axis. The deviation is of order of Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle 10^{-3}} , and only in the 0th node of the grid it is a little bit larger, than Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle 10^{-3}} .
The examples show, that the numerical approximation of the Fourier operator is much better, than the 1st order approximation of the function and its Fourier transform with the arrays Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle A} and Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle B} , the deviation of the segmented line from the smooth Gaussian is much larger than the deviation of the initial array from its discrete transform.
Everyone may load the code and play with the discrete implementation of the Fourier operator for various input arrays, approximating various functions.
References
- ↑ http://mathworld.wolfram.com/HermitePolynomial.html
- ↑ http://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1080/09500349908231393#preview R.Ortega, C.J.Román, D.Kouznetsov. On the second order characterization of ultrashort pulses. Journal of Modern Optics, v.46, No.15, p.2069-2077 (1999).
http://mathworld.wolfram.com/FourierTransform.html
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Fourier_transform
The content of this article is adopted from http://tori.ils.uec.ac.jp/TORI/index.php/Fourier_operator