User:John R. Brews/Coriolis effect: Difference between revisions
imported>John R. Brews |
imported>John R. Brews |
||
| Line 83: | Line 83: | ||
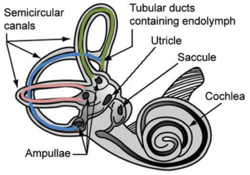
==Vestibular system== | ==Vestibular system== | ||
{{Image|Vestibular system of ear.PNG|right|250px|Vestibular system in the human ear.}} | {{Image|Vestibular system of ear.PNG|right|250px|Vestibular system in the human ear.}} | ||
The ''vestibular system'' of the ear senses balance, motion, and body position. The three semicircular canals observe acceleration in the three planes of motion: ''pitch'' (nod ''yes''), ''yaw'' (twist your head ''no''), and ''roll'' (pivot head from left to right shoulder without twisting). The ''otolith organs'' detect linear acceleration. | The ''vestibular system'' of the ear senses balance, motion, and body position. The three ''semicircular canals'' observe acceleration in the three planes of motion: ''pitch'' (nod ''yes''), ''yaw'' (twist your head ''no''), and ''roll'' (pivot head from left to right shoulder without twisting). The ''otolith organs'' detect linear acceleration. | ||
==Notes== | ==Notes== | ||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
Revision as of 12:21, 18 February 2011
In psychophysical perception, the Coriolis effect is a form of nausea induced by the Coriolis force (also referred to as the Coriolis illusion).[1][2][3][4] The Coriolis effect is a concern of pilots, where it can cause extreme discomfort and disorientation.[5][6][7][8]
Subjects in a rotating environment that reach to point at a target make errors consistent with the Coriolis force acting upon their arms.
A rotating subject that has reached equilibrium with their rotation finds that upon tilting the head the feeling is that a rotation is occurring about the new axis of the head, when in fact that is not occurring at all. http://books.google.com/books?id=_6hymYAgC6MC&pg=PA175&lpg=PA175&dq=VESTIBULAR+CORIOLIS+ILLUSION&source=bl&ots=Nv8fRQGIUr&sig=32jT7VepXv9mVOa0WmJDvYqpJuk&hl=en&ei=0j1eTZT5HoassAO4kdDSCA&sa=X&oi=book_result&ct=result&resnum=6&ved=0CDYQ6AEwBQ#v=onepage&q=VESTIBULAR%20CORIOLIS%20ILLUSION&f=false NASA
Vestibular system
The vestibular system of the ear senses balance, motion, and body position. The three semicircular canals observe acceleration in the three planes of motion: pitch (nod yes), yaw (twist your head no), and roll (pivot head from left to right shoulder without twisting). The otolith organs detect linear acceleration.
Notes
- ↑ Jeffrey W. Vincoli (1999). Lewis' dictionary of occupational and environmental safety and health. CRC Press, p. 245. ISBN 1566703999.
- ↑ Mark S Sanders & Ernest J McCormick (1993). Human Factors in Engineering and Design, 7th Edition. McGraw-Hill, p. 644. ISBN 0071128263.
- ↑ Sheldon M. Ebenholtz (2001). Oculomotor Systems and Perception. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0521804590.
- ↑ George Mather (2006). Foundations of perception. Taylor & Francis. ISBN 0863778356.
- ↑ Arnauld E. Nicogossian (1996). Space biology and medicine. Reston, VA: American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics, Inc, p. 337. ISBN 1563471809.
- ↑ Thomas Brandt (2003). Vertigo: Its Multisensory Syndromes. Springer, p. 416. ISBN 0387405003.
- ↑ Fred H. Previc, William R. Ercoline (2004). Spatial Disorientation in Aviation. Reston, VA: American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics, Inc, p. 249. ISBN 1563476541.
- ↑ Gilles Clément (2003). Fundamentals of Space Medicine. Springer, p. 41. ISBN 1402015984.