Chloroplast/Related Articles: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search

imported>Chris Day |
imported>Chris Day No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{subpages}} | {{subpages}} | ||
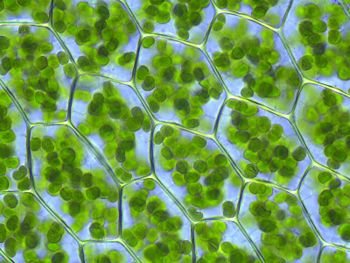
[[Image:Plagiomnium affine laminazellen.jpeg|thumb|right|350px|A collection of links to articles, or potential articles relating to chloroplast topics in biochemistry, cell biology and physiology.<br>Tasks include:<br> | |||
'''1)''' write a definition for each topic. <br> | |||
'''2)''' start a new article (click a red link).<br> | |||
'''3)''' expand an existing stub or article.]] | |||
==Parent topics== | ==Parent topics== | ||
{{r|Cell (biology)|Cell}} | {{r|Cell (biology)|Cell}} | ||
Revision as of 23:04, 19 September 2008
- See also changes related to Chloroplast, or pages that link to Chloroplast or to this page or whose text contains "Chloroplast".
Parent topics
- Cell [r]: The basic unit of life, consisting of biochemical networks enclosed by a membrane. [e]
- Cell biology [r]: The study of the components of biological cells and their interactions. [e]
- Leaf [r]: Please do not use this term in your topic list, because there is no single article for it. Please substitute a more precise term. See Leaf (disambiguation) for a list of available, more precise, topics. Please add a new usage if needed.
- Metabolism [r]: The modification of chemical substances by living organisms. [e]
- Organelle [r]: Specialized subunit within a cell that has a specific function, and is usually separately enclosed within its own lipid membrane, found in all eukaryotic cells. [e]
- Plastid [r]: Add brief definition or description
Subtopics
- Stroma [r]: The matrix of a plastid that contains the enzymes for carbon fixation and the organelles DNA; thylakoid membranes are surrounded by this matrix. [e]
- Thylakoid [r]: A system of membranes inside chloroplasts, housing the proteins that carry out the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis. [e]
- Photosynthesis [r]: The process by which an organism captures and stores energy from sunlight, energy it uses to power its cellular activities. [e]
- Light reactions [r]: Chemical reactions that occur in the stroma of the chloroplast during photosynthesis and use the ATP and NADPH synthesized during the light-dependent reactions to fix carbon atoms from CO2. [e]
- Photophosphorylation [r]: Add brief definition or description
- Chemiosmosis [r]: Add brief definition or description
- Electron transport chain [r]: (ETC) A series of biochemical reactions that couple a chemical reaction between an electron donor and an electron acceptor to the transfer of protons across a membrane. [e]
- Photosystem [r]: Add brief definition or description
- Light-independent reactions [r]: Add brief definition or description
- Calvin cycle [r]: A metabolic cycle, discovered by Melvin Calvin, that is responsible for the reduction of carbon dioxide to sugar in the stroma of chloroplasts. [e]
- C4 carbon fixation [r]: A carbon fixation reaction that fixes carbon dioxide into the four carbon molecule oxaloacetate; usually found in the mesophyll cells of plants that use the Hatch-Slack pathway. [e]
- Crassulacean acid metabolism [r]: (CAM) Typical in succulent plants and characterised by the ability to fix carbon dioxide to malate in the dark; this is then stored in the vacuole as malic acid until the following light period when it is converted to carbon dioxide for fixation by the Calvin cycle. [e]
- Photorespiration [r]: A salvage pathway utilised to remove the products of Rubisco's oxygenase activity during photosynthesis; involves reactions in three organelles, the chloroplast, the peroxisome and the mitochondria. [e]
- RuBisCO [r]: Add brief definition or description
- Bioenergetics [r]: Add brief definition or description
- Cytoplasmic streaming [r]: Add brief definition or description
- Glyoxysome [r]: Add brief definition or description
- Gravitropism [r]: Add brief definition or description
- Mitochondrion [r]: Add brief definition or description
- Oxidative phosphorylation [r]: Add brief definition or description
- Palisade cell [r]: Add brief definition or description
- Protein targeting [r]: Add brief definition or description
- Ribosome [r]: Add brief definition or description
- Signal peptide [r]: Add brief definition or description
- Algae [r]: Add brief definition or description
- Chlamydomonas reinhardtii [r]: Add brief definition or description
- Cyanobacteria [r]: Add brief definition or description
- Prokaryote [r]: Add brief definition or description
- Symbiogenesis [r]: Add brief definition or description