Chief of Naval Operations: Difference between revisions
imported>Chris Day (→CNO Staff: might as well have full size so no blurring) |
imported>Chris Day (→CNO list and especially notable CNOs: move to catalog) |
||
| Line 10: | Line 10: | ||
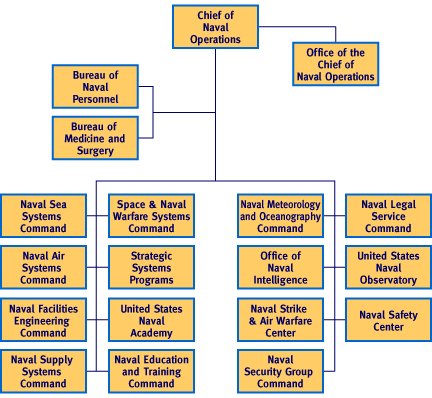
A large staff organization, headed by the Director of Navy Staff, does report to the CNO, and he has a major role in developing naval doctrine, planning the navy of the future, preparing its budget, etc. | A large staff organization, headed by the Director of Navy Staff, does report to the CNO, and he has a major role in developing naval doctrine, planning the navy of the future, preparing its budget, etc. | ||
Revision as of 21:48, 28 May 2008
Unless the Chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff or the Vice Chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff is a naval officer, the Chief of Naval Operations (CNO) is the senior officer of the United States Navy. He is appointed by the President and confirmed by the Senate, currently for a four-year term, and usually retires after the term. Admiral Arleigh Burke, however, served three terms, then of two years each.
A member of the Joint Chiefs of Staff (JCS), he does not directly command operational forces of the Navy, which are under Unified Combatant Commands that report to the Secretary of Defense and the President of the United States; the latter two constitute the National Command Authority.
The CNO reports to the Secretary of the Navy, especially in matters such as Congressional relations, but has complex relationships with the Joint Chiefs of Staff and Secretary of Defense. While he does not have operational command over naval forces, he has enormous influence.
CNO Staff
The Vice Chief of Naval Operations acts for the CNO in his absence. Each CNO and VCNO work out their particular responsibilities, but the CNO is often more concerned with JCS, White House, and Congressional relations, so the VCNO may be closer to the day-to-day naval structure.
A large staff organization, headed by the Director of Navy Staff, does report to the CNO, and he has a major role in developing naval doctrine, planning the navy of the future, preparing its budget, etc.