User:Milton Beychok/Sandbox: Difference between revisions
imported>Milton Beychok No edit summary |
imported>Milton Beychok No edit summary |
||
| Line 33: | Line 33: | ||
*[http://gpaglobal.org/gpsa Gas Processors Suppliers Association Website] | *[http://gpaglobal.org/gpsa Gas Processors Suppliers Association Website] | ||
*[http://www.bre.com/portals/0/technicalarticles/Design%20Glycol%20Units%20for%20Maximum%20Efficiency.pdf | *[http://www.bre.com/portals/0/technicalarticles/Design%20Glycol%20Units%20for%20Maximum%20Efficiency.pdf Design Glycol Units for Maximum Efficiency] Vincente N. Hernandez-Valencia, Michael W. Hlavinka and Jerry A. Bullin, Proceedings of the Seventy-First GPA Annual Convention, [[Tulsa, OK]], 1992, pp 310-317. An excellent discussion on the design details of glycol units. | ||
* | *{{cite journal|author=Kh. Mohamadbeigy|title=Studying of the Effectiveness Parameters on Gas Dehydration Plant|journal=Petroleum & Coal|volume=50|issue=2| pages=pp 47-51|date=2008|id=ISSN 1337-7027|url=http://www.vurup.sk/pc/vol50_2008/issue2/pdf/PC_2_2008_Mohamadbeigy.pdf}} | ||
*[http://articles.compressionjobs.com/articles/oilfield-101/1454-dehydration-adsorption-glycol-reflux-reboiler-foaming Practical oil-field oriented description of Glycol Dehydration including Operating problems and Glycol care] | *[http://articles.compressionjobs.com/articles/oilfield-101/1454-dehydration-adsorption-glycol-reflux-reboiler-foaming Practical oil-field oriented description of Glycol Dehydration including Operating problems and Glycol care] | ||
Revision as of 19:00, 29 April 2010
Glycol dehydration is a liquid desiccant system for the removal of water from natural gas and natural gas liquids (NGL). It is the most common and economic means of water removal from these streams.[1] Glycols typically seen in industry include triethylene glycol (TEG), diethylene glycol (DEG), ethylene glycol (MEG), and tetraethylene glycol (TREG). TEG is the most commonly used glycol in industry.[1]
Purpose
The purpose of a glycol dehydration unit is to remove water from natural gas and natural gas liquids. When produced from a reservoir, natural gas usually contains a large amount of water and is typically completely saturated or at the water dew point. Without dehydration, a free water phase (liquid water) could drop out of the natural gas as it is either cooled or the pressure is lowered as the gas flows through pipelines and processing equipment. This free water phase will contain some amount of acid gas (such as H2S and CO2) and can cause corrosion.[1]
At low temperatures, hydrates may form with CO2 and hydrocarbons. Depending on the gas composition, these hydrates can form at relatively high temperatures and cause plugging of equipment and piping.[1] Drying the gas with glycol dehydration unit depresses the hydrate formation point of the gas.
For the above reasons, pipeline quality specifications for natural gas usually mandate that the water content should not exceed 7 pounds per million SCF (kg per ). Glycol dehydration units must typically meet this specification at a minimum, although further removal may be required if additional hydrate formation temperature depression is required.
Process description
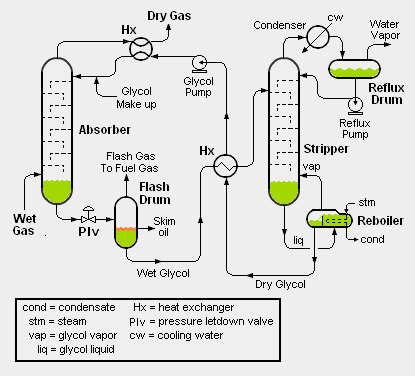
Lean, water-free glycol (purity >99%) is fed to the top of an absorber where it is contacted with the wet natural gas stream. The glycol removes water from the natural gas by physical absorption and is carried out the bottom of the column. Upon exiting the absorber the glycol stream is often referred to as "rich glycol". The dry natural gas leaves the top of the absorption column and is fed either to a pipeline system or to a gas plant. Glycol absorbers can be either tray columns or packed columns.
After leaving the absorber, the rich glycol is fed to a flash vessel where hydrocarbon vapors are removed and any liquid hydrocarbons are skimmed from the glycol. This step is necessary as the absorber is typically operated at high pressure and the pressure must be reduced before the regeneration step. Due to the composition of the rich glycol, a vapor phase having a high hydrocarbon content will form when the pressure is lowered.
After leaving the flash vessel, the rich glycol is heated in a cross-exchanger and fed to the stripper (also known as a regenerator). The glycol stripper consists of a column, an overhead condenser, and a reboiler. The glycol is thermally regenerated to remove excess water and regain the high glycol purity.
The hot, lean glycol is cooled by cross-exchange with rich glycol entering the stripper. It is then fed to a lean pump where its pressure is elevated to that of the glycol absorber. The lean solvent is cooled again with a trim cooler before being fed back into the absorber. This trim cooler can either be a cross-exchanger with the dry gas leaving the absorber or an aerial type cooler.
Enhanced Stripping Methods
Most glycol units are fairly uniform except for the regeneration step. Several methods are used to enhance the stripping of the glycol to higher purities (higher purities are required for dryer gas out of the absorber). Since the reboiler temperature is limited to 400F or less to prevent thermal degradation of the glycol, almost all of the enhanced systems center on lowering the partial pressure of water in the system to increase stripping.
Common enhanced methods include the use of stripping gas, the use of a vacuum system (lowering the entire stripper pressure), the DRIZO process, which is similar to the use of stripping gas but uses a recoverable hydrocarbon solvent, and the Coldfinger process where the vapors in the reboiler are partially condensed and drawn out separately from the bulk liquid.
References
++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++ External links
- Gas Processors Suppliers Association Website
- Design Glycol Units for Maximum Efficiency Vincente N. Hernandez-Valencia, Michael W. Hlavinka and Jerry A. Bullin, Proceedings of the Seventy-First GPA Annual Convention, Tulsa, OK, 1992, pp 310-317. An excellent discussion on the design details of glycol units.
- Kh. Mohamadbeigy (2008). "Studying of the Effectiveness Parameters on Gas Dehydration Plant". Petroleum & Coal 50 (2): pp 47-51. ISSN 1337-7027.