Kenya: Difference between revisions
imported>Richard Jensen mNo edit summary |
imported>Richard Jensen m (typos) |
||
| Line 30: | Line 30: | ||
==Education== | ==Education== | ||
Kenyan education can be divided into three periods: Colonial era (1890s to 1961), 1961-73, 1973-88, and 1988- present. Western education was pioneered by Protestant and Catholic missionaries, but missionary influence has diminished as the public education system has been extended. During the colonial period most schooling was segregated by race. Since independence all its schools have become multiracial. By the 1980s 2/3 of children of school age attended, including 77% at the primary level and 13% at the secondary. In 1990 5.4 million children attended 14,700 primary schools, with 640,000 students in some 2,650 secondary schools. More than half the secondary schools are aided or maintained by the government. | Kenyan education can be divided into three periods: Colonial era (1890s to 1961), 1961-73, 1973-88, and 1988- present. Western education was pioneered by Protestant and Catholic missionaries, but missionary influence has diminished as the public education system has been extended. During the colonial period most schooling was segregated by race. Since independence all its schools have become multiracial. By the 1980s 2/3 of children of school age attended, including 77% at the primary level and 13% at the secondary. In 1990 5.4 million children attended 14,700 primary schools, with 640,000 students in some 2,650 secondary schools. More than half the secondary schools are aided or maintained by the government. A majority of the adult population remains literate. | ||
The leading center is the University of Nairobi, with 200 programs in six colleges on seven campuses. Founded in 1956 as the Royal Technical College, it had links with the University of London, and took its present name in 1970, when it had 2700 students. By 1992 it had about 14,000 students, mostly Kenyans. By 2004 it enrolled 29,000 undergraduates, and 7,000 graduate students. There are 4,000 staff members, and 90,000 alumni.<ref> See [http://www.uonbi.ac.ke/] and [http://www.uonbi.ac.ke/management/downloads/Info_Booklet.pdf]</ref> Many Kenyans study at universities abroad. | The leading center is the University of Nairobi, with 200 programs in six colleges on seven campuses. Founded in 1956 as the Royal Technical College, it had links with the University of London, and took its present name in 1970, when it had 2700 students. By 1992 it had about 14,000 students, mostly Kenyans. By 2004 it enrolled 29,000 undergraduates, and 7,000 graduate students. There are 4,000 staff members, and 90,000 alumni.<ref> See [http://www.uonbi.ac.ke/] and [http://www.uonbi.ac.ke/management/downloads/Info_Booklet.pdf]</ref> Many Kenyans study at universities abroad. | ||
| Line 40: | Line 40: | ||
==History== | ==History== | ||
The interior is a history of migrations, and the activities of most of the major tribes are not well known before the 19th century. On the coast, trading settlements were established by 150 AD. By 1000 AD Persian and Arab traders were well established. A [[Swahili]] culture developed in the towns, notably Pate, Malindi, and Mombasa. The Portuguese arrived in 1498, with a powerful navy. The goal was not settlement but the establishment of naval bases that would give Portugal control of the Indian Ocean. After decades of small-scale conflict the | The interior is a history of migrations, and the activities of most of the major tribes are not well known before the 19th century. On the coast, trading settlements were established by 150 AD. By 1000 AD Persian and Arab traders were well established. A [[Swahili]] culture developed in the towns, notably Pate, Malindi, and Mombasa. The Portuguese arrived in 1498, with a powerful navy. The goal was not settlement but the establishment of naval bases that would give Portugal control of the Indian Ocean. After decades of small-scale conflict the Portuguese were defeated in Kenya by Arabs from Oman. Under Seyyid Said, the Omani sultan who moved his capital to [[Zanzibar]] in the early 19th century, the Arabs created long-distance trade routes into the interior. The dry reaches of the north were lightly inhabited by seminomadic pastoralists. In the south, pastoralists and cultivators bartered goods and competed for land as long-distance caravan routes linked them to the Kenya coast on the east and the kingdoms of Uganda on the west. Arab, Shirazi, and coastal African cultures produced an Islamic Swahili people trading in a variety of up-country commodities, including slaves. | ||
===1850-1920=== | ===1850-1920=== | ||
By 1850 European explorers had begun mapping the interior. British interest in the area developed later in the century, stimulated by German competition, and in 1887 the Imperial British East Africa Company, a private concern, leased from Seyyid Said his mainland holdings, a 10-mile (16-km)-wide strip of land along the coast. In 1895 the British government took over and claimed the interior as far west as Lake Naivasha; it set up the '''East Africa Protectorate'''. The border was extended to Uganda in 1902, and in 1920 the enlarged protectorate, except for the original coastal strip, which remained a protectorate, became a crown colony. | By 1850 European explorers had begun mapping the interior. British interest in the area developed later in the century, stimulated by German competition, and in 1887 the Imperial British East Africa Company, a private concern, leased from Seyyid Said his mainland holdings, a 10-mile (16-km)-wide strip of land along the coast. In 1895 the British government took over and claimed the interior as far west as Lake Naivasha; it set up the '''East Africa Protectorate'''. The border was extended to Uganda in 1902, and in 1920 the enlarged protectorate, except for the original coastal strip, which remained a protectorate, became a crown colony. | ||
| Line 67: | Line 67: | ||
===Independence=== | ===Independence=== | ||
In 1962 a KANU-KADU coalition government, including both Kenyatta and Ngala, was formed. The 1962 constitution established a bicameral legislature consisting of a 117-member House of Representatives and a 41-member Senate. The country was divided into 7 semi-autonomous regions, each with its own regional assembly. The quota principle of reserved seats for non-Africans was abandoned, and open elections were held in May 1963. KADU gained control of the assemblies in the Rift Valley, Coast, and Western regions. KANU won majorities in the Senate and House of Representatives, and in the assemblies in the Central, Eastern, and Nyanza regions.<ref> No assembly could be formed in the Northeast Region, because separatist Somalis had boycotted the elections, and its House and Senate seats also remained vacant.</ref> Kenya now achieved internal self-government with Jomo Kenyatta as its first prime minister. The British and KANU agreed, over KADU protests, to constitutional changes in October 1963 strengthening the central government. Kenya became independent on Dec. 12, 1963. In 1964 Kenya became a republic, and constitutional changes further centralized the government | In 1962 a KANU-KADU coalition government, including both Kenyatta and Ngala, was formed. The 1962 constitution established a bicameral legislature consisting of a 117-member House of Representatives and a 41-member Senate. The country was divided into 7 semi-autonomous regions, each with its own regional assembly. The quota principle of reserved seats for non-Africans was abandoned, and open elections were held in May 1963. KADU gained control of the assemblies in the Rift Valley, Coast, and Western regions. KANU won majorities in the Senate and House of Representatives, and in the assemblies in the Central, Eastern, and Nyanza regions.<ref> No assembly could be formed in the Northeast Region, because separatist Somalis had boycotted the elections, and its House and Senate seats also remained vacant.</ref> Kenya now achieved internal self-government with Jomo Kenyatta as its first prime minister. The British and KANU agreed, over KADU protests, to constitutional changes in October 1963 strengthening the central government. Kenya became independent on Dec. 12, 1963. In 1964 Kenya became a republic, and constitutional changes further centralized the government | ||
=== | ===Kenyatta regime 1963-1978=== | ||
KADU disbanded in 1964 and KANU was the only party until 1966 when a faction broke away as the Kenya People's Union (KPU). KPU advocated a more "scientific" route to socialism--criticizing the slow progress in land redistribution and employment opportunities-- as well as a realignment of foreign policy in favour of the | KADU disbanded in 1964 and KANU was the only party until 1966 when a faction broke away as the Kenya People's Union (KPU). KPU advocated a more "scientific" route to socialism--criticizing the slow progress in land redistribution and employment opportunities-- as well as a realignment of foreign policy in favour of the Soviet Union. KPU failed to gain widespread support outside of Luo areas. In June 1969 Tom Mboya, a Luo member of the government considered a potential successor to Kenyatta, was assassinated. Hostility between Kikuyu and Luo was heightened, and after riots broke out in Luo country KPU was banned. Kenya thereby became a one-party state. Despite continued factionalism within KANU and the government, Kenya continued to enjoy political stability under Mzee ("Old Man") Kenyatta, who had led the country since independence. Underlying social tensions were evident, however. Kenya's very rapid population growth rate and considerable rural to urban migration were in large part responsible for high unemployment and disorder in the cities. There also was much resentment by blacks at the privileged economic position in the country of Asians and Europeans. | ||
====Foreign policies==== | ====Foreign policies==== | ||
| Line 134: | Line 134: | ||
====Notes==== | ====Notes==== | ||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
[[Category:History Workgroup]] | |||
[[Category:Politics Workgroup]] | |||
[[Category:CZ Live]] | |||
Revision as of 13:20, 6 January 2008
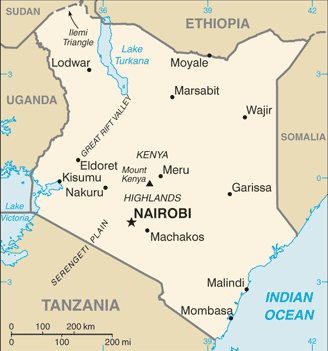
The Republic of Kenya is a country in Eastern Africa. It shares borders with Ethiopia, Somalia, Tanzania, Uganda and Sudan. Its coastline borders the Indian Ocean.
Government
Kenya is a Presidential Representative Republic, where the President acts both as head of State and head of Government. Executive power is wielded by the Government. Legislative power is shared between the government and the National Assembly. The Judiciary acts independently of both legislative and executive organs of government.
Kenya has had a relatively stable political history since independence (omitting recent political unrest and rioting). It escaped much of the internal tribal warfare and civil war which crippled neighbouring nations such as Ethiopia, Uganda and Somalia. It held elections in December 2002 which were deemed free and fair by international observers. Kenya has until recently been used as an example of a recovering African nation free of many of the domestic problems which beset many of her neighbouring states. The 2002 election heralded a peaceful transfer of power from the Kenya African Union to the National Rainbow Coalition.
Kenya exploded into violence following a disputed election in December 2007 in which the government proclaimed incumbent president Kibaki had defeated Raila Odinga, leader of the Orange Democratic Movement, by 4.58m votes to 4.35m.[1] Wide civil strife displaced over 180,000 people, with over 350 killed. [2]
Geography & natural history
Kenya elevates from low lying coastal lands along the Indian Ocean to the Highlands in the center of the country. The Kenyan highlands are one of the most productive agricultural regions in Africa. The highlands have one of the highest points in Kenya, Mount Kenya and is also home to a rare specimen to Africa, glaciers. Mount Kilimanjaro, the highest mountain in Africa lies along the Kenya/Tanzania border.
Kenya enjoys a rich variety of flora and fauna within its borders; Several safari parks operate under its jurisdiction and it provides a healthy income in tourism for the nation.
Economy
Immediately following independence Kenya enjoyed a period of economic growth, mainly due to public investment and high levels of foreign investment. From the mid 1970s to 1993, her economic performance declined as a direct result in the downturn in the international agriculture market, poor credit and higher oil prices. In the mid 1990s, Kenya began a economic liberalisation effort in tandem with the International Monetary Fund and the World Bank. This allowed a sharp increase in economic fortunes despite setbacks in the early 21st century. However, the IMF suspended Kenya's Enhanced Structural Adjustment Program due to the government's failure to maintain reforms and curb corruption. [3] Over the following few years efforts at reform were top priority in order to get the IMF back on board. Recent efforts at the highest level has been to combat corruption in government which is believed to be widespread from the local level to the very highest level of government.
Demographics
Kenya's ethnic groups comprise the following: Kikuyu 22%, Luhya 14%, Luo 13%, Kalenjin 12%, Kamba 11%, Kisii 6%, Meru 6%, other African 15% and non-African (Asian, European, and Arab) 1%.[4] The 1999 census stopped asking ethnic categories in order to ease social tension in which questions of ethnic identity had created a climate of distrust and suspicion among Kenyans. Recent elections have seen these groups generally vote along ethnic and tribal lines, but with exceptions. In the cities, such as Nairobi, old ethnic divisions are less stark than in the more traditional countryside.[5]
Kenya's religious groups comprise the following: Protestant 45%, Roman Catholic 33%, Muslim 10%, indigenous beliefs 10% and other 2%.
Education
Kenyan education can be divided into three periods: Colonial era (1890s to 1961), 1961-73, 1973-88, and 1988- present. Western education was pioneered by Protestant and Catholic missionaries, but missionary influence has diminished as the public education system has been extended. During the colonial period most schooling was segregated by race. Since independence all its schools have become multiracial. By the 1980s 2/3 of children of school age attended, including 77% at the primary level and 13% at the secondary. In 1990 5.4 million children attended 14,700 primary schools, with 640,000 students in some 2,650 secondary schools. More than half the secondary schools are aided or maintained by the government. A majority of the adult population remains literate.
The leading center is the University of Nairobi, with 200 programs in six colleges on seven campuses. Founded in 1956 as the Royal Technical College, it had links with the University of London, and took its present name in 1970, when it had 2700 students. By 1992 it had about 14,000 students, mostly Kenyans. By 2004 it enrolled 29,000 undergraduates, and 7,000 graduate students. There are 4,000 staff members, and 90,000 alumni.[6] Many Kenyans study at universities abroad.
The recent period since 1980 has been marked by a major reduction in funding and attendance at the primary level.
Culture
History
The interior is a history of migrations, and the activities of most of the major tribes are not well known before the 19th century. On the coast, trading settlements were established by 150 AD. By 1000 AD Persian and Arab traders were well established. A Swahili culture developed in the towns, notably Pate, Malindi, and Mombasa. The Portuguese arrived in 1498, with a powerful navy. The goal was not settlement but the establishment of naval bases that would give Portugal control of the Indian Ocean. After decades of small-scale conflict the Portuguese were defeated in Kenya by Arabs from Oman. Under Seyyid Said, the Omani sultan who moved his capital to Zanzibar in the early 19th century, the Arabs created long-distance trade routes into the interior. The dry reaches of the north were lightly inhabited by seminomadic pastoralists. In the south, pastoralists and cultivators bartered goods and competed for land as long-distance caravan routes linked them to the Kenya coast on the east and the kingdoms of Uganda on the west. Arab, Shirazi, and coastal African cultures produced an Islamic Swahili people trading in a variety of up-country commodities, including slaves.
1850-1920
By 1850 European explorers had begun mapping the interior. British interest in the area developed later in the century, stimulated by German competition, and in 1887 the Imperial British East Africa Company, a private concern, leased from Seyyid Said his mainland holdings, a 10-mile (16-km)-wide strip of land along the coast. In 1895 the British government took over and claimed the interior as far west as Lake Naivasha; it set up the East Africa Protectorate. The border was extended to Uganda in 1902, and in 1920 the enlarged protectorate, except for the original coastal strip, which remained a protectorate, became a crown colony.
Railways
The British government decided, primarily for strategic reasons, to build a railway linking Mombasa with the British protectorate of Uganda. A major feat of engineering, the "Uganda railway" (that is the railway inside Kenya leading to Uganda) was completed in 1903 and was a decisive event in modernizing the area. As governor of Kenya, Sir Percy Girouard was instrumental in initiating railway extension policy that led to construction of the Nairobi-Thika and Konza-Magadi railways.[7]
Large numbers of workers were imported from British India to do the manual labor. Many Indians stayed, as did the many Indian traders and small businessmen who saw opportunity in the opening up of the interior of Kenya. Rapid economic development was seen as necessary to make the railroad pay, and since the African population was accustomed to subsistence rather than export agriculture, the government decided to encourage European settlement in the fertile highlands, which had small African populations. The railway opened up the interior, not only to the European farmers, missionaries, and administrators, but also to systematic government programs to attack slavery, witchcraft,[8] disease, and famine. By the time the railroad was built, military resistance by the African population to the original British takeover had petered out. However new grievances were being generated by the process of European settlement. Governor Percy Girouard is associated with the debacle of the Second Maasai Agreement of 1911, which led to their forceful removal from the fertile Laikipia plateau to semi-arid Ngong. To make way for the Europeans (largely Britons and whites from South Africans), the Masai were restricted to the southern Loieta plains in 1913. The Kikuyu claimed some of the land reserved for Europeans and continued to feel that they had been deprived of their inheritance.
Representation
Although power remained concentrated in the governor's hands, legislative and executive councils made up of official appointees were created in 1906. The European settlers were allowed to elect representatives to the Legislative Council in 1920, when the colony was established. The settlers hoped to achieve responsible government, as did the settlers in Rhodesia in 1923, and they pressed for extensions of representative government for themselves while opposing similar demands by the far more numerous Indian community. In 1923 the Colonial Office declared that the interests of the African population must be paramount. But although the settlers failed to achieve self-government, representation on the Legislative Council for Indians and Arabs, first introduced in 1924, remained disproportionately small. A European was nominated to represent African interests.
Second World War
In the Second World War (1939-45) Kenya became an important British military base for successful campaigns against Italy in the Italian Somaliland and Ethiopia. The war brought money and an opportunity for military service for 98,000 men, called "askaris". It stimulated African nationalism. After the war, African ex-servicemen in Kenya sought to maintain the socioeconomic gains they had accrued through service in the King's African Rifles (KAR). Looking for middle-class employment and social privileges, they challenged existing relationships within the colonial state. For the most part, veterans did not participate in national politics, believing that their aspirations could best be achieved within the confines of colonial society. The social and economic connotations of KAR service, combined with the massive wartime expansion of Kenyan defense forces, created a new class of modernized Africans with distinctive characteristics and interests. These socioeconomic perceptions proved powerful after the war.[9]
In 1944 the first African, appointed by the governor, took his seat in the Legislative Council, and the first pan-tribal African party, the Kenya African Union, was formed. It soon became dominated by the Kikuyu, the African group most affected by the European presence and the most politically active. In 1947 Jomo Kenyatta, former president of the moderate Kikuyu Central Association, became president of the more aggressive Kenya African Union, a political organization demanding a greater voice for Africans.
Mau-Mau Rising
In response to the rising pressures the British Colonial Office broadened the membership of the Legislative Council and increased its role. By 1952 a multiracial pattern of quotas allowed for 14 European, 1 Arab, and 6 Asian elected members, together with an additional 6 African and 1 Arab member chosen by the governor. The council of ministers became the principal instrument of government in 1954.
A key watershed came from 1952 to 1956, during the "Mau Mau" rising, a terrorist movement directed principally against the colonial government and the European settlers. It was the largest and most successful such movement in British Africa, but it was not emulated by the other colonies. The protest was supported almost exclusively by the Kikuyu, despite issues of land rights and anti-European, anti-Western appeals designed to attract other groups. The Mau Mau movement was also a bitter internal struggle among the Kikuyu, with many assassinations and killings on all sides reflecting the ferocity of the movement and the ruthlessness with which the British suppressed it.[10] Kenyatta denied he was a leader of the Mau Mau but was convicted at trial and was sent to prison in 1953, gaining his freedom in 1961.
Constitutional debates
After the suppression of the Mau Mau rising, the British provided for the election of the six African members to the Legislative Council under a weighted franchise based on education. The new colonial constitution of 1958 increased African representation, but African nationalists began to demand a democratic franchise on the principle of "one man, one vote." However, Europeans and Asians, because of their minority position, feared the effects of universal suffrage.
At a conference held in 1960 in London, agreement was reached between the African members and the English settlers of the New Kenya Group, led by Michael Blundell. However many whites rejected the New Kenya Group and condemned the London agreement, because it move away from racial quotas and toward independence. Following the agreement a new African party, the Kenya African National Union (KANU), with the slogan "Uhuru," or "Freedom," was formed under the leadership of Kikuyu leader James S. Gichuru and labor leader Tom Mboya. A split in KANU produced the breakaway rival party, the Kenya African Democratic Union (KADU), led by R. Ngala and M. Muliro. In the elections of February 1961, KANU won 18 of the 33 African seats while KADU won 11. (Twenty seats were reserved by quota for Europeans, Asians, and Arabs.) Kenyatta was finally released in August and became president of KANU in October.
Independence
In 1962 a KANU-KADU coalition government, including both Kenyatta and Ngala, was formed. The 1962 constitution established a bicameral legislature consisting of a 117-member House of Representatives and a 41-member Senate. The country was divided into 7 semi-autonomous regions, each with its own regional assembly. The quota principle of reserved seats for non-Africans was abandoned, and open elections were held in May 1963. KADU gained control of the assemblies in the Rift Valley, Coast, and Western regions. KANU won majorities in the Senate and House of Representatives, and in the assemblies in the Central, Eastern, and Nyanza regions.[11] Kenya now achieved internal self-government with Jomo Kenyatta as its first prime minister. The British and KANU agreed, over KADU protests, to constitutional changes in October 1963 strengthening the central government. Kenya became independent on Dec. 12, 1963. In 1964 Kenya became a republic, and constitutional changes further centralized the government
Kenyatta regime 1963-1978
KADU disbanded in 1964 and KANU was the only party until 1966 when a faction broke away as the Kenya People's Union (KPU). KPU advocated a more "scientific" route to socialism--criticizing the slow progress in land redistribution and employment opportunities-- as well as a realignment of foreign policy in favour of the Soviet Union. KPU failed to gain widespread support outside of Luo areas. In June 1969 Tom Mboya, a Luo member of the government considered a potential successor to Kenyatta, was assassinated. Hostility between Kikuyu and Luo was heightened, and after riots broke out in Luo country KPU was banned. Kenya thereby became a one-party state. Despite continued factionalism within KANU and the government, Kenya continued to enjoy political stability under Mzee ("Old Man") Kenyatta, who had led the country since independence. Underlying social tensions were evident, however. Kenya's very rapid population growth rate and considerable rural to urban migration were in large part responsible for high unemployment and disorder in the cities. There also was much resentment by blacks at the privileged economic position in the country of Asians and Europeans.
Foreign policies
Independent Kenya, although officially non-aligned, adopted a pro-Western stance.[12] Kenya worked unsuccessfully for East African union; the proposal to unite Kenya, Tanzania, and Uganda did not win approval. However, the three nations did form a loose East African Community (EAC) in 1967, that maintained the customs union and some common services that they had shared under British rule. The EAC collapsed in 1977 and it was officially dissolved in 1984. Kenya's relations with Somalia deteriorated over the problem of Somalis in the North Eastern Province who tried to secede and were supported by Somalia. In 1968, however, Kenya and Somalia agreed to restore normal relations, and the Somali rebellion effectively ended.
Moi regime, 1978-2002
Kenyatta died in 1978 and was succeeded by Daniel Arap Moi (b. 1924) who ruled as President 1978-2002. Moi, a member of the Kalenjin ethnic group, quickly consolidated his position and governed in an authoritarian and corrupt manner. In mid-1982 lower-level air force personnel backed by university students attempted a coup to oust Moi. It failed and was followed by looting of Asian-owned stores by Nairobi's poor blacks and by attacks on Asian population. Robert Ouko, the senior Luo in Moi's cabinet, was appointed to expose corruption at high levels but was murdered a few months later. Moi's closest associate was implicated in Ouko's murder; Moi dismissed him but not before his remaining Luo support had evaporated. Germany recalled its ambassador to protest the "increasing brutality" of the regime, and foreign donors pressed Moi to allow other parties, which was done in December 1991 through a constitutional amendment. The Forum for the Restoration of Democracy (FORD) emerged as the leading opposition to KANU, and dozens of leading KANU figures switched parties. But FORD, led by Oginga Odinga (1911–1994), a Luo, and Kenneth Matiba, a Kikuyu, split into two ethnically based factions. In the first open presidential elections in a quarter century, in December 1992, Moi won with 37 percent of the vote, Matiba received 26 percent, Mwai Kibaki (of the mostly Kikuyu Democratic Party) 19 percent, and Odinga 18 percent. In the Assembly, KANU won 97 of the 188 seats at stake. Moi's government in 1993 agreed to economic reforms long urged by the World Bank and the International Monetary Fund, which restored enough aid for Kenya to service its $7.5 billion foreign debt. Obstructing the press both before and after the 1992 elections, Moi continually maintained that multiparty politics would only promote tribal conflict.
Moi ruled using a strategic mixture of ethnic favoritism, state repression, and marginalization of opposition forces. He utilized detention and torture, looted public finances, and appropriated land and and other property. Moi sponsored irregular army units that attacked the Luo, Luhya, and Kikuyu communities, and he disclaimed responsibility by assigning the violence to ethnic clashes arising from a land dispute.[13] Beginning in 1998, Moi engaged in a carefully calculated strategy to manage the presidential succession in his and his party's favor. Faced with the challenge of a new, multiethnic political coalition, Moi shifted the axis of the 2002 electoral contest from ethnicity to the politics of generational conflict. The strategy backfired, ripping his party wide open and resulting in its humiliating defeat of his candidate, Kenyatta's son, in the December 2002 general elections. [14]
21st century
On 27 December 2002 the voters overwhelmingly elected members of the National Rainbow Coalition (NaRC) to parliament and NaRC candidate Mwai Kibaki (1931- ) to the presidency. Voters rejected the Kenya African National Union's (KANU) presidential candidate, Uhuru Kenyatta, the handpicked candidate of outgoing president Moi. International and local observers reported the 2002 elections to be generally more fair and less violent than those of both 1992 and 1997. His strong showing allowed Kibaki to choose a strong cabinet, to seek international support, and to balance power within the NaRC. Once regarded as the world's "most optimistic," Kibaki's regime quickly lost much of its power because it became too closely linked with the discredited Moi forces. The continuity between Kibaki and Moi set the stage for the self-destruction of Kibaki's National Rainbow Coalition, which was dominated by Kikuyus. The western Luo and Kalenjin groups, demanding greater autonomy, back Raila Amolo Odinga (1945- ) and his Orange Democratic Movement (ODM).[15]
Social Change
Fertility decline
Between 1980 and 2000 total fertility in Kenya fell by about 40%, from some eight births per woman to around five. During the same period, fertility in Uganda declined by less than 10%. The difference was due primarily to greater contraceptive use in Kenya, though in Uganda there was also a reduction in pathological sterility. The Demographic and Health Surveys carried out every five years show that women in Kenya wanted fewer children than those in Uganda and that in Uganda there was also a greater unmet need for contraception. These differences may be attributed, in part at least, to the divergent paths of economic development followed by the two countries since independence and to the Kenya government's active promotion of family planning, which the Uganda government did not promote until 1995.[16]
Luo
The Luo population of the southwest had enjoyed an advantageous position during the late colonial and early independence periods of the 1950s, 1960s, and early 1970s, particularly in terms of the the prominence of its modern elite compared to those of other groups. However the Luo lost prominence due to the success of Kikuyu and related groups (Embu and Meru) in gaining and exercising political power during the Jomo Kenyatta era (1963-1978). While measurements of poverty and health by the early 2000s showed the Luo disadvantaged relative to other Kenyans, the growing presence of non-Luo in the professions reflected a dilution of Luo professionals due to the arrival of others rather than a absolute decline in the Luo numbers.[17]
Bibliography
- Barsby, Jane. Kenya (Culture Smart!: a quick guide to customs and etiquette) (2007)
- Haugerud, Angelique. The Culture of Politics in Modern Kenya. Cambridge U. Press, 1995. 266 pp. excerpt and text search
- Mwaura, Ndirangu. Kenya Today: Breaking the Yoke of Colonialism in Africa. Algora, 2005. 238 pp.
- Parkinson, Tom, and Matt Phillips. Lonely Planet Kenya (2006) except and text search
- Rough Guide To Kenya (8th ed. 2006)
History
- Anderson, David. Histories of the Hanged: The Dirty War in Kenya and the End of Empire. W. W. Norton, 2005. 406 pp. excerpt and text search
- Berman, Bruce and Lonsdale, John. Unhappy Valley: Conflict in Kenya and Africa. 2 vol. Ohio U. Press, 1992. 504 pp.
- Bravman, Bill. Making Ethnic Ways: Communities and Their Transformations in Taita, Kenya, 1800-1950. James Currey, 1998. 283 pp.
- Collier, Paul and Lal, Deepak. Labour and Poverty in Kenya, 1900-1980. Oxford U. Press, 1986. 296 pp.
- Eliot, Charles. The East Africa Protectorate (1905), by the well-informed former governor; full text online
- Elkins, Caroline. Imperial Reckoning: The Untold Story of Britain's Gulag in Kenya. Holt, 2005. 496 pp.
- Gatheru, R. Mugo. Kenya: From Colonization to Independence, 1888-1970. McFarland, 2005. 236 pp.
- Harper, James C., II. Western Educated Elites in Kenya, 1900-1963. Routledge, 2006. 193 pp. excerpt and text search
- Kanogo, Tabitha. African Womanhood in Colonial Kenya, 1900-50. Ohio U. Press, 2005. 268 pp. excerpt and text search
- Kyle, Keith. The Politics of the Independence of Kenya St. Martin's, 1999. 258 pp.
- Lewis, Joanna. Empire State-Building: War and Welfare in Kenya, 1925-52. James Currey, 2000. 393 pp.
- Mackenzie, A. Fiona D. Land, Ecology and Resistance in Kenya, 1880-1952. Edinburgh U. Pr., 1998. 286 pp.
- Maloba, Wunyabari O. Mau Mau and Kenya: An Analysis of Peasant Revolt. Indiana U. Press, 1993. 288 pp.
- Maxon, Robert M. and Ofcansky, Thomas P. Historical Dictionary of Kenya. (2nd ed. Scarecrow, 2000). 449 pp.
- Maxon, Robert M. Going Their Separate Ways: Agrarian Transformation in Kenya, 1930-1950. Fairleigh Dickinson U. Pr., 2003. 353 pp
- Miller, Norman, and Rodger Yeager. Kenya: The Quest for Prosperity (2nd ed. 1984) online edition at Questia
- Ndege, George Oduor. Health, State, and Society in Kenya. U. of Rochester Press, 2001. 224 pp.
- Ochieng, William R., ed. Themes in Kenyan History. Ohio U. Press, 1991. 261 pp.
- Ochieng, William R., ed. A Modern History of Kenya: In Honour of Professor B. A. Ogot. Nairobi, Kenya: Evans Brothers, 1989. 259 pp.
- Odhiambo, E. S. Atieno and Lonsdale, John, eds. Mau Mau and Nationhood: Arms, Authority and Narration. Ohio U. Press 2003. 306 pp.
- Odhiambo, E. S. Atieno. "Ethnic Cleansing and Civil Society in Kenya 1969-1992." Journal of Contemporary African Studies 2004 22(1): 29-42. Issn: 0258-9001 Fulltext: Ebsco
- Ogot, B. A. and Ochieng, W. R., eds. Decolonization and Independence in Kenya, 1940-93. Ohio U. Press, 1996. 270 pp. online edition from Questia
- Percox, David A. Britain, Kenya and the Cold War: Imperial Defence, Colonial Security and Decolonisation. Tauris, 2004. 252 pp. excerpt and text search
- Pinkney, Robert. The International Politics of East Africa. Manchester U. Pr., 2001. 242 pp. compares Kenya, Uganda and Tanzania.
- Press, Robert M. Peaceful Resistance: Advancing Human Rights and Democratic Freedoms. Ashgate, 2006. 227 pp.
- Sabar, Galia. Church, State, and Society in Kenya: From Mediation to Opposition, 1963-1993. F. Cass, 2002. 334 pp.
- Sandgren, David P. Christianity and the Kikuyu: Religious Divisions and Social Conflict. Peter Lang, 1989. 209 pp.
- Smith, David Lovatt. Kenya, the Kikuyu and Mau Mau. Mawenzi, 2005. 359 pp.
- Steinhart, Edward O. Black Poachers, White Hunters: A Social History of Hunting in Colonial Kenya. Oxford: James Currey, 2006. 248 pp.
- Tignor, Robert L. Capitalism and Nationalism at the End of Empire: State and Business in Decolonizing Egypt, Nigeria, and Kenya, 1945-1963. Princeton U. Press, 1998. 419 pp.
Primary sources
- Kareri, Charles Muhuro. The Life of Charles Muhoro Kareri. U. of Wisconsin-Madison, African Studies Program, 2003. 104 pp.
- Lewis, Joanna, ed. From Mau Mau to Harambee: Memoirs and Memoranda of Colonial Kenya, Tom Askwith. Cambridge U. Press, 1995. 221 pp.
- Maathai, Wangari Muta. Unbowed: A Memoir. Knopf, 2006. 314 pp.
External links
Notes
- ↑ See The Economist Dec 30, 2007 at [1]
- ↑ See BBC report at [2]
- ↑ See [3]
- ↑ See [4]
- ↑ See E. S. Atieno Odhiambo, "Ethnic Cleansing and Civil Society in Kenya 1969-1992." Journal of Contemporary African Studies 2004 22(1): 29-42.
- ↑ See [5] and [6]
- ↑ John M. Mwaruvie, "Kenya's 'Forgotten' Engineer and Colonial Proconsul: Sir Percy Girouard and Departmental Railway Construction in Africa, 1896-1912." Canadian Journal of History 2006 41(1): 1-22. Issn: 0008-4107 Fulltext: Ebsco
- ↑ Richard D. Waller, "Witchcraft and Colonial Law in Kenya." Past & Present 2003 (180): 241-275. Issn: 0031-2746 Fulltext: OUP The Africans saw witchcraft as a powerful influence on their lives and frequently took violent action against suspected witches. To control this aggression, the British colonial administration passed laws, beginning in 1909, which made the practice of witchcraft illegal. These laws gave the local population a legal, nonviolent way to stem the activities of witches.
- ↑ Hal Brands, "Wartime Recruiting Practices, Martial Identity and Post-world War II Demobilization in Colonial Kenya." Journal of African History 2005 46(1): 103-125. Issn: 0021-8537; Meshack Owino, "'For Your Tomorrow, We Gave Our Today': A History of Kenya African Soldiers in the Second World War." PhD dissertation Rice U. 2004. 671 pp. DAI 2004 65(2): 651-A. DA3122519 Fulltext: ProQuest Dissertations & Theses
- ↑ Demographers have refuted the often repeated allegation that 300,000 Kikuyu died in the uprising. The number was exaggerated by a factor of 10 according to John Blacker, "The Demography of Mau Mau: Fertility and Mortality in Kenya in the 1950s: a Demographer's Viewpoint." African Affairs 2007 106(423): 205-227. Issn: 0001-9909 Fulltext: OUP
- ↑ No assembly could be formed in the Northeast Region, because separatist Somalis had boycotted the elections, and its House and Senate seats also remained vacant.
- ↑ David A. Percox, Britain, Kenya and the Cold War: Imperial Defence, Colonial Security and Decolonisation. (2004)
- ↑ Philip G. Roessler, "Donor-induced Democratization and the Privatization of State Violence in Kenya and Rwanda." Comparative Politics 2005 37(2): 207-227. Issn: 0010-4159
- ↑ Jeffrey Steeves, "Presidential Succession in Kenya: the Transition from Moi to Kibaki." Commonwealth & Comparative Politics 2006 44(2): 211-233. Issn: 1466-2043 Fulltext: Ebsco; Peter Mwangi Kagwanja, "'Power to Uhuru': Youth Identity and Generational Politics in Kenya's 2002 Elections." African Affairs 2006 105(418): 51-75. Issn: 0001-9909 Fulltext: OUP
- ↑ Godwin R. Murunga, and Shadrack W. Nasong'o, "Bent on Self-destruction: the Kibaki Regime in Kenya." Journal of Contemporary African Studies 2006 24(1): 1-28. Issn: 0258-9001 Fulltext: Ebsco
- ↑ : John Blacker, et al. "Fertility in Kenya and Uganda: a Comparative Study of Trends and Determinants." Population Studies 2005 59(3): 355-373. Issn: 0032-4728
- ↑ Lesa Morrison, "The Nature of Decline: Distinguishing Myth from Reality in the Case of the Luo of Kenya." Journal of Modern African Studies 2007 45(1): 117-142. Issn: 0022-278x