Hyaenidae: Difference between revisions
imported>Caesar Schinas m (Update image code) |
imported>Meg Taylor m (spelling: Univeristy -> University) |
||
| Line 30: | Line 30: | ||
Spotted hyaenas (Crocuta) have short rounded ears, and short spotted coats. Spotted hyaenas (adults) lack the upper first molar. Sexual dimorphism favours the females. | Spotted hyaenas (Crocuta) have short rounded ears, and short spotted coats. Spotted hyaenas (adults) lack the upper first molar. Sexual dimorphism favours the females. | ||
Striped hyaenas and brown hyaenas (Hyaena) have long pointed ears, stripes on the legs and manes that they can erect when excited. Upper first molar present. | Striped hyaenas and brown hyaenas (Hyaena) have long pointed ears, stripes on the legs and manes that they can erect when excited. Upper first molar present. | ||
<ref name=”Skinner”>{{cite book|title=The mammals of the southern african subregion=|author=J. Skinner and C. Chimimba|authorlink= |coauthors= |date=2005 |format= |work=third edition|publisher=Cambridge | <ref name=”Skinner”>{{cite book|title=The mammals of the southern african subregion=|author=J. Skinner and C. Chimimba|authorlink= |coauthors= |date=2005 |format= |work=third edition|publisher=Cambridge University Presspages= |language= |archiveurl= |archivedate= |quote=}}</ref> | ||
==Geographical distribution of protelinae== | ==Geographical distribution of protelinae== | ||
Revision as of 21:55, 14 February 2010
| Hyaenas | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Scientific classification | ||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||
| [[taxon|Subfamilies and Genera]] | ||||||||||||
The family Hyaenidae is made up of two sub families, the protelinae and the hyaeninae. The protelinae is made up of one species, the aardwolf (Proteles cristatus). The hyaeninae is comprised of three extant species, the striped hyaena (Hyaena hyaena), the brown hyaena (Parahyaena brunnea), and the spotted hyaena (Crocuta crocuta).
Keys to genera, Proteles, Crocuta and Hyaena (includes Parahyaena)
Aardwolf (Proteles) has five digits on the fore foot, whereas the hyaeninae have only four. Additionally, with the exception of the canines, the aardwolf teeth are very small and pin like. Spotted hyaenas (Crocuta) have short rounded ears, and short spotted coats. Spotted hyaenas (adults) lack the upper first molar. Sexual dimorphism favours the females. Striped hyaenas and brown hyaenas (Hyaena) have long pointed ears, stripes on the legs and manes that they can erect when excited. Upper first molar present. [1]
Geographical distribution of protelinae
Aardwolves are found in two distinct regions of Africa. In southern Africa they are found throughout South Africa and Botswana and through most of Namibia and Zimbabwe and in parts of Angola, Zambia and Mozambique. They also occur in eastern Africa in most of Tanzania, all of Kenya and Somalia, parts of Uganda, Ethiopia, Eritrea, Dijibouti, Sudan and Egypt. [2].
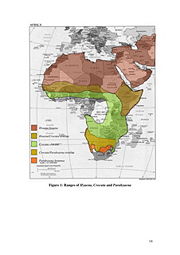
Geographical distribution of hyaeninae
The three extant species of Hyaeninae cover the majority of Africa, being absent from the far south and the Congo basin (see map). There is overlap between spotted hyaenas and brown hyaenas in the southern regions of the spotted hyaenas range in Botswana, Namibia and the northern areas of South Africa. Striped hyaenas and spotted hyaenas overlap at the northern range of spotted hyaenas, most notably Kenya, Ethiopia, Somalia and across West Africa just south of the Sahara desert. The range of striped hyaenas extends beyond Africa, covering the Middle East and parts of India, Kazakhstan and Turkey.